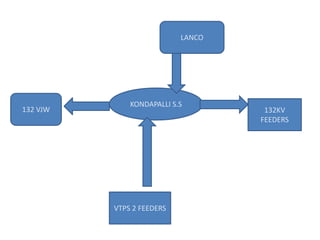
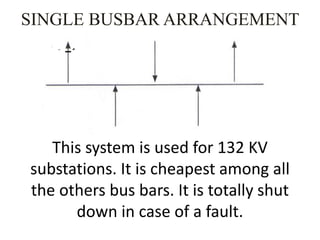
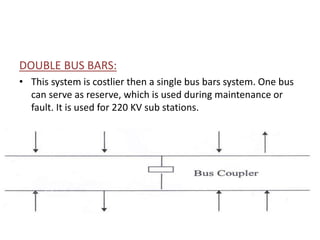
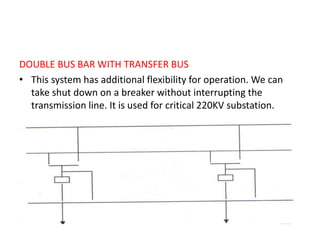
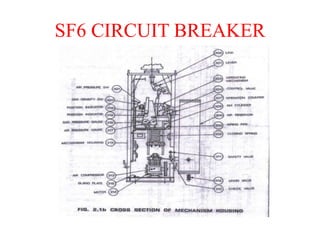
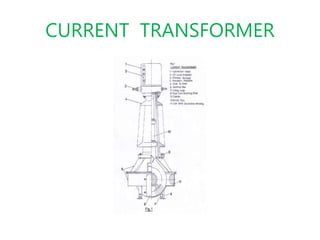
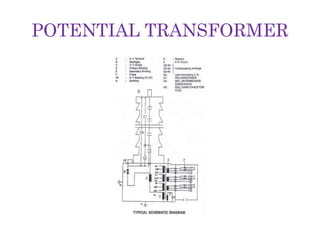
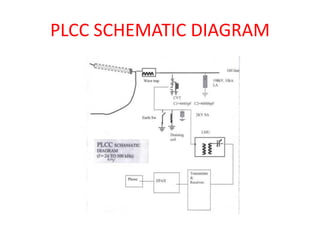
This document summarizes a study of the 220kV switchyard at Dr. NTTPS power plant. It discusses the six batch members who conducted the study and provides an introduction to Dr. NTTPS and the switchyard. The switchyard receives power from various sources via transmission lines and distributes it to several substations. It contains various equipment like bus bars, isolators, circuit breakers, transformers, and insulators. The document describes the different types and components of insulators, bus bars, circuit breakers including SF6 circuit breakers, instrument transformers, and the power line carrier communication system used at the switchyard. It concludes with discussing the tasks and purpose of the switchyard.