4.2 energy flow
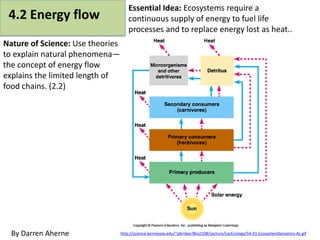
- 1. 4.2 Energy flow Nature of Science: Use theories to explain natural phenomena— the concept of energy flow explains the limited length of food chains. (2.2) http://science.kennesaw.edu/~jdirnber/Bio2108/Lecture/LecEcology/54-01-EcosystemDynamics-AL.gifBy Darren Aherne Essential Idea: Ecosystems require a continuous supply of energy to fuel life processes and to replace energy lost as heat..
- 2. 4.2 The Kidney & Osmoregulation Essential Idea: All animals excrete nitrogenous waste products and some animals also balance water and solute concentrations. Assessment Statement Guidance 4.2 U1 Most ecosystems rely on a supply of energy from sunlight. 4.2 U2 Light energy is converted to chemical energy in carbon compounds by photosynthesis. 4.2 U3 Chemical energy in carbon compounds flows through food chains by means of feeding. 4.2 U4 Energy released from carbon compounds by respiration is used in living organisms and converted to heat.. 4.2 U5 Living organisms cannot convert heat to other forms of energy. 4.2 U6 Heat is lost from ecosystems.
- 3. Assessment Statement Guidance 4.2 U7 Energy losses between trophic levels restrict the length of food chains and the biomass of higher trophic levels.. Pyramids of number and biomass are not required. Students should be clear that biomass in terrestrial ecosystems diminishes with energy along food chains due to loss of carbon dioxide, water and other waste products, such as urea. 4.2 S1 Skill: Quantitative representations of energy flow using pyramids of energy.
- 4. 4.2 U1 Most ecosystems rely on a supply of energy from sunlight. 4.2 U2 Light energy is converted to chemical energy in carbon compounds by photosynthesis. http://animalstime.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/polar-bear.jpg Producers capture the sun’s light energy and convert it to chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis. • CO2 + H2O + light C6H12O6 + O2 Chemical energy is used to create BIOMASS. The stored energy in biomass is passed on when consumers feed. And converted to chemical energy light energy is captured Organisms in most ecosystems get their energy from the sun, though consumers get it indirectly by feeding. Biomass is the total dry mass of organisms within an area or volume.
- 5. 4.2 U3 Chemical energy in carbon compounds flows through food chains by means of feeding. http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-y_gc1LQluFk/Uyf9hKfXFeI/AAAAAAAAC6g/hzb2a419L3k/s1600/food+chain.png A food chain shows a linear sequence of organisms, starting with a producer and ending with a predator, that feed on each other. • There are between 2-5 organisms in a food chain, but not more. • Arrows show the flow of energy between organisms. Why aren’t there more organisms in a food chain?
- 6. 4.2 U4 Energy released from carbon compounds by respiration is used in living organisms and converted to heat. Cell respiration is the conversion of chemical energy into a form that cells can use. • C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP Cell respiration releases heat when organic compounds are converted to ATP. Where does the heat go? Sugar- stored chemical energy ATP- the energy currency of the cell Heat is produced too
- 7. 4.2 U5 Living organisms cannot convert heat to other forms of energy.. Organisms can convert many types of energy: • Light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. • Chemical energy to kinetic energy in muscle contraction. • Chemical energy to electric energy in neurons. • Chemical energy to heat energy in heat generating adipose tissue (for homeostasis) But once the energy becomes heat, organisms cannot convert it to any other form of energy.
- 8. 4.2 U5 Heat is lost from ecosystems. • The heat generated by cell respiration is useful to organisms. • It makes ectothermic (cold-blooded) animals warmer, which allows them to be more active. • It is used by endothermic (warm-blooded) animals to maintain a constant body temperature in homeostasis. • Heat moves from warmer areas to colder areas, so the heat is lost to the environment. The heat in the ecosystem is eventually lost into space. Cold-blooded reptiles can be more active when they are warm Image: Wikipedia
- 10. 4.2 Energy losses between trophic levels restrict the length of food chains and the biomass of higher trophic levels. Trophic level: the position of the organism in a food chain. Producers are on the first trophic level, primary consumers on the second. When biomass is consumed, energy is transferred. Energy transfers between trophic levels is inefficient. Only about 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is passed on to the next. Energy is lost: • As heat from respiration • Not consumed (bones, fur, etc.) • As feces http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/tlw3/eBridge/Chp29/animations/ch29 /ecosystem_organization.swf
- 12. Problem: The production of a rainforest is 2.56 X 105 KJm-2yr-1. Construct a pyramid of energy, assuming that 10% of energy is passed on to each trophic level.
- 13. Problem: The production of a rainforest is 2.56 X 105 KJm-2yr-1. Construct a pyramid of energy, assuming that 10% of energy is passed on to each trophic level. Producers: 256,000 KJm-2yr-1 Primary Consumers: 25,600 KJm-2yr-1 Secondary Consumers: 2,560 KJm-2yr-1 Tertiary Consumers: 256KJm-2yr-1 Why are food chains and biomass limited by energy loss between trophic levels?
- 14. Problem: The production in a tropical rainforest biome is 2.56 X 105 KJm-2yr-1. Construct a pyramid of energy, assuming that 10% of energy is passed on to each trophic level. Producers: 256,000 KJm-2yr-1 Primary Consumers: 25,600 KJm-2yr-1 Secondary Consumers: 2,560 KJm-2yr-1 Tertiary Consumers: 256KJm-2yr-1 Why are food chains and biomass limited by energy loss between trophic levels?Because there is not much energy available at higher trophic levels- just 0.1% or less That’s why you see fewer tigers (apex predators) than trees (producers)!
- 15. Outline how energy is passed through ecosystems. (6 marks)
- 16. Outline how energy is passed through ecosystems. (6 marks) The sun is the initial source of energy for most ecosystems; Producers capture the sun’s energy in photosynthesis; Light energy is converted to chemical energy; Energy is passed from producers to consumers in feeding; Energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient/only about 10% of energy is passed between trophic levels; Energy is lost as heat/materials not eaten/waste as feces/not assimilated; Organisms cannot convert heat energy to other forms of energy; Food chains & biomass are limited by energy availability at top trophic levels