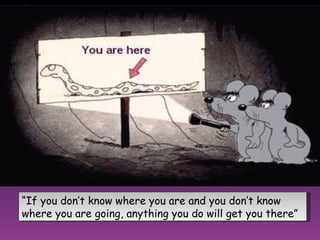
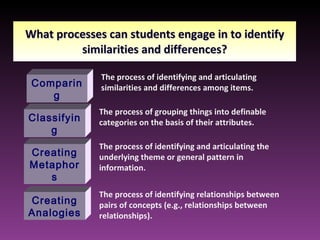
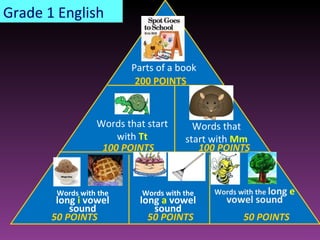
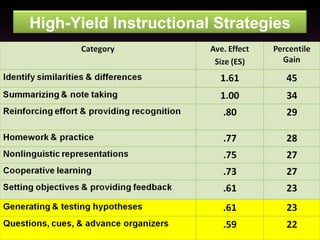
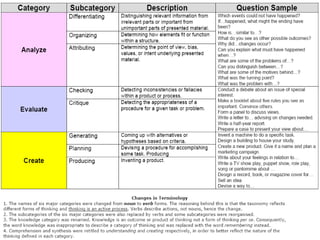
The document discusses three types of curricula: the intended curriculum set by the state, the implemented curriculum delivered by teachers, and the attained curriculum actually learned by students. It notes that the implemented curriculum has the strongest relationship to student achievement. It also discusses essential skills, knowledge and vocabulary for learning targets and content validity.