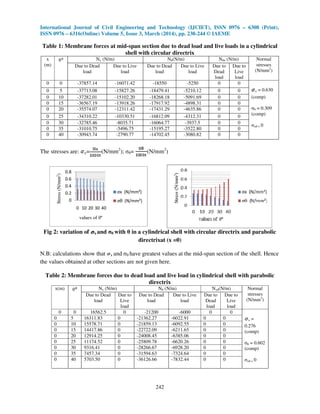
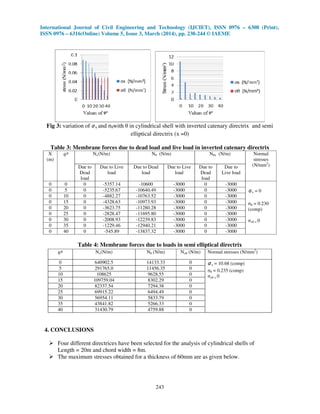
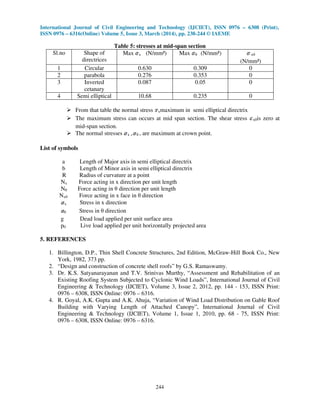
This document analyzes the effect of different directrix shapes (circular, parabolic, elliptical, inverted catenary) on membrane stresses in cylindrical shell roofs. Membrane theory is used to determine the normal forces (Nx, Nθ, Nxθ) and stresses under self-weight and live loads. Equations for each directrix are presented. An example problem is solved and results are shown in tables comparing stresses for each directrix. The analysis found that stresses are lowest with an inverted catenary directrix and highest with an elliptical directrix to cover the same area.


![International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), ISSN 0976 – 6308 (Print),
ISSN 0976 – 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue 3, March (2014), pp. 238-244 © IAEME
241
Stresses due to live load
Nθ = - p0R0 ,Nxθ = - p0 x sin θ cos θ and Nx= - 0.50 ( - x²) cos 2θ cos² θ
2.6 Stresses due to dead and live loads in cylindrical shells with semiellipse directrix Stresses
due to dead load
Nθ = -g Nxθ = - gx[ 2 + sin θ
Nx = - ( - x²) [ + ( cos ² θ – sin²θ ) ] cos θ
Stresses due to live load
Nθ = -p0 Nxθ = -3p0x ( )
Nx = - p0( - x²) [ ]
We can solve the problem and findout the stresses in different directrices by using the above
equations.
3. EXAMPLE PROBLEM
To determine membrane stress resultants Nx, NθandNxθof a circular cylindrical shell, the
following dimensions are assumed.
Span L= 20 m
Radius of curvature R = 7 m
Shell thickness d = 60 mm
Semi central angle = 40
Width of the shell = 8 m
Dead load = 2650 N/m² and
Live load = 750 N/m2
For all the directrices the span thickness and width of the shell are respectively the same. In
semi elliptical directrix the length of major axis a=4m and minor axis b=3m.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20320140503027-140520083655-phpapp02/85/20320140503027-4-320.jpg)