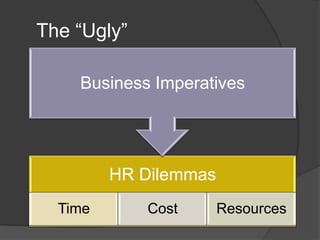
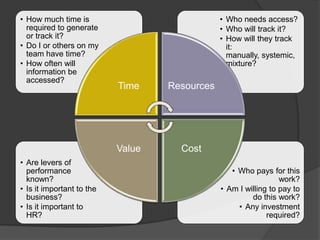
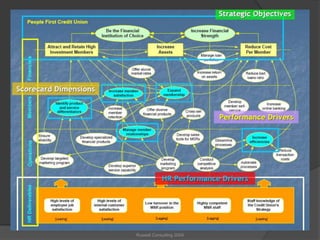
The presentation discusses the importance of HR metrics in enhancing business performance, emphasizing that HR can significantly influence the bottom line by utilizing data to make informed decisions. It outlines the challenges and best practices of implementing HR metrics, including the need for alignment with business strategy and distinguishing between leading and lagging indicators. Additionally, it stresses the importance of communicating metrics effectively to business partners to demonstrate HR's impact and contribution to organizational success.