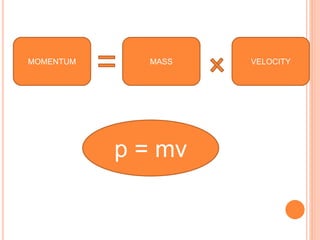
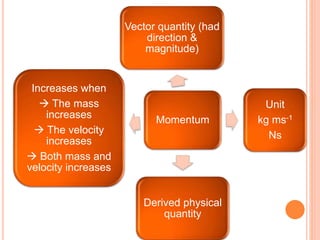
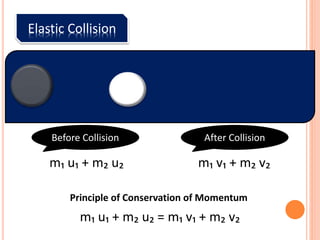
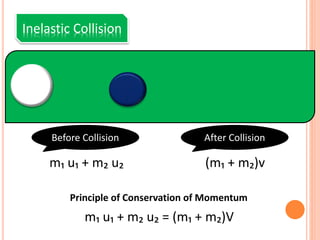
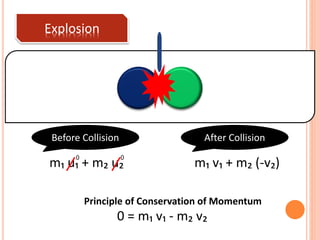
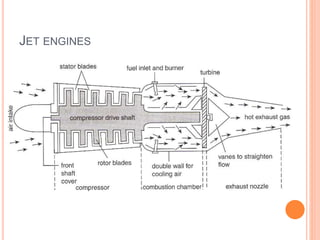
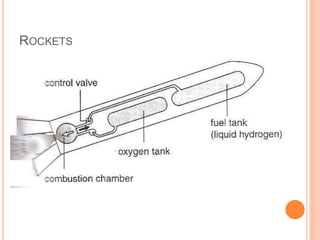
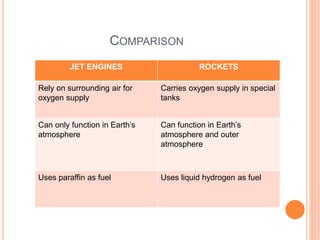
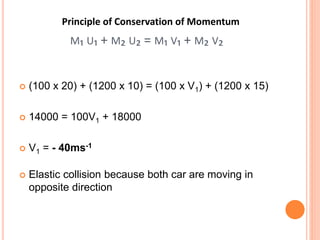
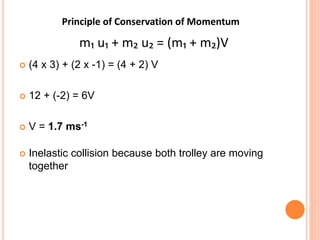
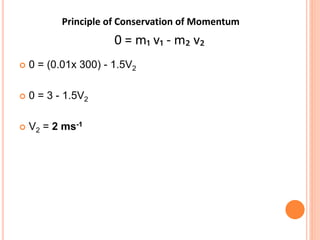
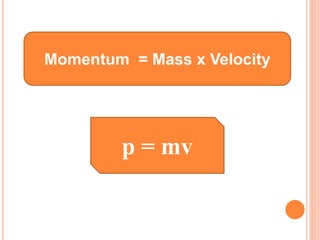
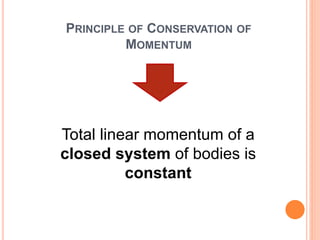
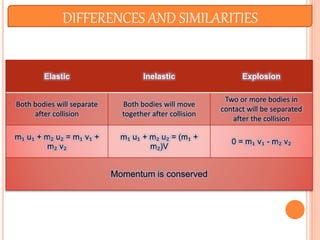
The document discusses linear momentum, the principle of conservation of momentum, and its applications. It defines momentum as the product of mass and velocity (p=mv) and explains that momentum is a vector quantity. The principle of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant. Elastic collisions result in bodies separating after collision while maintaining the total momentum, inelastic collisions result in bodies sticking together, and explosions involve contact before and separation after. Examples demonstrate applying the principle to calculate velocities and momentum in collisions and explosions.