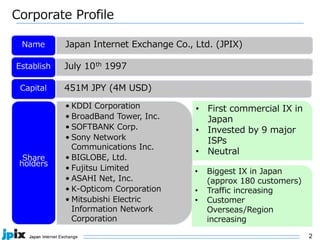
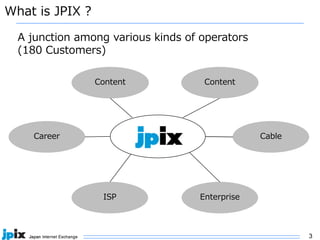
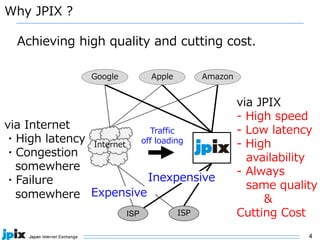
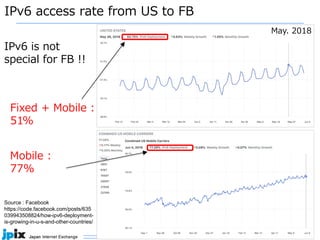
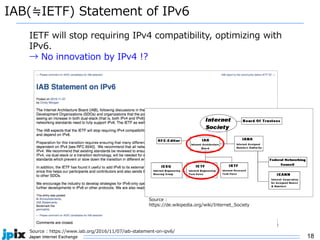
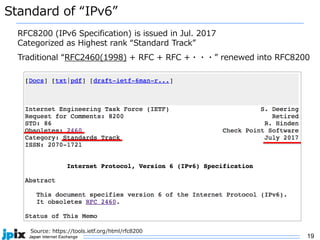
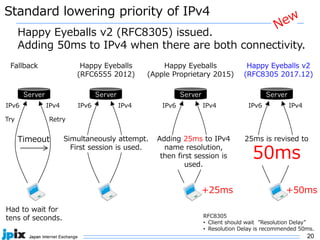
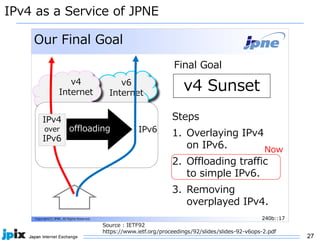
The document discusses the current state and future of IPv4 and IPv6. It provides the following summary:
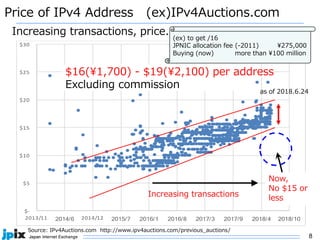
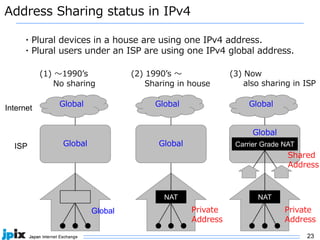
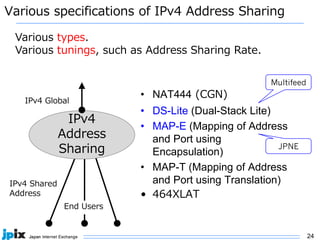
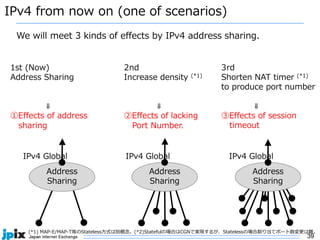
1. IPv4 addresses are becoming increasingly scarce and expensive as they are exhausted. Address sharing through Carrier Grade NAT is common but creates issues for identifying users.
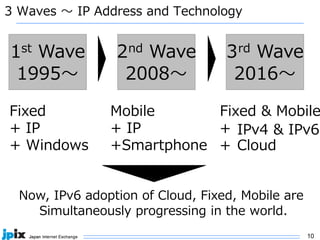
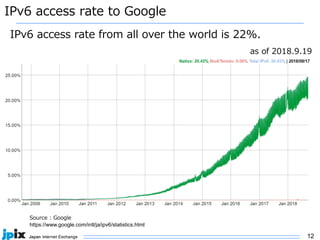
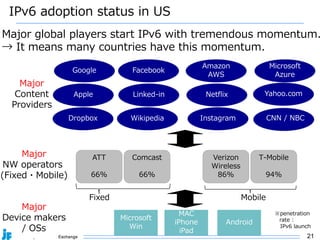
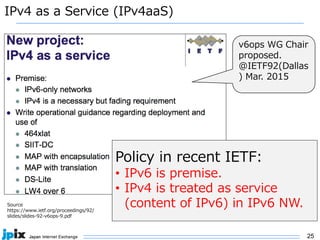
2. IPv6 adoption is growing globally, with over 20% of traffic now over IPv6. Major networks, cloud providers, device makers, and operating systems increasingly support IPv6-only.
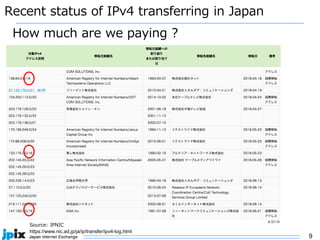
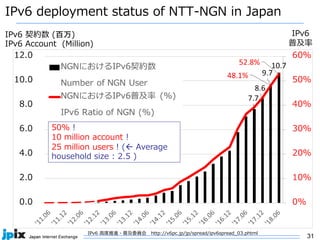
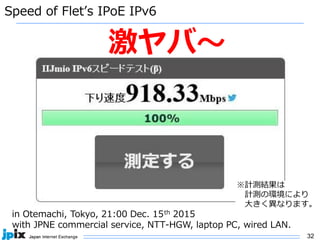
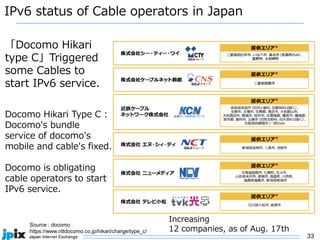
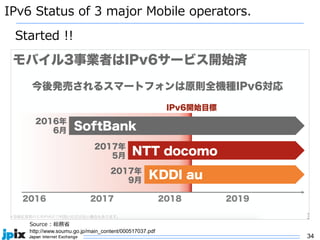
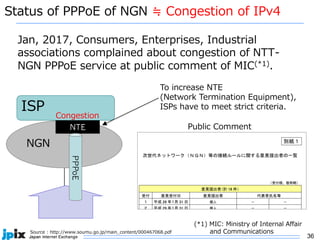
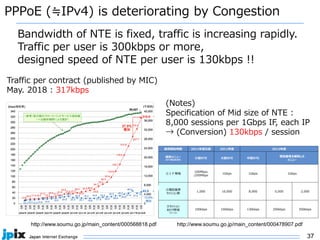
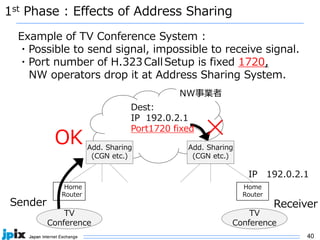
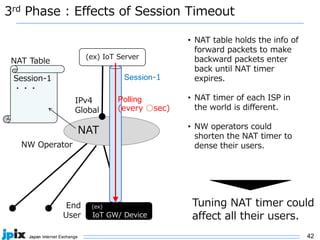
3. In Japan, major ISPs like NTT and mobile carriers have over 50% of customers using IPv6. However, IPv4 congestion is a problem due to overuse of CGN address sharing. The effects of IPv4