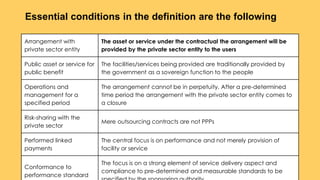
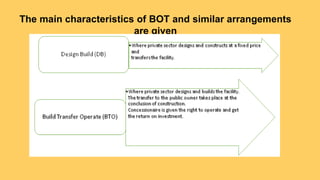
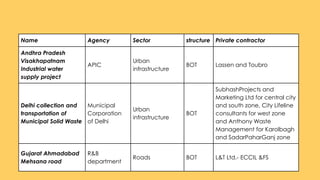
The document discusses public-private partnerships (PPPs) as long-term collaborations between government and private sector agencies for financing and operating infrastructure traditionally provided by governments. It covers various types of PPP models, particularly the Build Operate Transfer (BOT) model, and emphasizes the benefits and challenges of PPPs, including efficiency improvements and financial risks to private participants. The document also highlights the importance of strategic government policies to stimulate local entrepreneurship through PPPs, especially in rural areas.