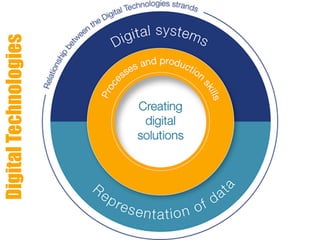
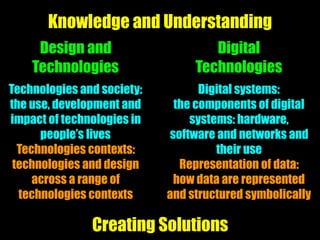
This document discusses teaching computational thinking through technologies education. It emphasizes developing students' thinking skills like design thinking, computational thinking, systems thinking and futures thinking through project-based learning. The document outlines curriculum outcomes, contexts, challenges and expectations for developing solutions across different year levels. It also discusses integrating different models of thinking, evaluating solutions, and the importance of creativity, innovation and accepting failure in the learning process.