This document describes a 3-D numerical model used to study supercritical flow in gradual channel expansions. The model was first verified against experimental data from a modified Rouse expansion, showing satisfactory agreement, particularly at lower Froude numbers. The model was then applied to optimize the design of a complex expansion structure with variable bottom elevation, piers, and walls. Calculations indicated flow conditions would be satisfactory if bottom ramps ensured uniform bottom variation.


![404 A.I. Stamou et al. Journal of Hydraulic Research Vol. 46, No. 3 (2008)
Reynolds stresses, which are calculated via the k−ε model (Rodi,
1980).
The above set of equations is solved by the finite-volume
based code FLOW-3D (Flow Science Inc., 2007), which employs
a structured, patched multi-block, orthogonal, coordinate grid
with a collocated variable arrangement. In FLOW-3D the “free-
griding” approach is combined with simple rectangular grids.The
geometric regions within rectangular grids are defined using
the Fractional Area/Volume Obstacle Representation method.
ThefreesurfaceismodeledwiththeVolumeofFluidmethod(Hirt
and Nichols, 1981). The equations of the model are integrated
over each control volume, such that the relevant quantity (mass
and momentum) is conserved, in a discrete sense, for each control
volume.A spatial discretization is achieved through the HYBRID
scheme, a second-order upwind scheme, and the third-order
QUICK scheme. The basic solution algorithm is the SIMPLEC
pressure correction scheme (Van Doormal and Raithby, 1984),
which uses a variety of linear equation solvers.
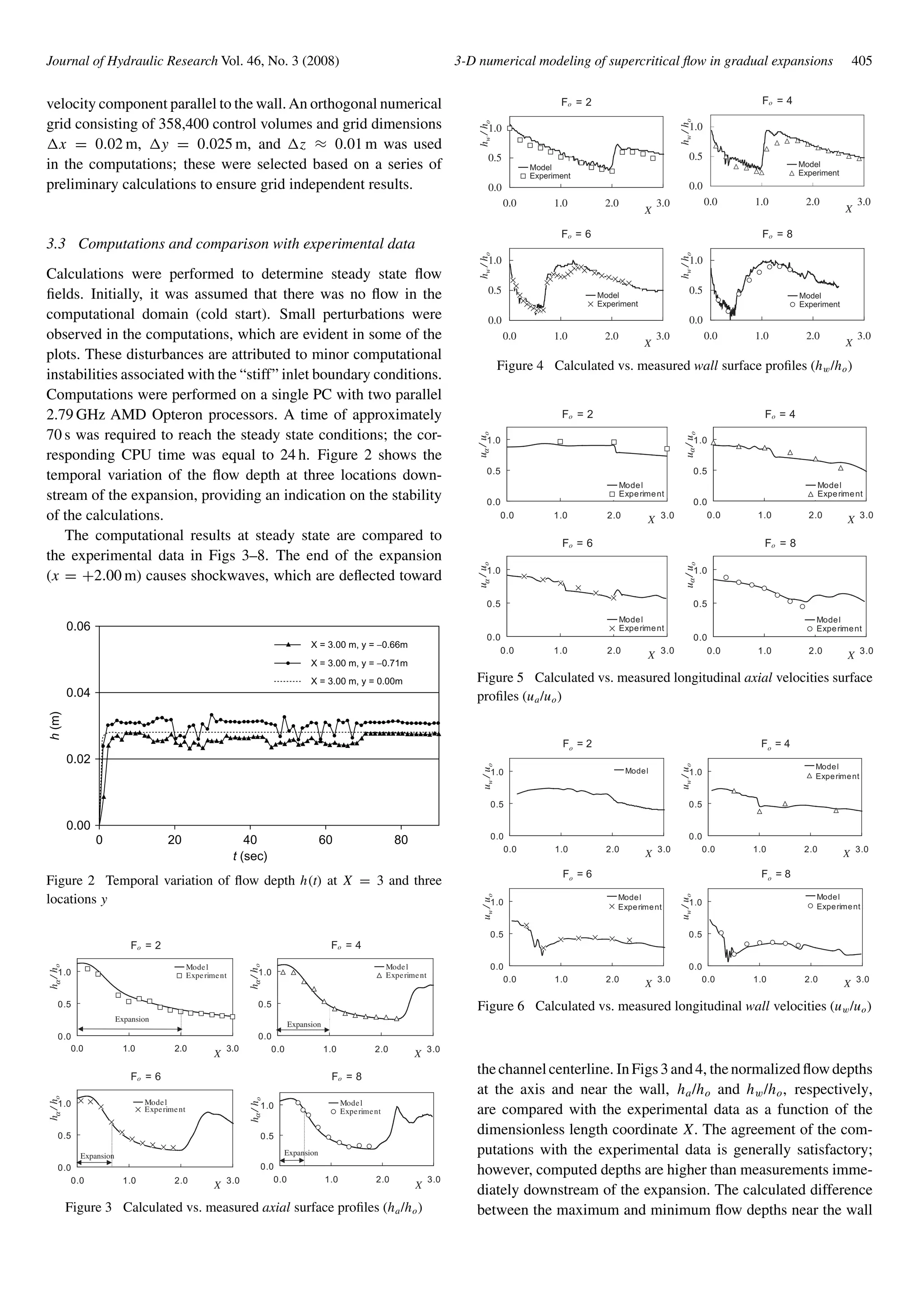
3 Verification of model
3.1 Experimental data
FoursetsofexperimentaldatainamodifiedRousewallexpansion
profile reported by Mazumder and Hager (1993) were used for
the verification of the model. These experiments were conducted
in a 10 m long rectangular, horizontal channel (Fig. 1). The
approach flow channel had a width bo = 0.50 m. The approach
flow depth ho was regulated with a gate on which a cover was
attached. In all experiments the downstream width b2 was equal
to 1.5 m, i.e. the expansion ratio was equal to β = b2/bo = 3.
The characteristics of the four runs are shown in Table 1.
The modified Rouse wall profile of Fig. 1 was determined
via the calculation of the transverse coordinate yb using (Chow,
1959)
yb
bo
=
1
2
1 +
1
4
X3/2
(5)
Figure 1 Scheme of modified Rouse wall expansion profile and the
computation domain; dimensions in [m]
Table 1 Characteristics of runs of Mazumder
and Hager (1993) used in present work
Run ho(m) Fo
27 0.048 2.0
24 0.048 4.0
25 0.048 6.0
26 0.048 8.0
with the normalized streamwise coordinate
X =
x
bo · Fo
, (6)
where x is the streamwise coordinate. The design Froude num-
ber was equal to Fo = FD = 1.0; i.e. the wall profile has the
dimensional equation with (x, yb) in [m]
yb = 0.25 + 0.177x3/2
. (7)
Its end is located at x = Lt = 2.0 m, where yb = 0.5 b2 =
0.75 m (Fig. 1).
The flow depths were measured with a conventional point gage
(±0.5 mm reading accuracy), the flow velocities were recorded
with a miniature current meter and the local streamline direc-
tion was determined with an angle probe. The local velocity was
found to vary only slightly in the vertical direction, except for the
boundary layer; thus, a representative velocity magnitude at half
of the local flow depth was taken. Extended preliminary observa-
tions indicated reliable results for flow depths down to 15 mm and
velocities up to 5.0 m/s. The experimental grid was x = 1.0 m
in the streamwise, and y = 0.05 m in the transverse directions.
3.2 Computational domain, boundary conditions,
and numerical grid
The boundary conditions are defined at the borders of the compu-
tation domain, i.e. −1.20 m ≤ x ≤ +10.00 m, −0.75 m ≤ y ≤
+0.75 m and +0.00 m ≤ z ≤ +0.078 m (Fig. 1).At the upstream
end of the approach flow channel (x = −1.20 m), which is called
“inlet,” a parallel flow was imposed, with uniform horizontal
velocity equal to uo = Q/(boho) and vertical velocity equal to
zero. The values of the turbulent energy and its dissipation ko and
εo were assumed to be uniform and were calculated as follows
(Lyn et al., 1992)
ko = au2
o (8)
εo = c0.75
µ
k1.5
o
lo
, (9)
where α is a constant chosen such that a large eddy viscosity
results at the inlet, cµ is an empirical constant and lo is the char-
acteristic inlet dimension taken equal to 0.1 ho. The values of ko
and εo resulted in values of the eddy viscosity at the inlet equal
to approximately 100 times the molecular viscosity of water. The
above-mentioned “inlet” boundary condition approximates geo-
metrically the real boundary condition in the experimental setup,
which consisted of a gate on which a cover was attached. It is
noted that imposing a uniform inflow velocity is a somewhat
“stiff” condition that may cause numerical instabilities and small
perturbations, as discussed below. However, there was no better
alternative available in the numerical code for the definition of a
more realistic velocity distribution.
At the downstream channel end (x = +10.00 m) an “out-
let” condition was used, which sets the discharge equal to the
inlet discharge and the vertical gradients of k and ε equal to
zero. At the rigid walls, the standard wall function approach was
applied, which relates the shear stress at the wall to the cell node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-dnumericalmodelingofsupercriticalflowingradualexpansions-171103133643/75/3-d-numerical-modeling-of-supercritical-flow-in-gradual-expansions-3-2048.jpg)
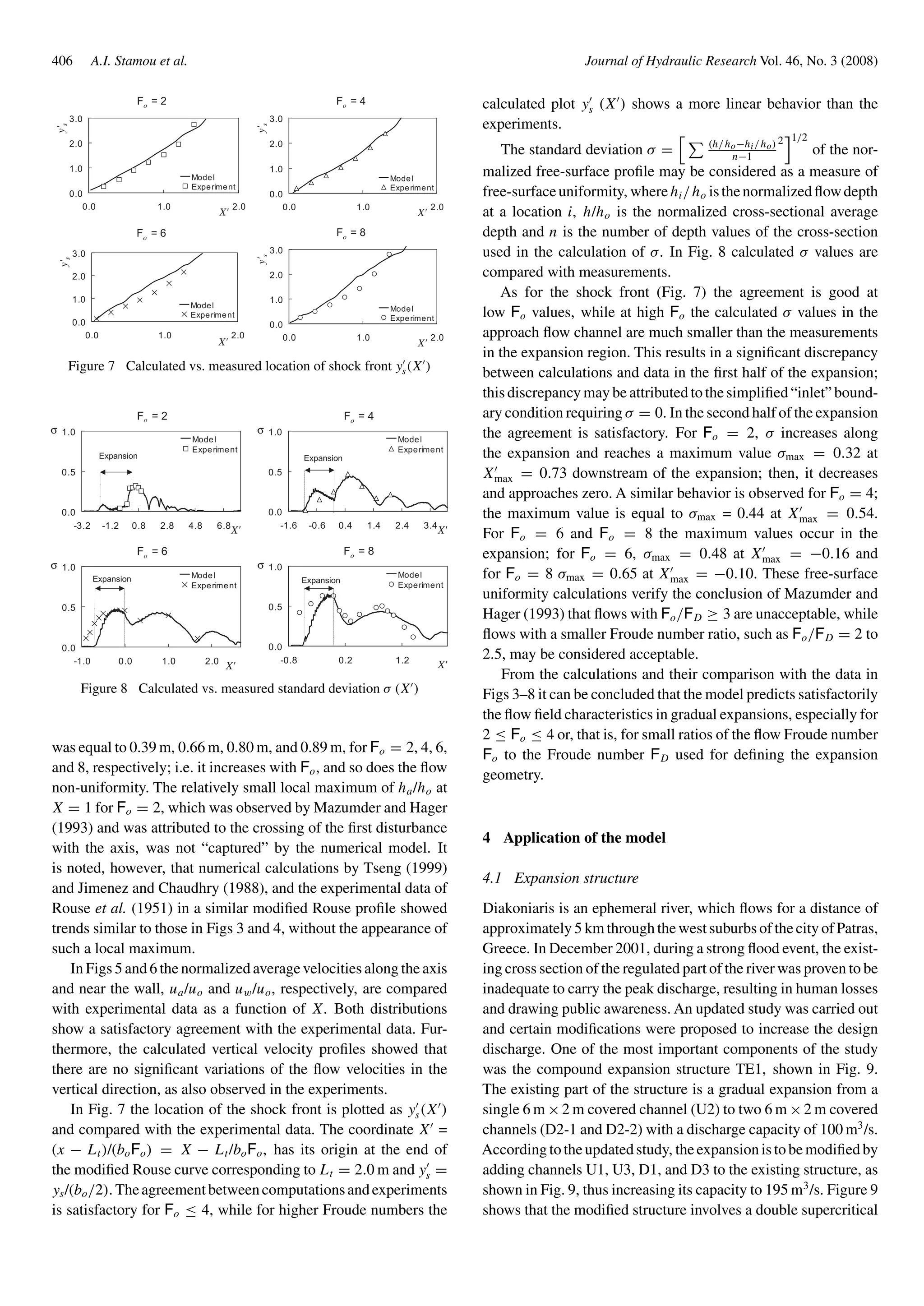
![Journal of Hydraulic Research Vol. 46, No. 3 (2008) 3-D numerical modeling of supercritical flow in gradual expansions 407
H=+1.30
H=+2.01
D1
D2-1
D3
D2-2
H=+2.22
H=+1.80
H=+1.80
H=+1.30
-30.0 0.0 22.9 82.9 x (m)
y (m)
0.0
+8.1
-8.1
3
2-2
2-1
1
Piers
Bottom
Ramps
-10.5
+10.3
U1
U2
U3 3
2-2
2-1
1
H=+2.22
H=+2.22 H=+2.01
Flow direction
Figure 9 Plan view of expansion structure (not in scale), with bottom
elevations (H) in [m]
expansion, which is approximately symmetrical, with variable
bottom elevation (channels D1 and D3 are deeper than D2-1 and
D2-2), two piers with circular cross section of diameter equal to
0.50 m, two inner (existing) walls upstream and three inner (exist-
ing) walls downstream of the expansion. The Froude number of
the approach flow is Fo = 1.6.
The 3-D model previously described was applied to optimize
the design of the expansion structure, aiming in particular at
(a) investigating the flow conditions in the expansion and (b)
ensuring that in all four channels downstream of the expansion
(b1) the water elevation is approximately the same and (b2) the
flow is distributed in proportion to the channel widths.
A linear expansion geometry was proposed by the Consult-
ing firm Hydrotech Hydraulic Studies Ltd, based on approx-
imate one-dimensional hydraulic calculations with HEC-RAS
(USACE, 2002). The geometry of the outer walls is an almost lin-
ear approximation to the respective modified Rouse wall profile
(Rouse et al., 1951), obtained by assuming a simple symmetrical
expansion with a ratio β = b2/bo = 20.40/16.20 = 1.26.
4.2 Computational details
The computation domain is shown in Fig. 9. Boundary condi-
tions were defined as discussed in Section 3.2. In particular, at
the “inlet” a parallel flow was imposed, with uniform approach
flow depth equal to ho = 2.02 m and velocity equal to uo =
6.90 m/s. An orthogonal numerical grid consisting of 753,300
control volumes and grid dimensions x = z = 0.25 m,
y = 0.20 m ÷ 0.27 m was used in the computations after
a series of preliminary calculations to ensure grid independent
results.
4.3 Results and discussion
Several series of calculations were performed to determine the
characteristics of the flow field and to investigate the effects of:
(i) Presence of piers, which are necessary for structural reasons,
and (ii) Presence of the bottom ramps in the second half of the
expansion, between channels U1 and D1, and channels U3 and
D3. The bottom ramps permit a gradual decrease of the bottom
elevation from mid-way of the expansion (H = +2.01 m) to the
beginning of channels D1 and D3 (H = +1.30 m); Fig. 9.
Figure 10 presents a top view of the calculated flow field for
the proposed final design, showing the generation of four shock
Figure 10 View of water surface
waves. The waves initially strike on the sides of the two inner
and the two outer walls defining the first contact points, which
are denoted with (1). Each of the four waves follows its own
path in each of the four downstream channels, being reflected
on the walls of the channel in locations noted as (2), (3), and
(4); then, the waves are dissipated at a distance of approximately
45 m downstream of the beginning of the expansion. Significant
flow disturbances are also observed immediately downstream of
the piers.
In Fig. 11, the water surface profiles are shown along 4 longi-
tudinal sections in the expansion and adjacent channels, namely
1, 2-1, 2-2, and 3, as defined in Fig. 9. From the calculations and
Figs 10 and 11, it is noted that the flow surface never reaches
the soffit of the channels and the minimum freeboards in the four
downstream channels D1, D2-1, D2-2, and D3 are of the order
of 0.40 m. The average elevations of the free surface in the four
downstream channels at the outlet boundary range from 2.82 m
to 2.92 m.
Also, Fig. 11 compares calculated elevations with HEC-
RAS calculations (USACE, 2002). Upstream (−30.00 m ≤ x ≤
0.00 m) and sufficiently downstream (x ≥ 50.00 m) of the expan-
sion, calculations with HEC-RAS can be considered as satisfac-
tory and conservative. As expected, surface elevations (mainly
superelevations) within the expansion (0.00 m ≤ x ≤ 22.90 m)
and immediately downstream (22.90 m ≤ x ≤ 50.00 m) cannot
be captured with the one-dimensional HEC-RAS; in the expan-
sion, thecalculateddepthsarehigherupto0.40 mthanHEC-RAS
−30 0
0
2
4
6
Expansion
Elevation(m)
30 60
Soffit
HEC-RAS
Section 3
Section 2-2
Section 2-1
Section 1
x (m)
Figure 11 Calculated water surface profiles in longitudinal sections 1,
3, 2-2, and 2-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-dnumericalmodelingofsupercriticalflowingradualexpansions-171103133643/75/3-d-numerical-modeling-of-supercritical-flow-in-gradual-expansions-6-2048.jpg)

