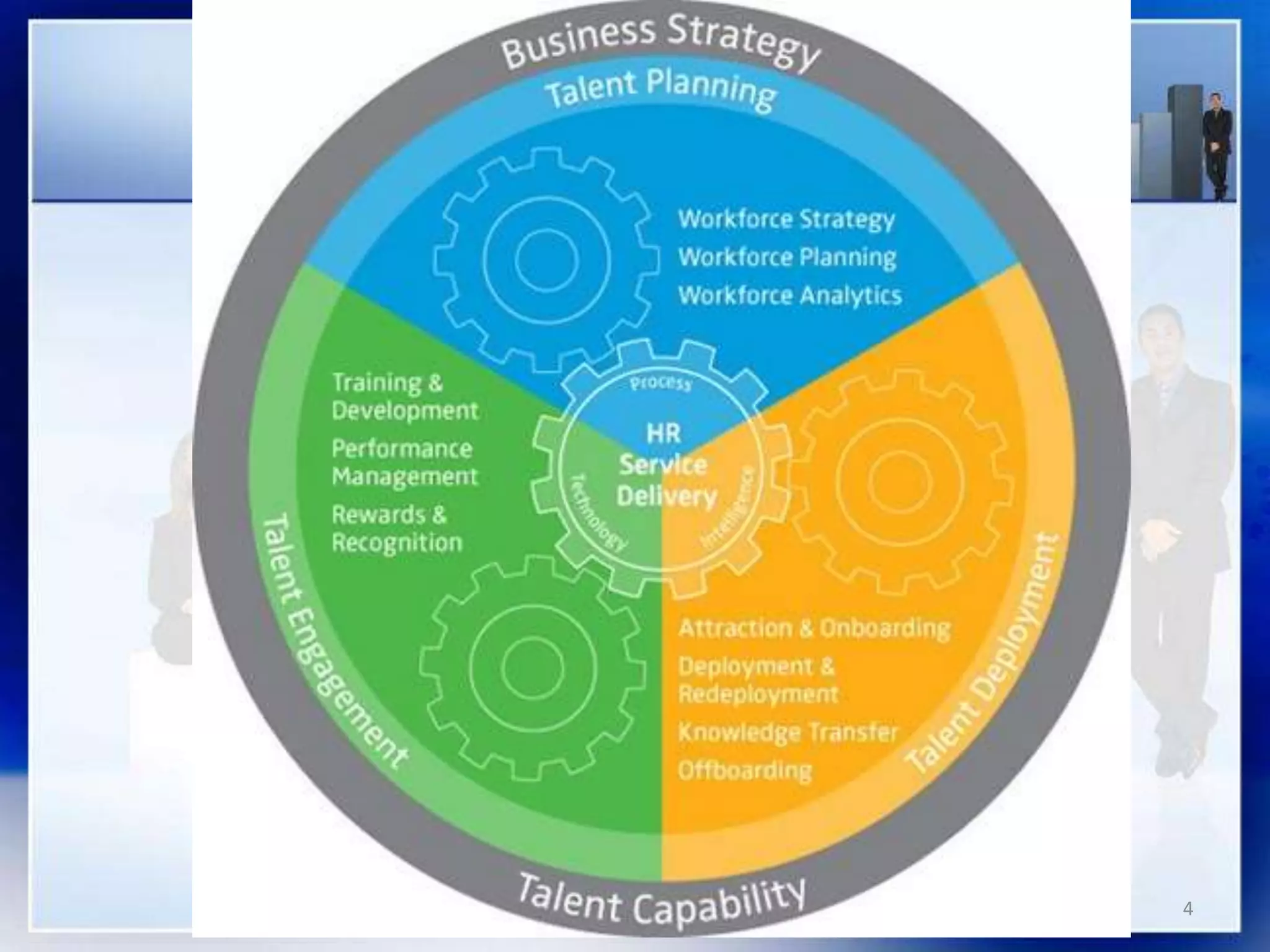
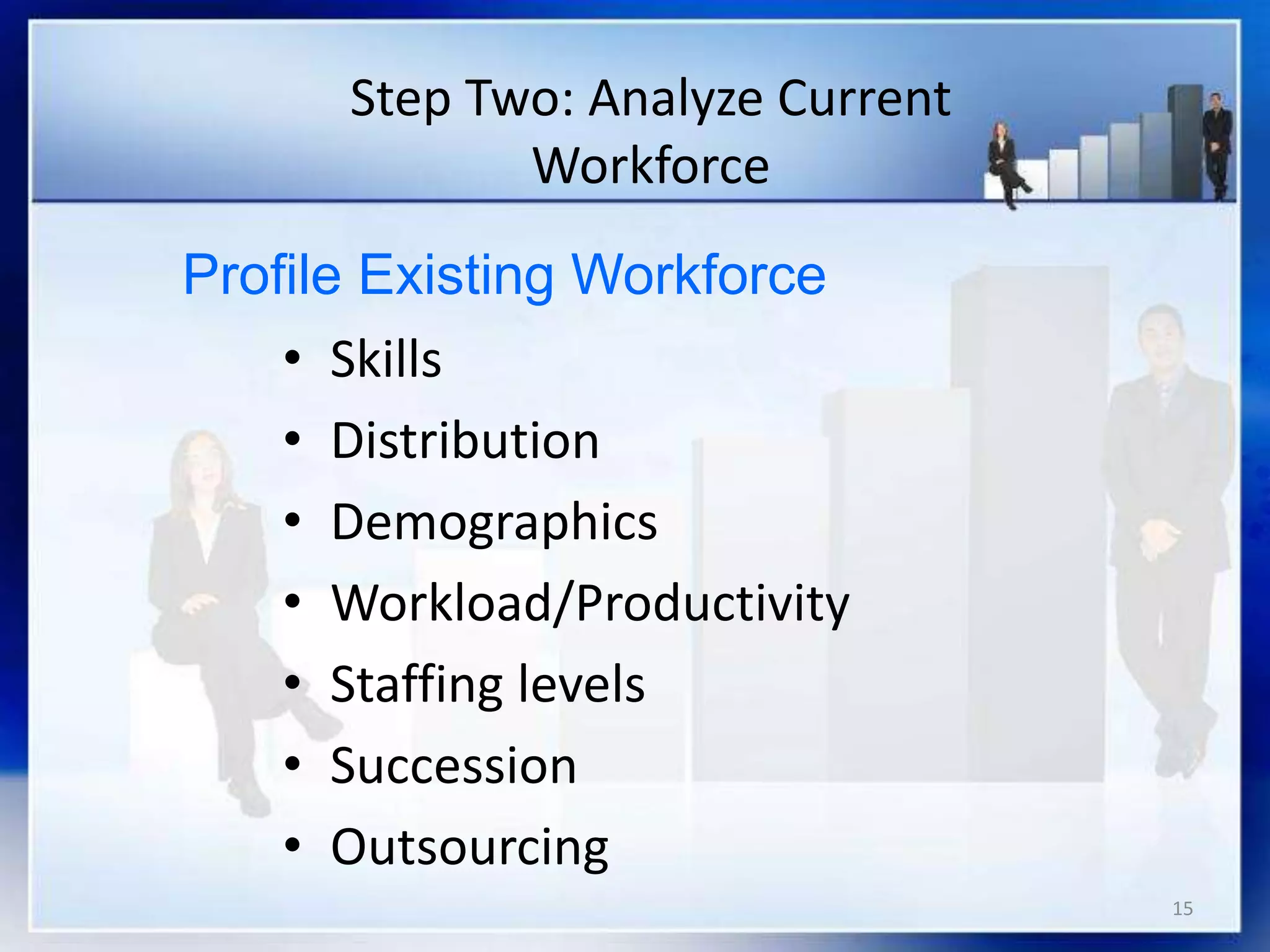
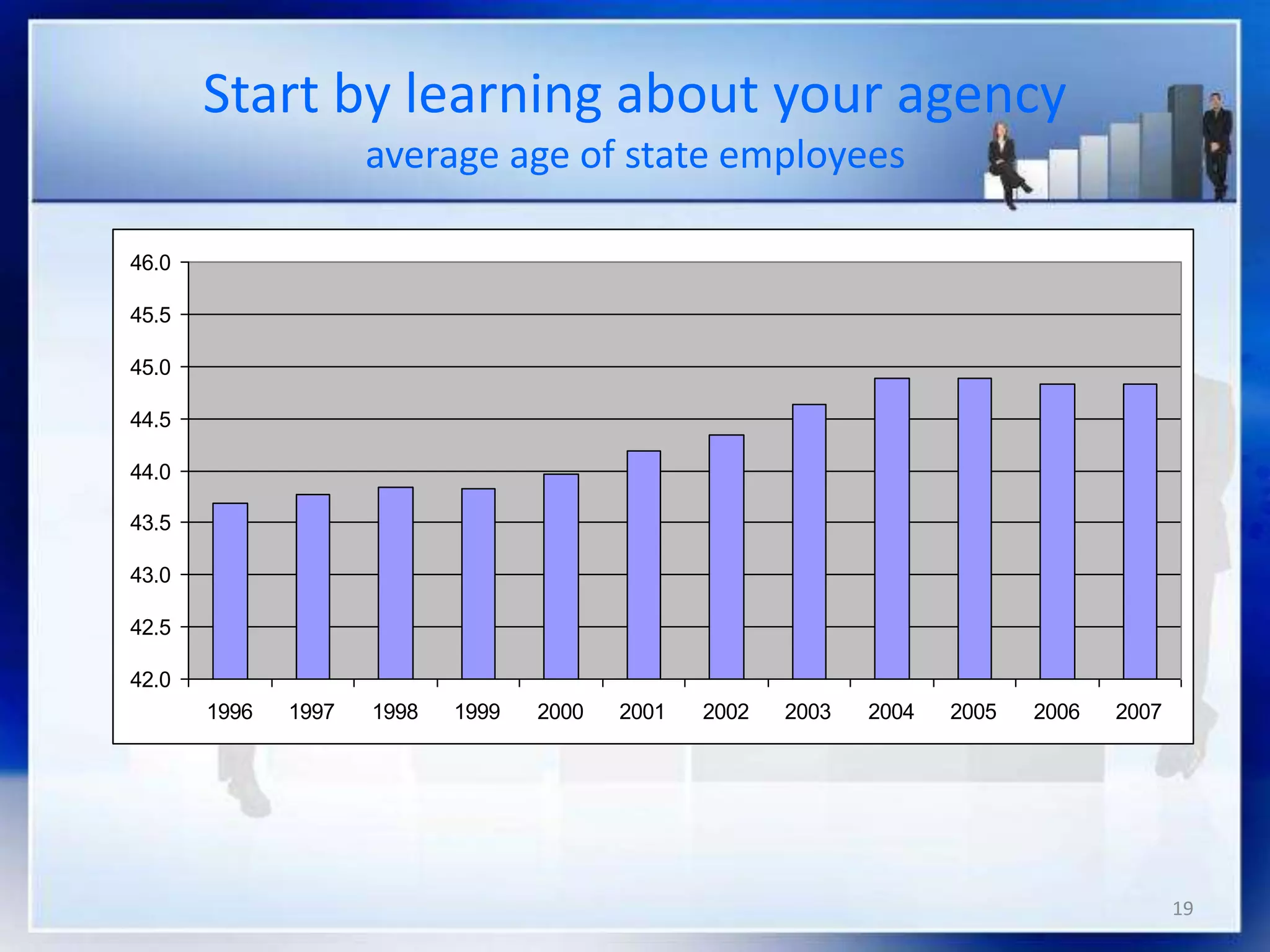
This document provides an overview of talent planning and deployment. It discusses strategic talent planning and identifies workforce planning as a systematic process for identifying gaps between today's workforce and tomorrow's workforce. The document outlines the key steps in workforce planning, including defining the future needs of the organization, analyzing the current workforce, identifying gaps, and monitoring and revising the plan. It also discusses using tools like SWOT analysis, opportunity matrices, and threat matrices to aid in talent planning.






































![MEASURES MONITOR PLAN OUTCOMES With Supported
Analysis
Completion, attendance ratios
Program, certification expenses
Activity profitability
Performance outcome ratios
Satisfaction ratings
...
Workforce Analytics – Process Flow
ROI per employee
Headcount cost
Headcount variance
Requisition fulfillment cycle time
Termination cost per employee
Termination cost
Turnover rate
Absence rate
Accident rate
Exposure hours
Accept ratio
Agency effectiveness
Cost to hire
Vacation days balance
Vacation days entitlement
Performance review result
Contribution factor
Maintained qualification count
Review result
Scarcity level
Succession percentage
Training % of revenue
….
Company
Organization
Location
Responsibility Center
Job Position
Job Category
Vendor
Assignment
Salary Plan Grade Step
Calendar Month
Fiscal Period
Employee
Hiring Manager
HR agent
Annual compensation
Benefit plan enrollment
Compensation % increase
Increase Variance
]Customer service award variance
Dependant count
Employee, Employer contribution
Employee opt out ratio
Incentive award
Hourly pay rate
….
Absence days count
Accident Severity Rate
Accident Lost time Rate
High Performance ratio
Low Performance ratio
Employee Development cost
Development cost per employee
High Performance turnover rate
Incentive Pool variance
Benefit cost per employee
Merit Pool Variance
increase variance count
termination rate
FTE count
Human capital ROI
Time to hire
Turnover rate
....
Headcount,
Planning
Compensation &
Salary Planning
Improve
Growth
and
Profitability
Headcount & Turnover
Compensation, Incentive
Performance,
Succession
Recruiting , Absence &
Accident Analysis
Learning Management
Benefits Planning
Restructuring
planning
Payroll &
Reconciliation Analysis
Payroll Liability
Planning
Recruitment
Planning
Trained, certified headcount
Investment factors
Training cost factors
Revenue/expense ratios](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-160826155623/75/3-talent-planning-deployment-42-2048.jpg)























