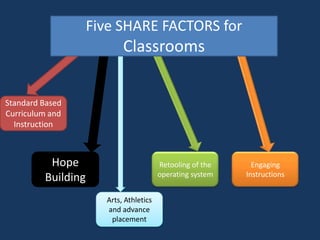
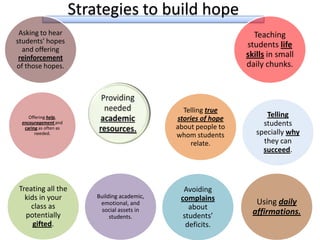
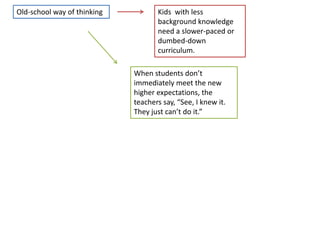
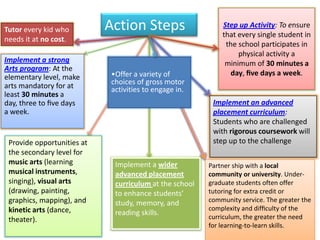
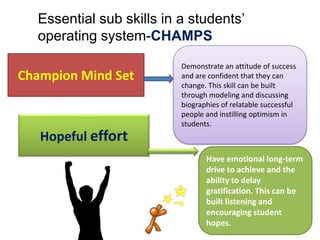
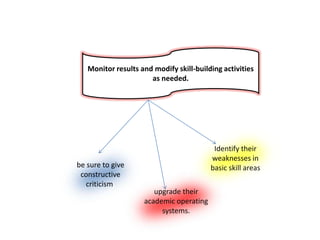
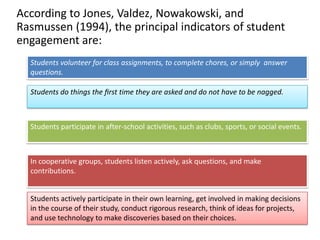
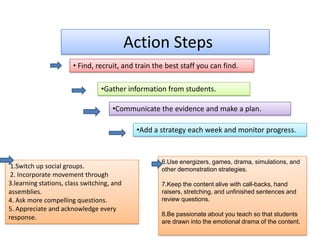
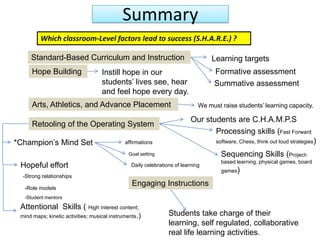
1. A document outlines factors for success in high-poverty classrooms, including using standards-based curriculum and instruction, building hope, retooling systems, engaging instruction, and arts/athletics/advanced placement.
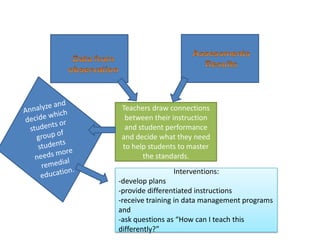
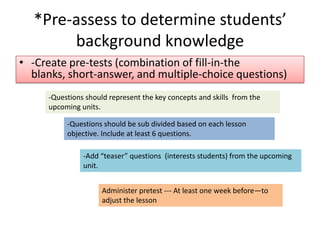
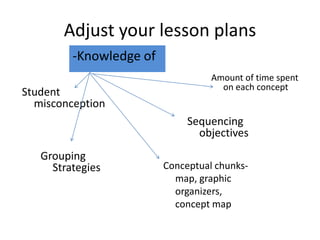
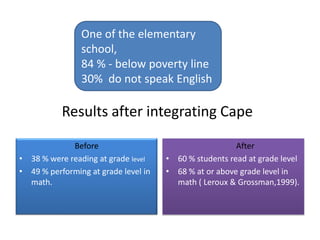
2. It discusses how one school achieved nearly 100% graduation and college attendance rates through ensuring students master standards, using interim assessments, and having teachers analyze data to improve instruction.
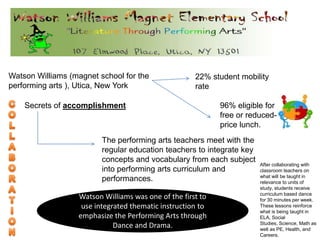
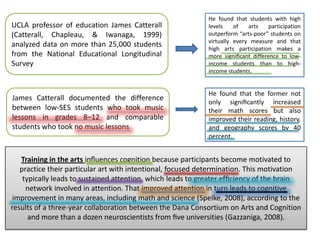
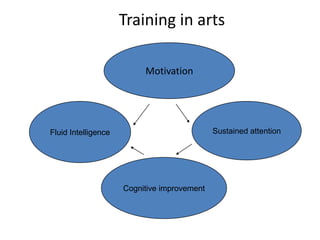
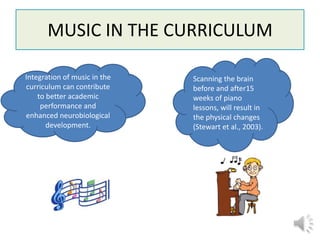
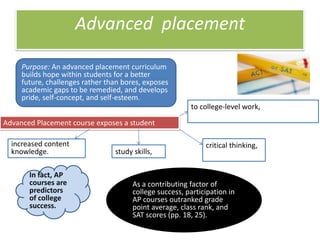
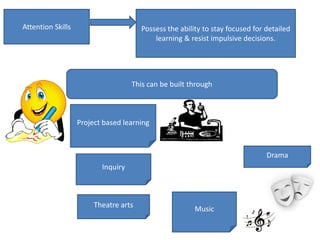
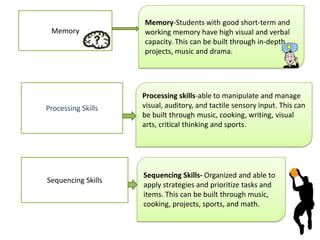
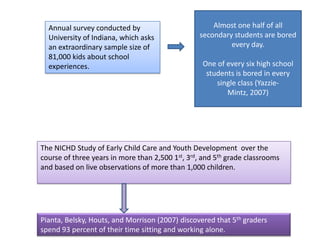
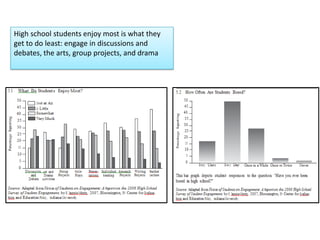
3. The document also emphasizes how arts, athletics, and advanced placement can be essential for high-poverty schools by developing skills, motivating students, and improving academic performance, especially for low-income students. Research shows students with more arts involvement outperform peers on various measures.