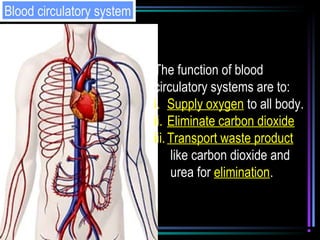
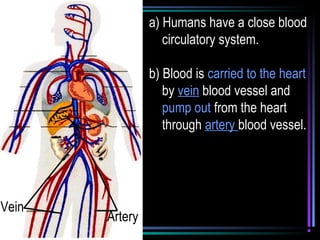
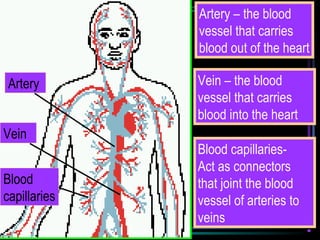
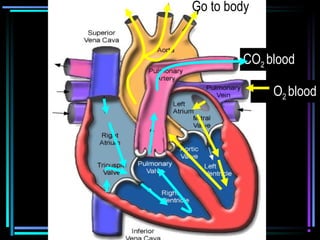
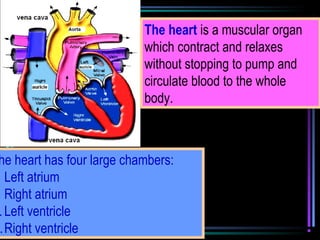
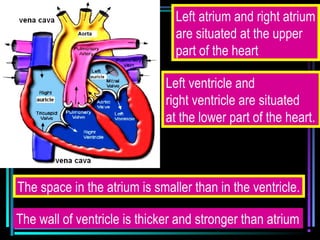
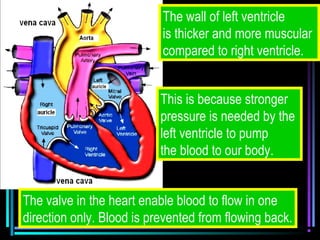
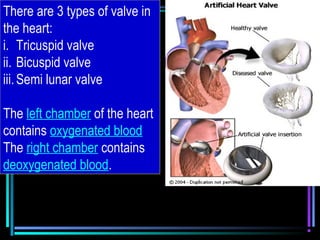
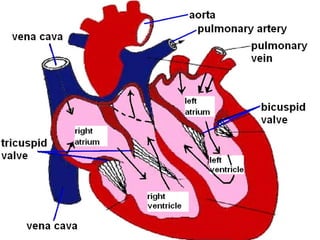
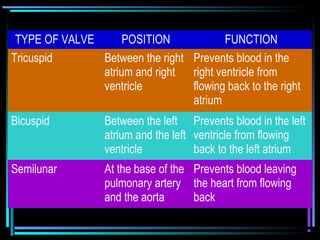
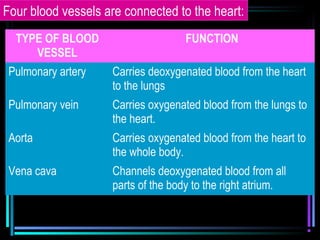
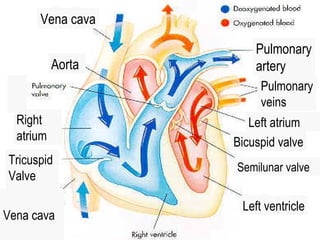
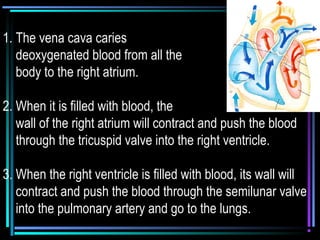
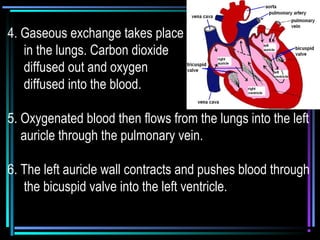
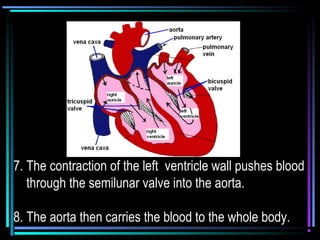
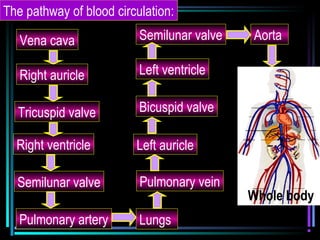
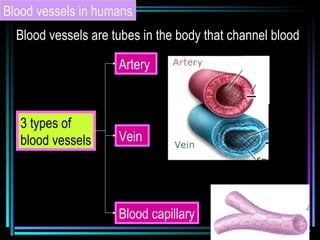
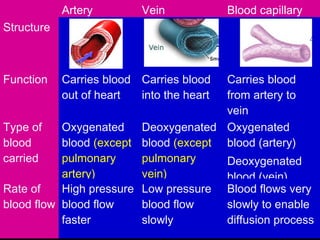
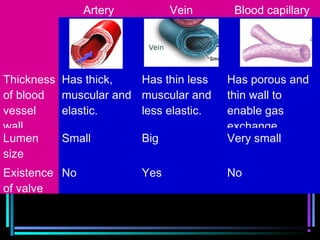
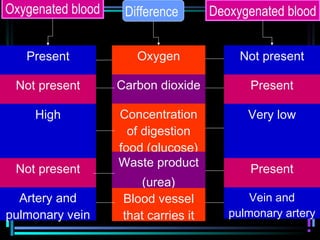
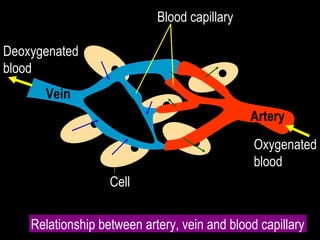
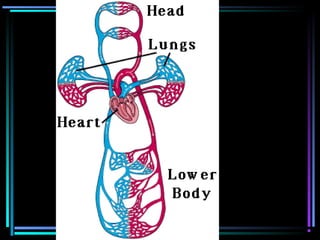
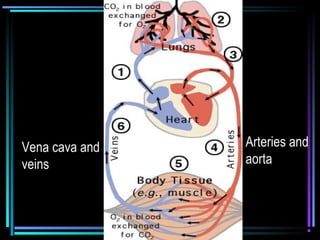
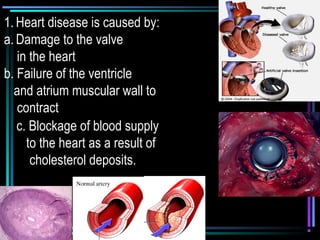
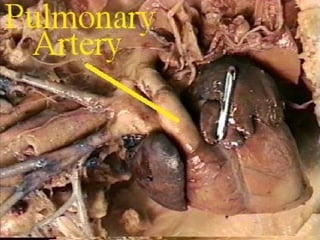
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body via arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, waste, and more. The heart pumps blood through four chambers, with deoxygenated blood entering the right side and oxygenated blood leaving the left side, via the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Oxygenated blood leaves the heart through arteries and delivers oxygen to tissues via capillaries before returning to the heart as deoxygenated blood through veins. This process continuously supplies cells and removes wastes.