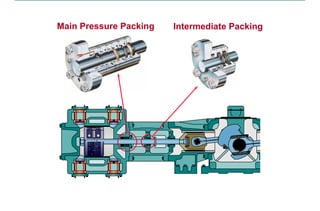
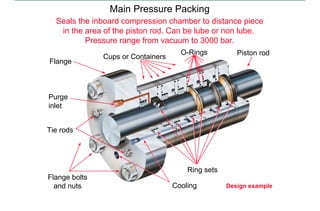
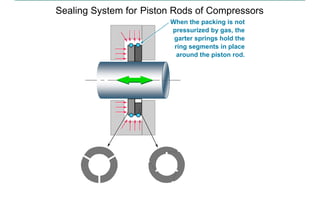
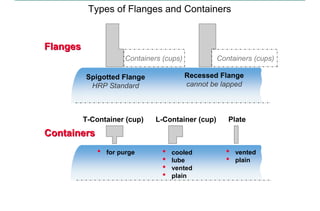
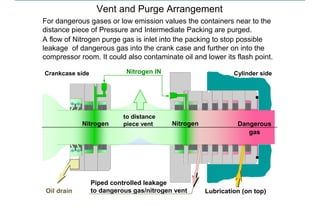
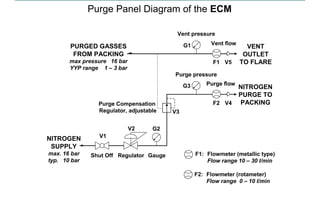
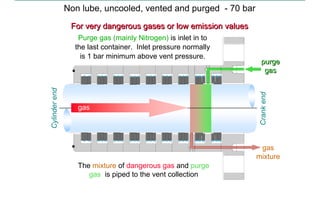
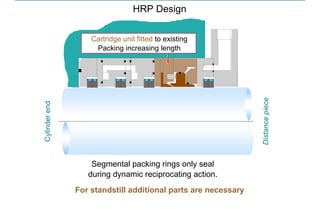
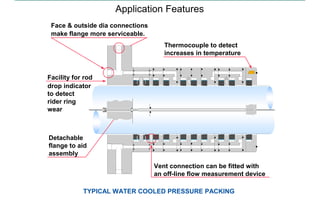
This document discusses pressure packings used for piston compressors. It provides information on the basic understanding, ring theory, and typical types of pressure packings. Main pressure packings seal the compression chamber from the distance piece around the piston rod, while intermediate packings seal between distance pieces. Segmented rings are used with garter springs or gas pressure to create a seal around the piston rod, which allows for rod movement. Common ring types include single acting, double acting, and those with backup rings for higher pressures.