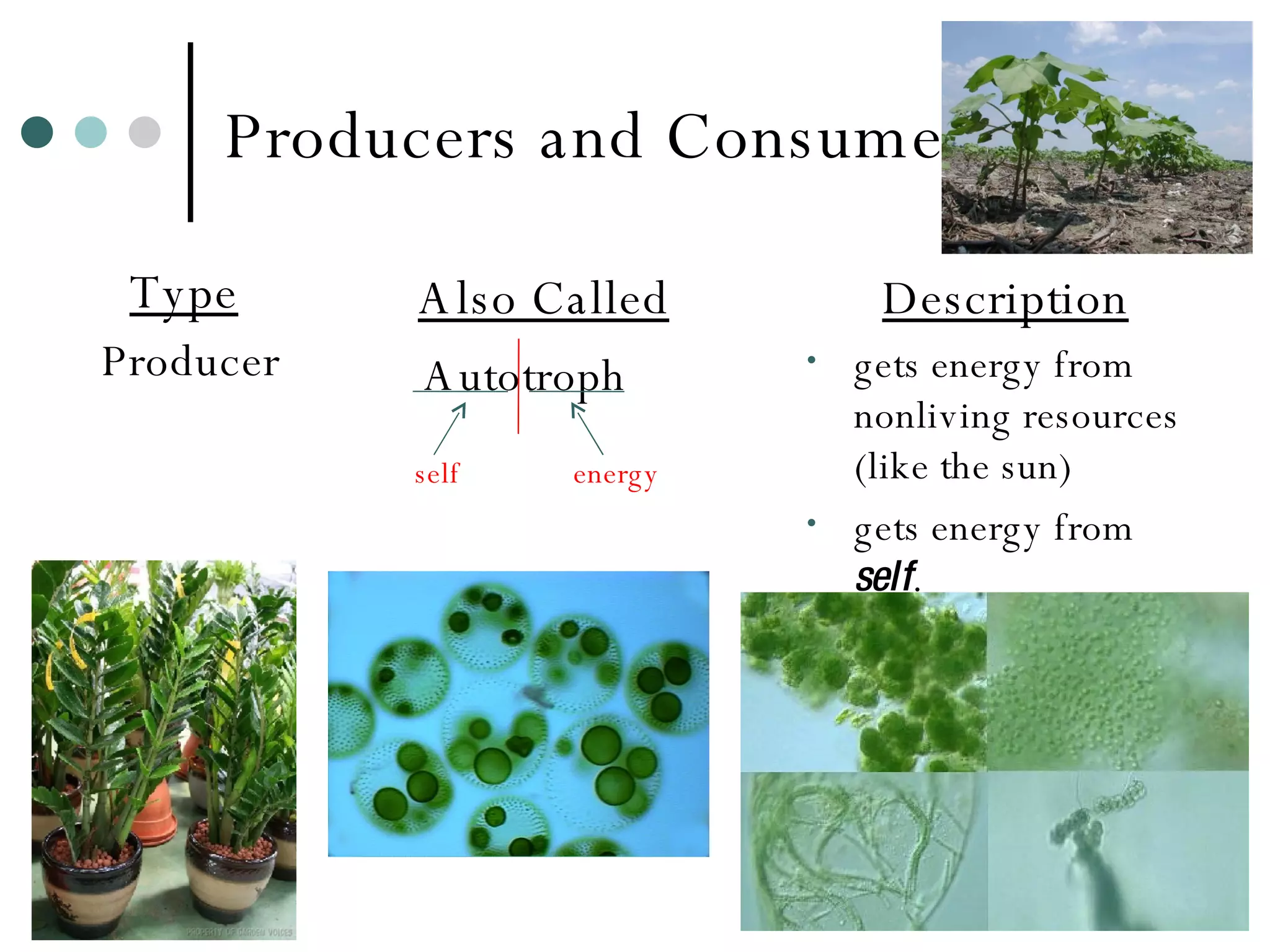
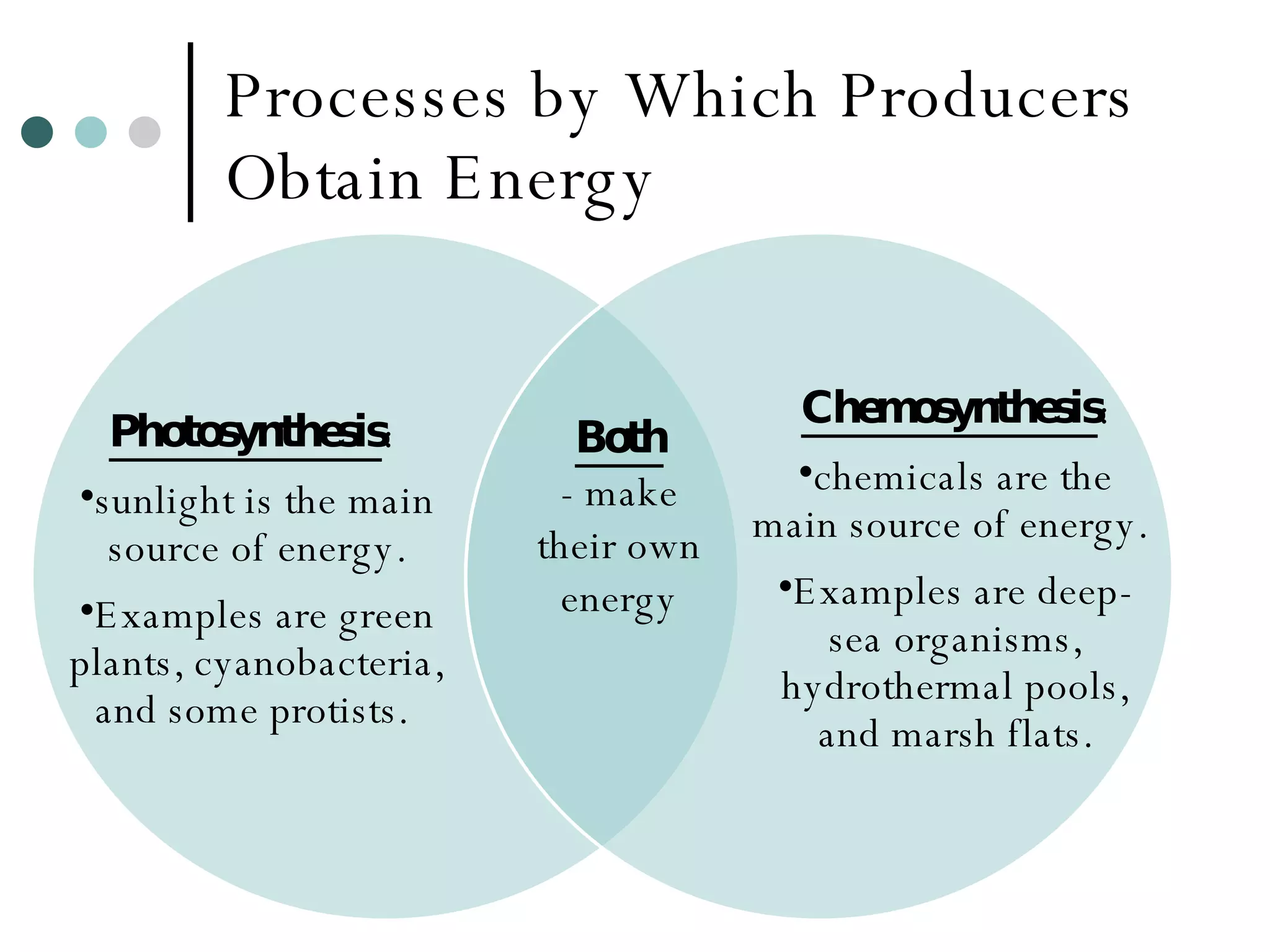
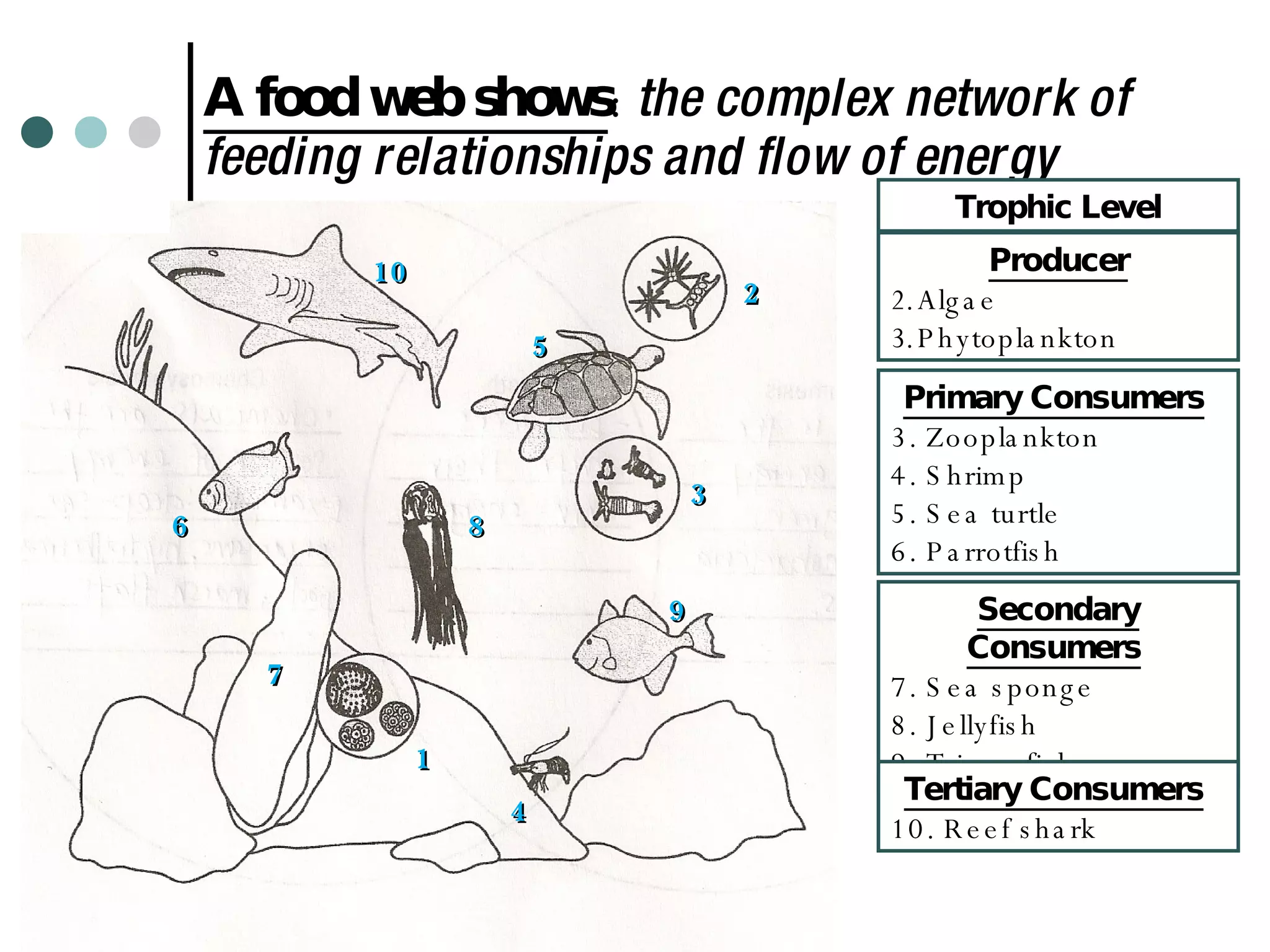
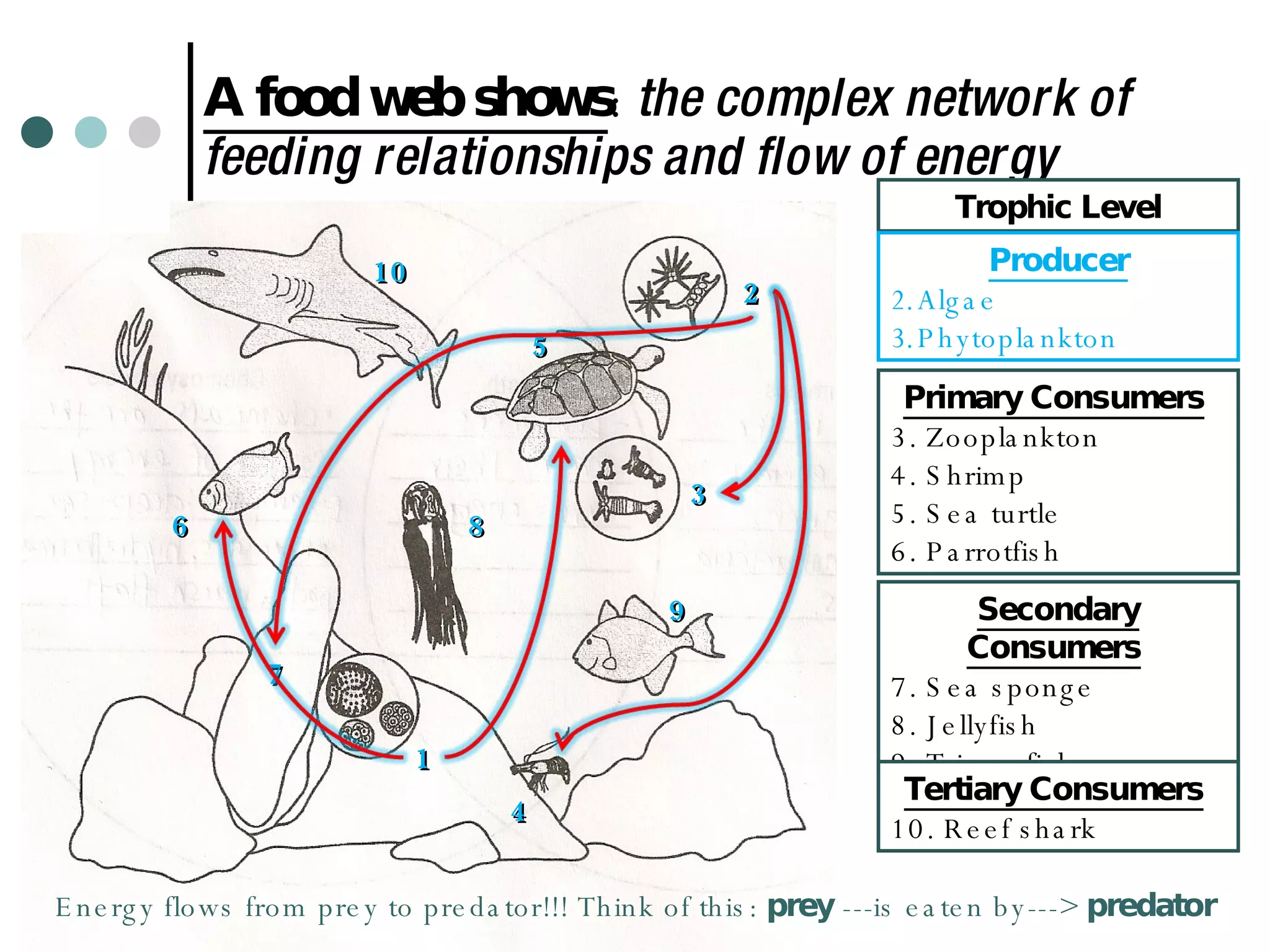
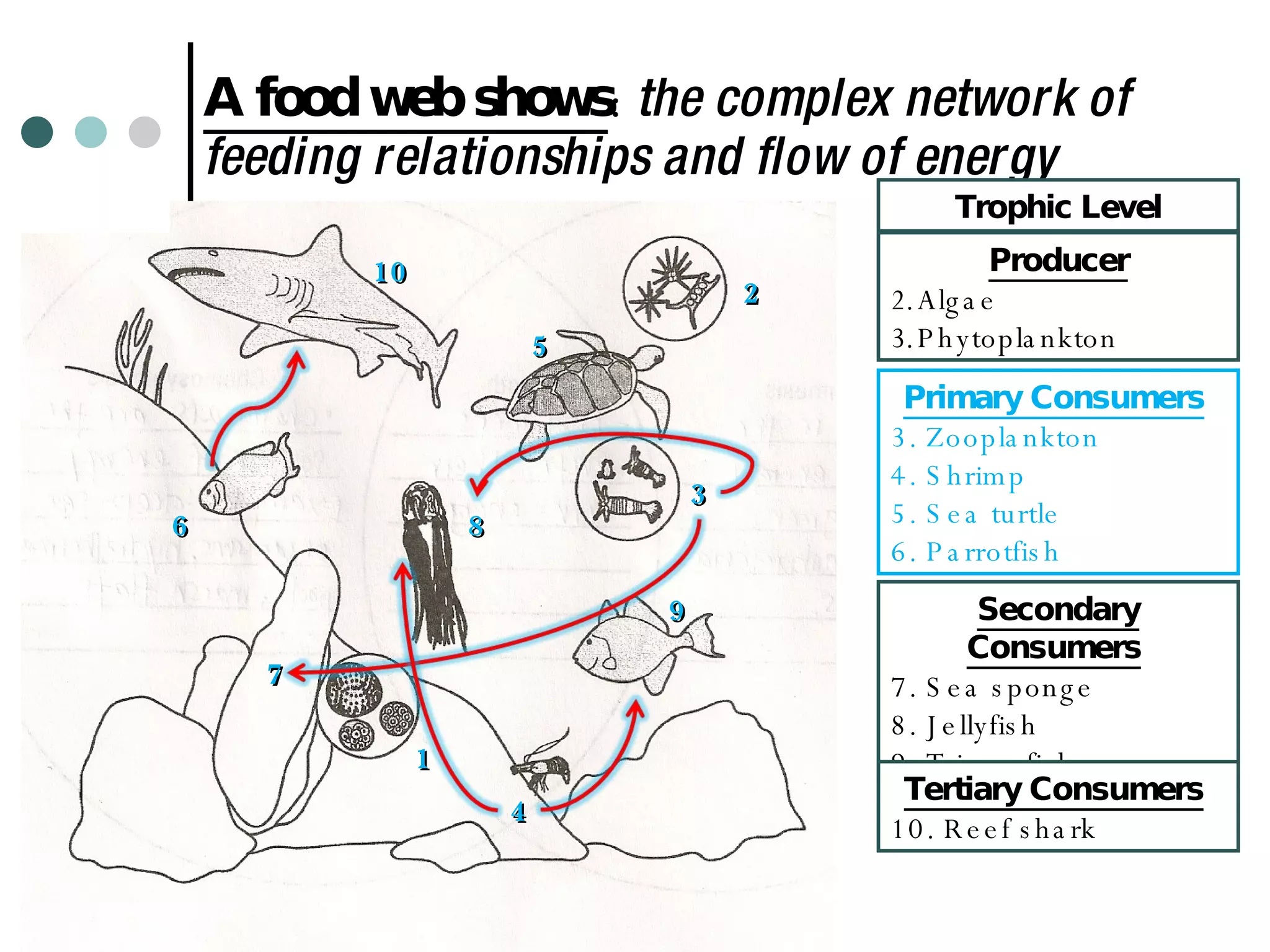
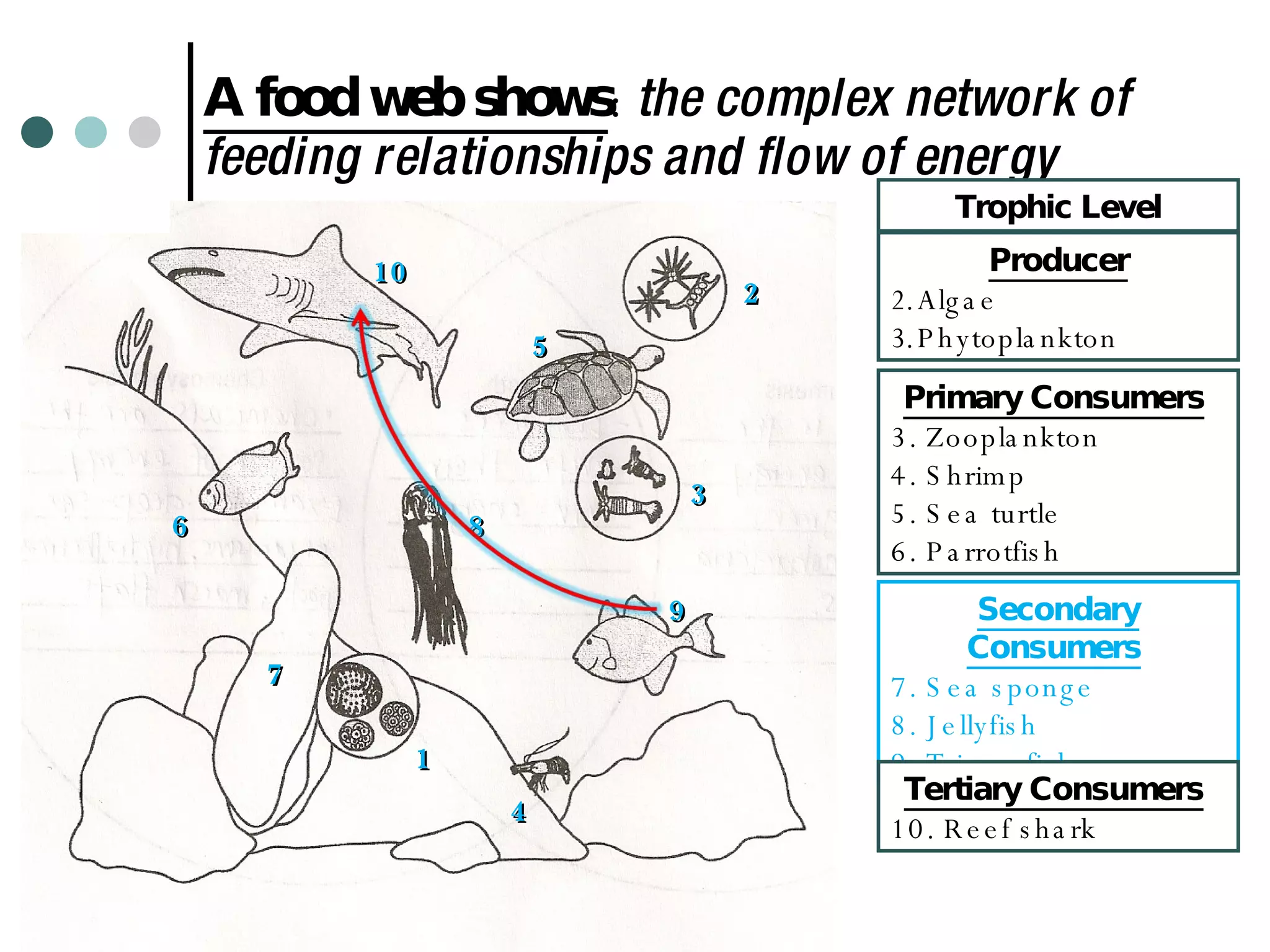
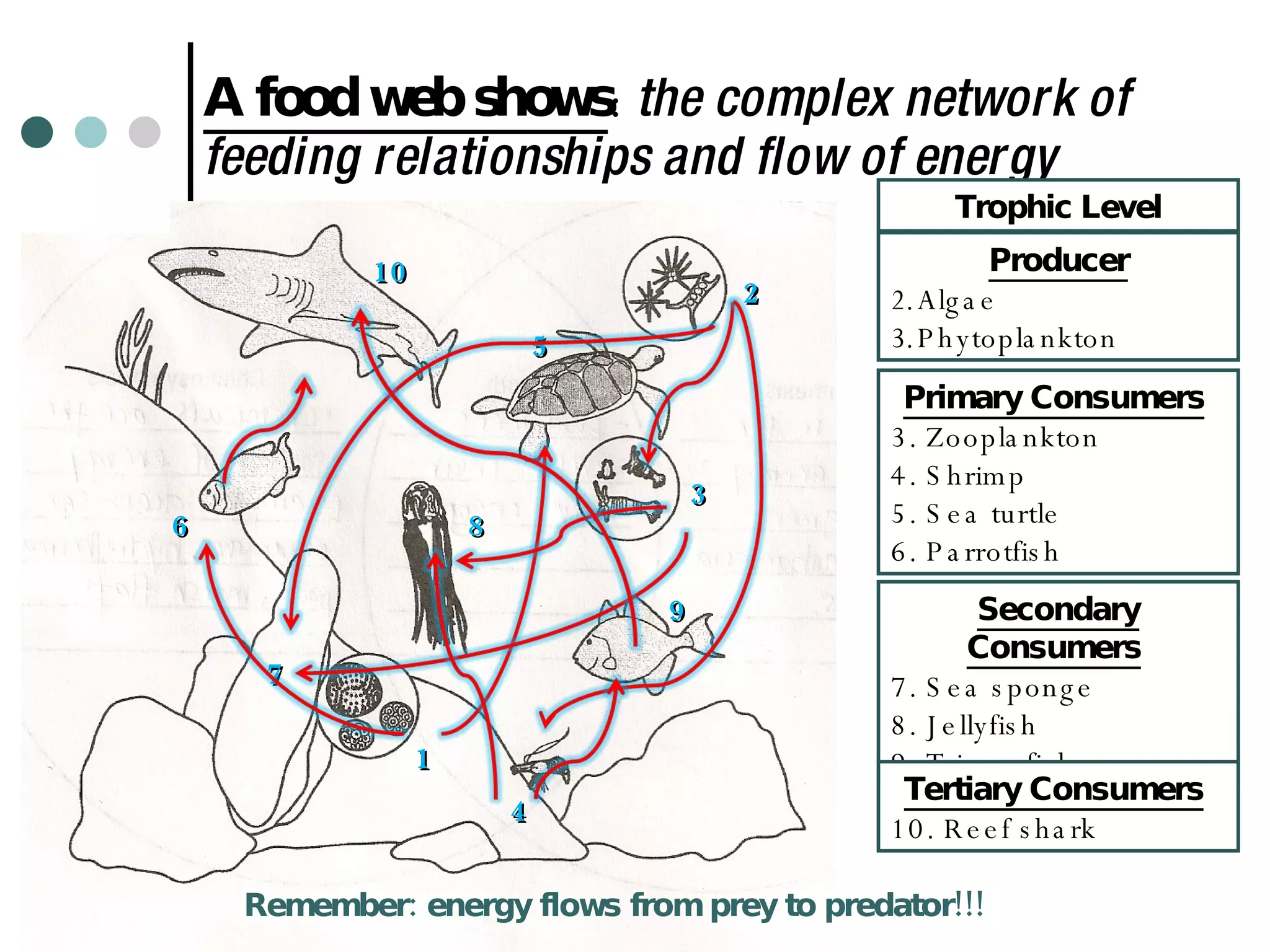
This document discusses energy flow through ecosystems and food webs. It defines producers as organisms like plants that get energy from sunlight or chemicals through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Consumers are defined as organisms that get energy by eating other organisms and are divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers. Food chains and food webs show the network of organisms that eat each other and how energy flows from producers that capture energy to higher level consumers.