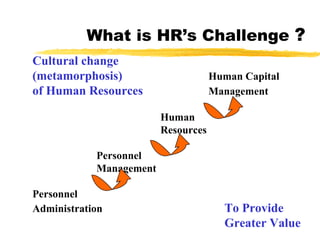
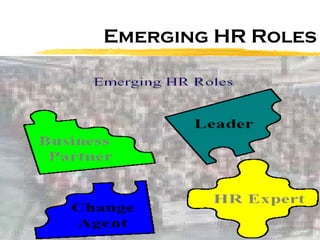
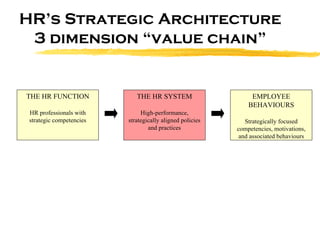
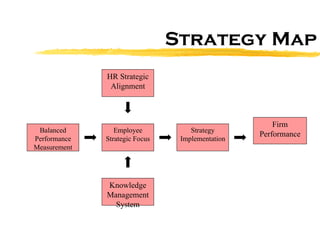
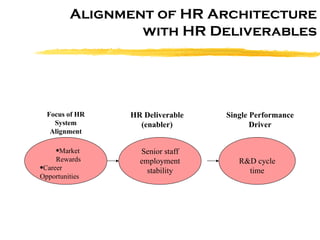
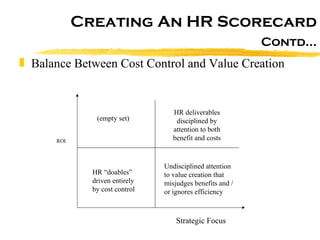
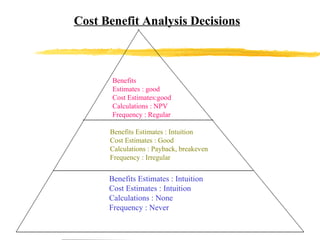
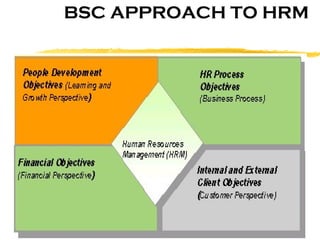
The document discusses HR scorecards and balanced scorecards. It provides an overview of how HR has evolved from an administrative function to a strategic partner. It then discusses the benefits of HR scorecards in measuring HR's contribution to business strategy. It outlines the key components of developing an effective HR scorecard and balanced scorecard, including defining value drivers, specifying actions, measuring accomplishments, and reporting results to stakeholders.