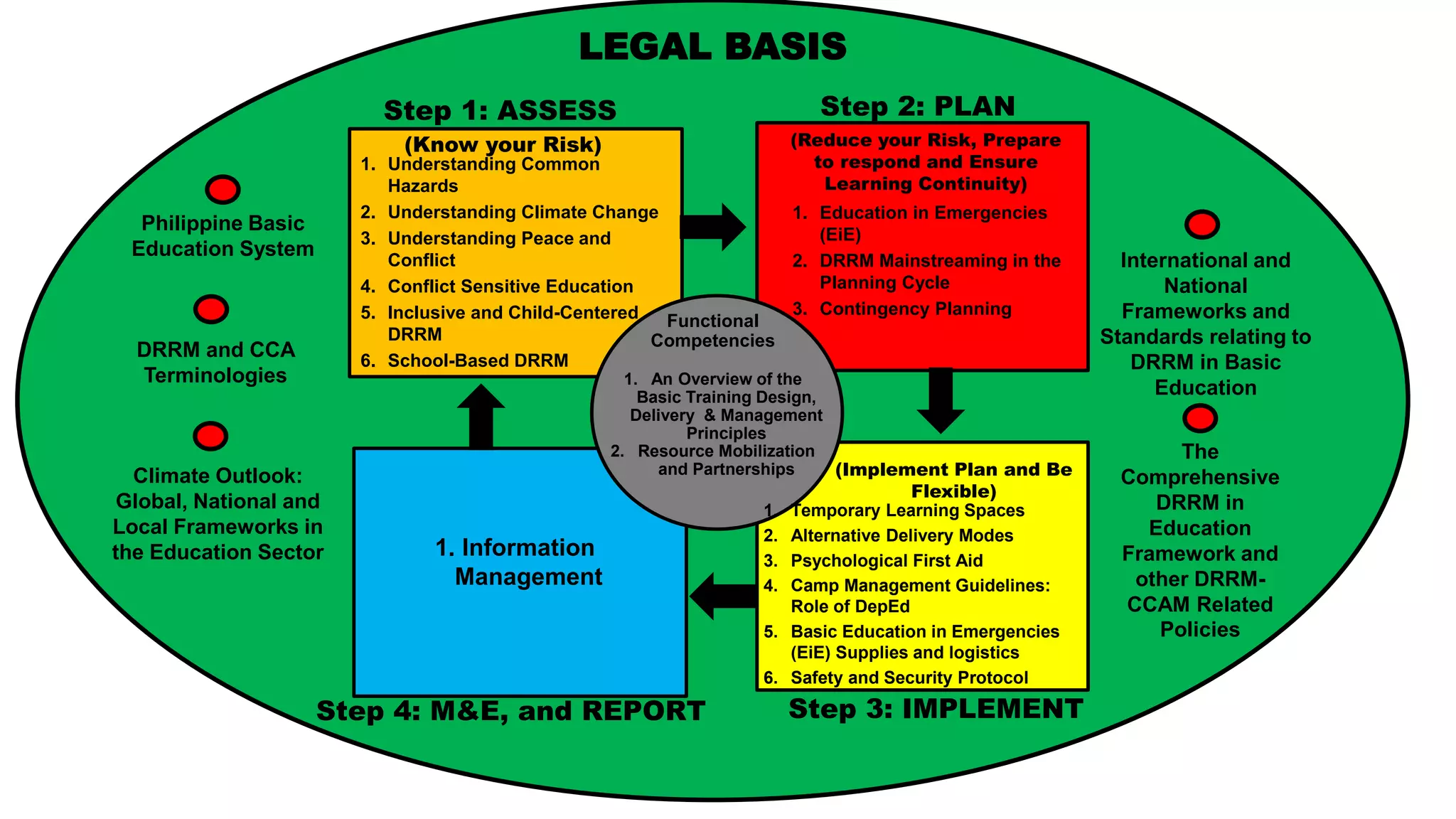
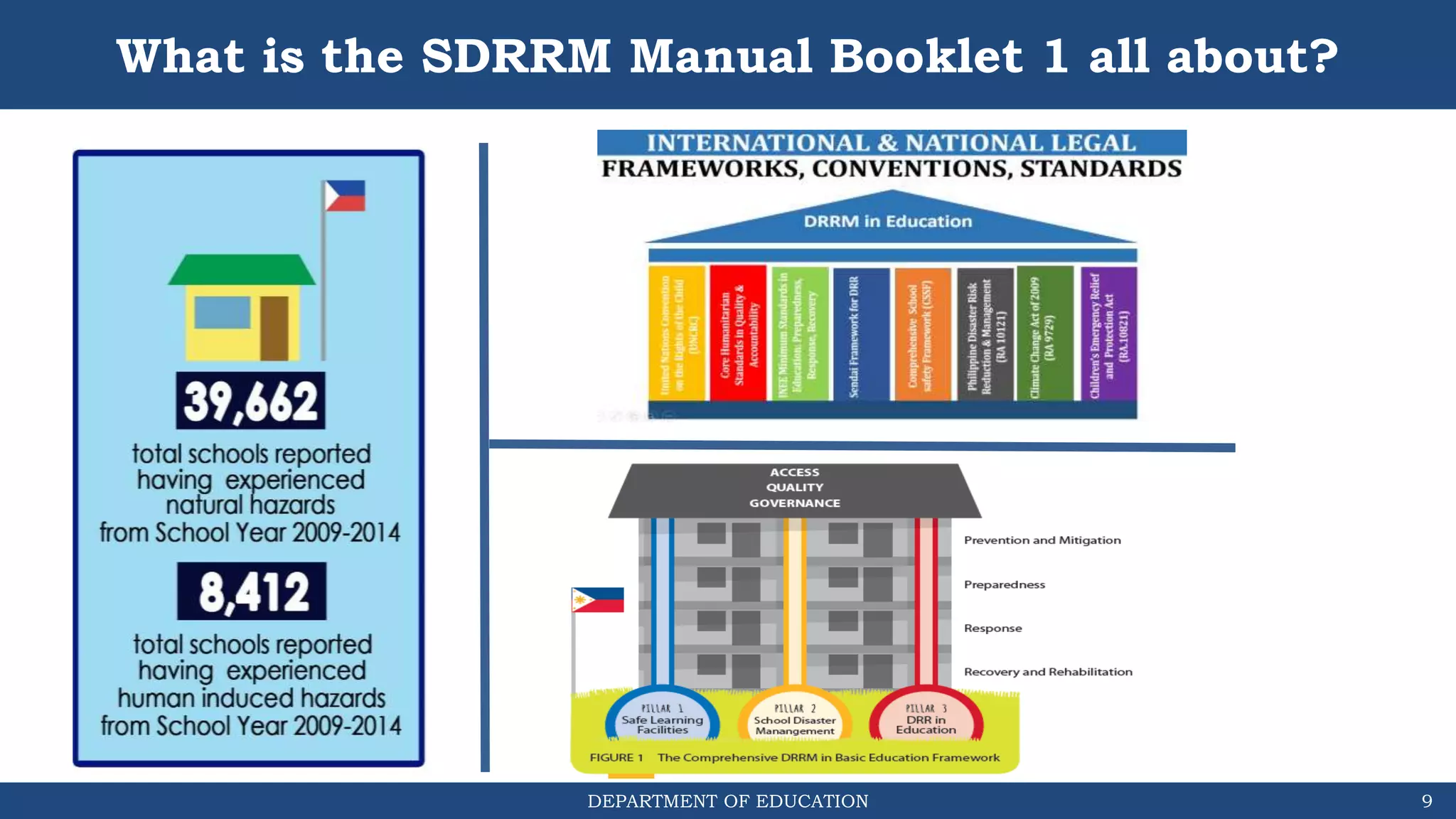
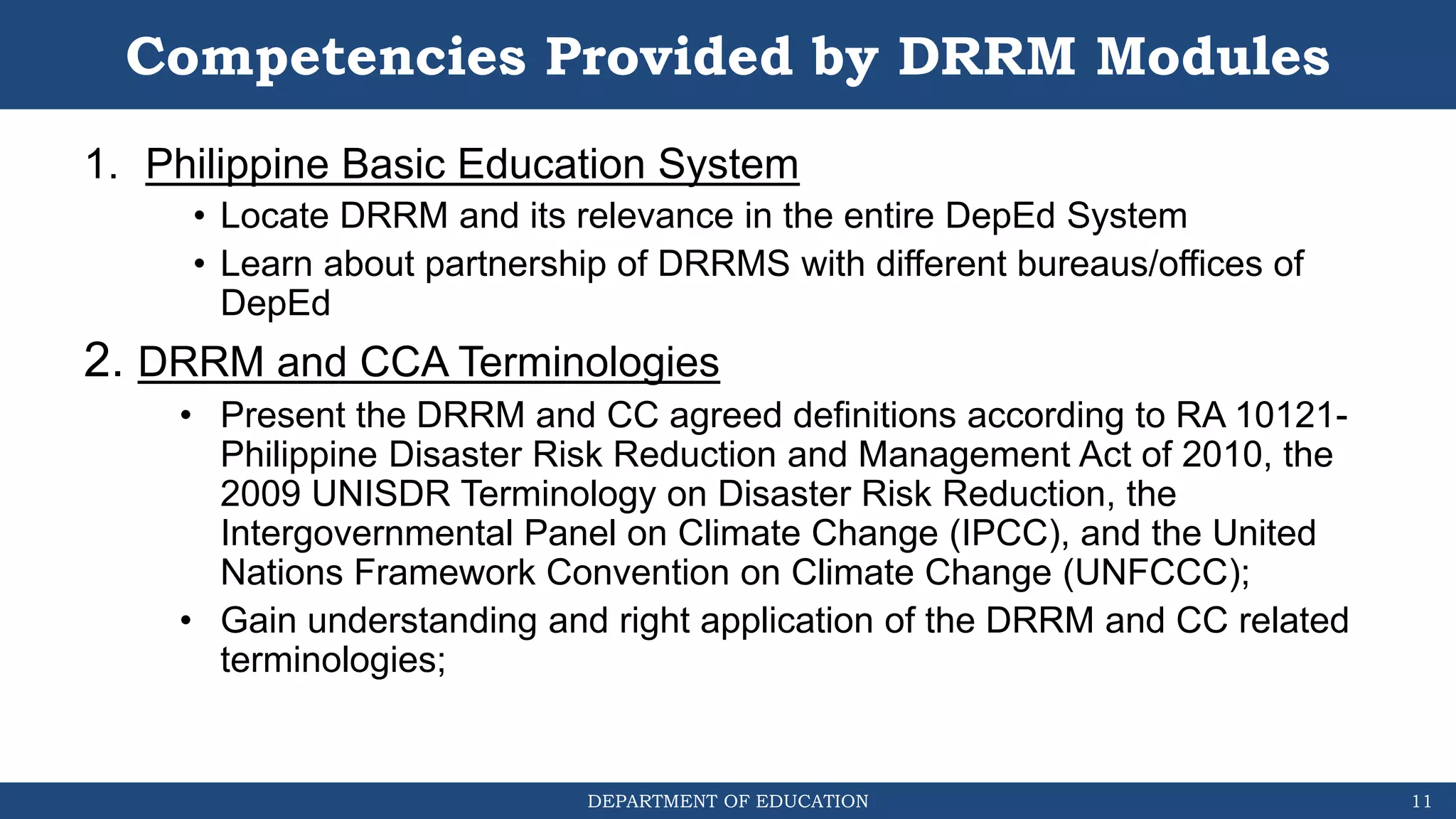
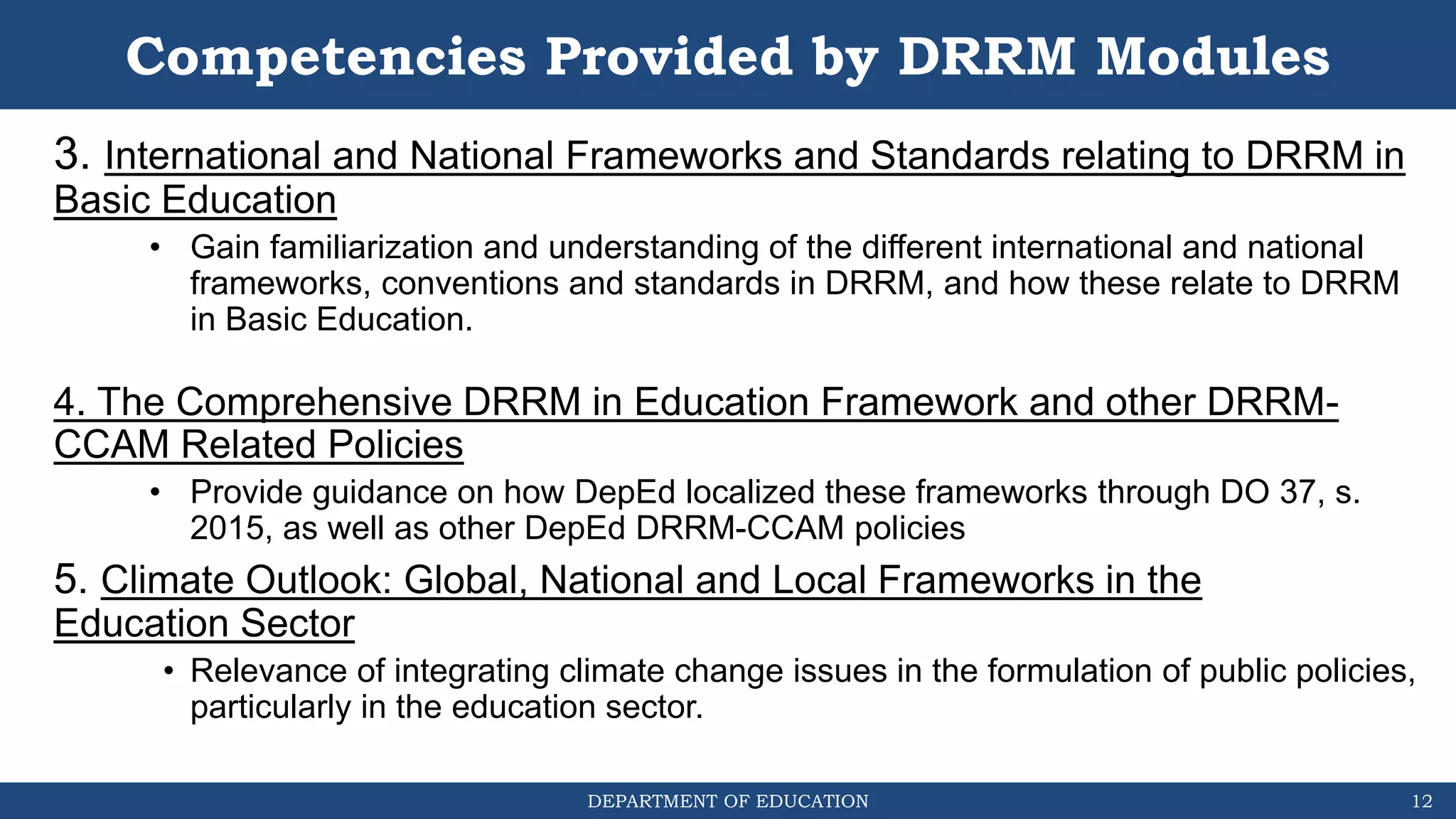
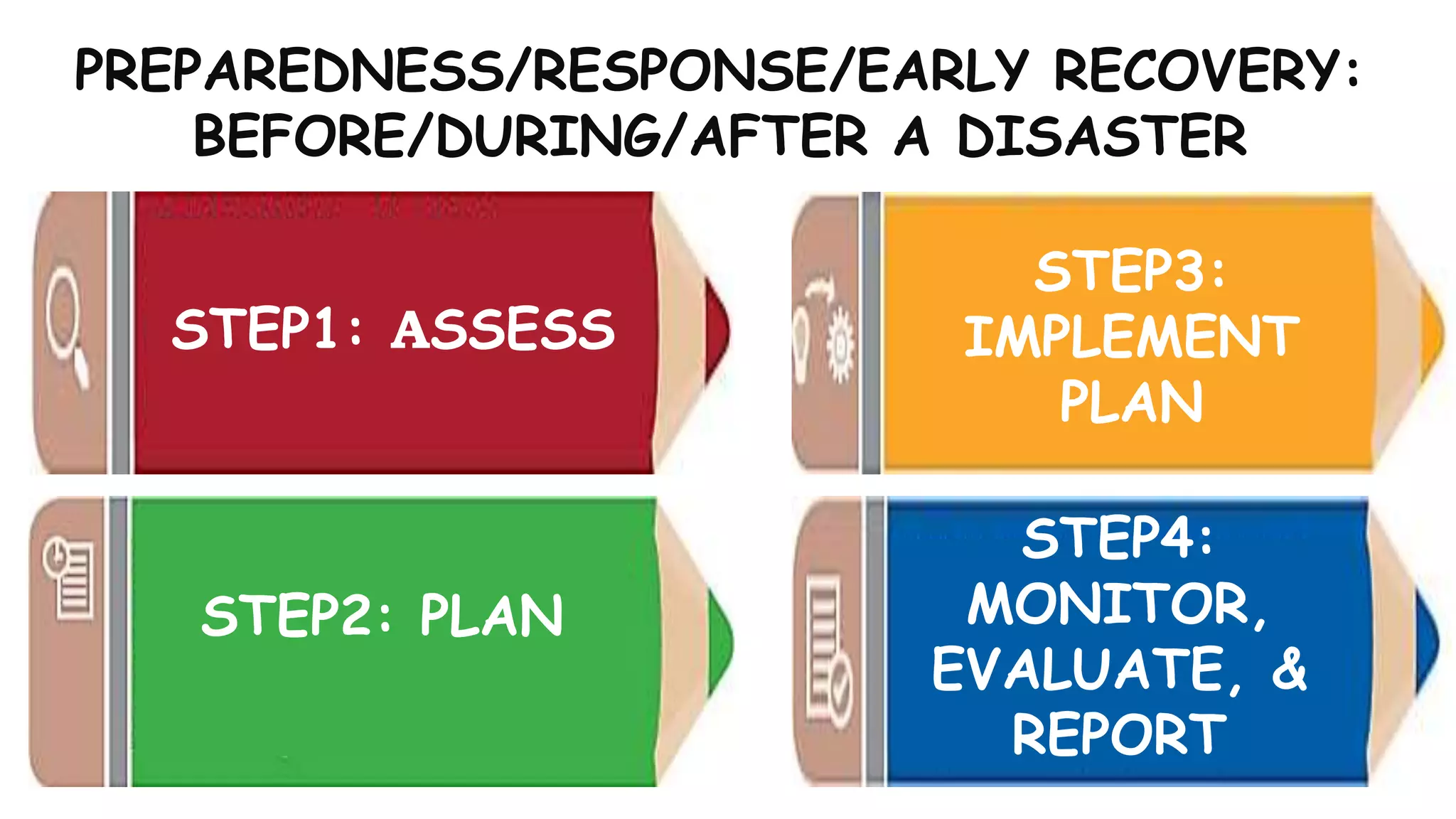
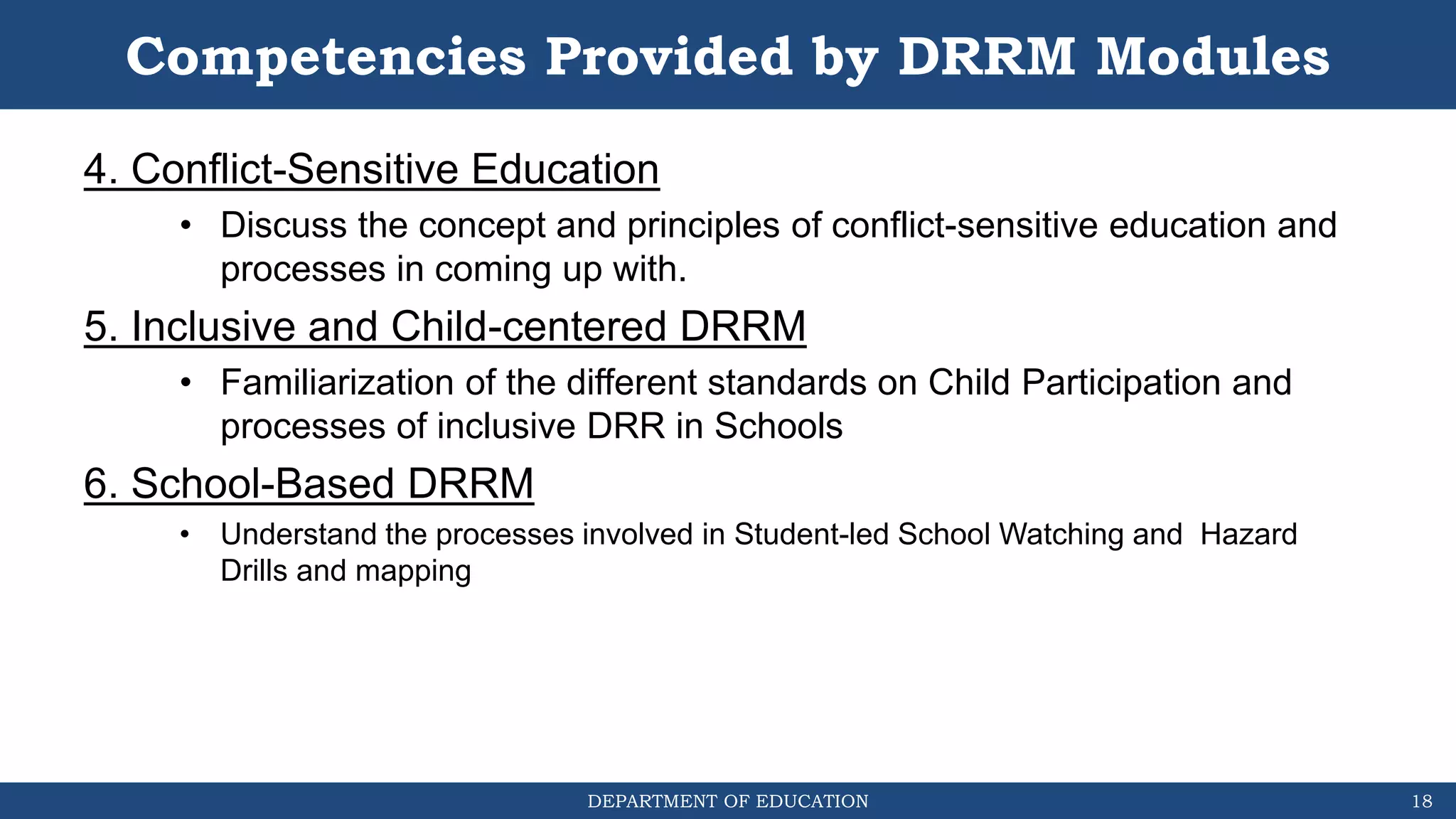
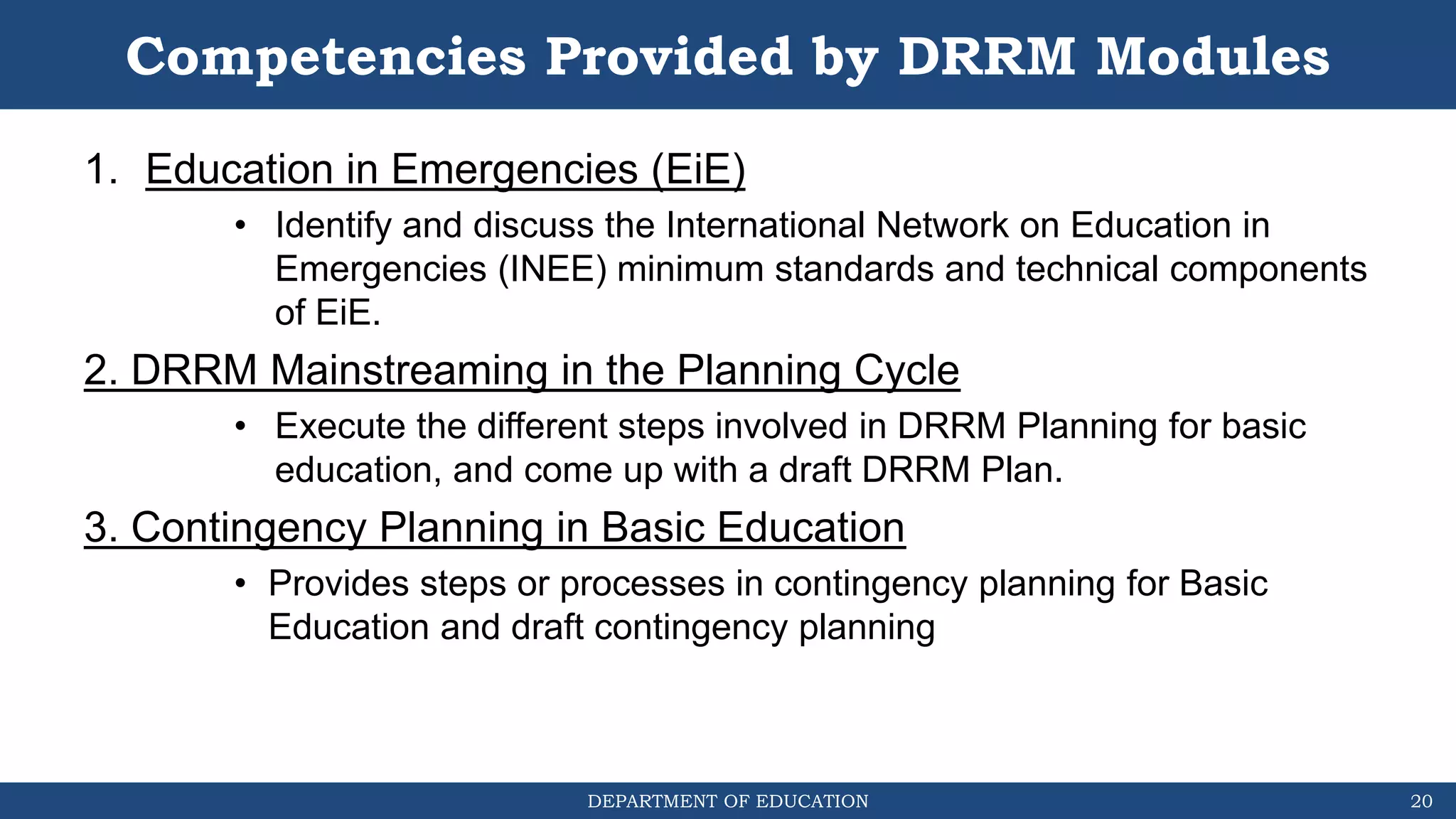
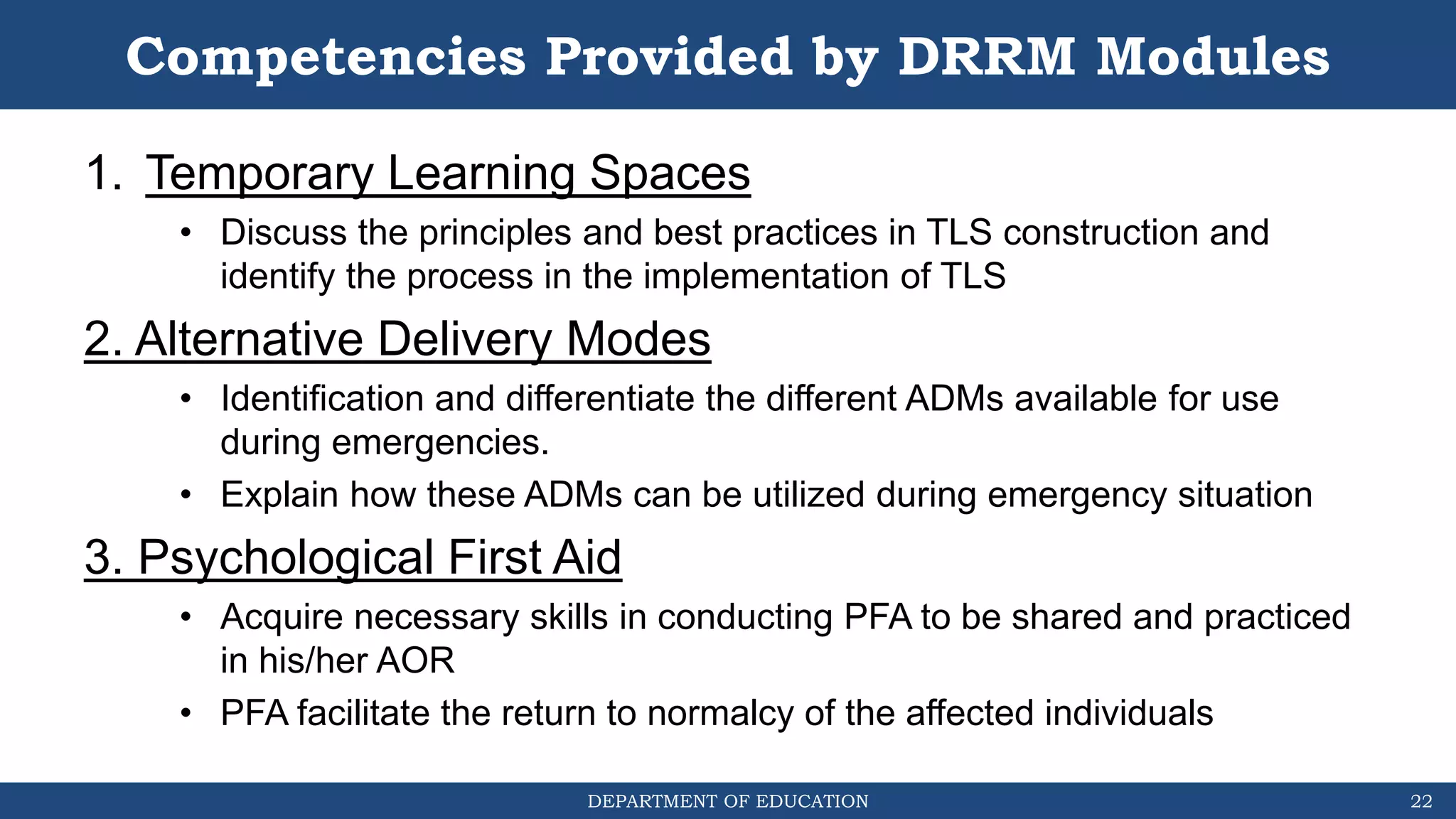
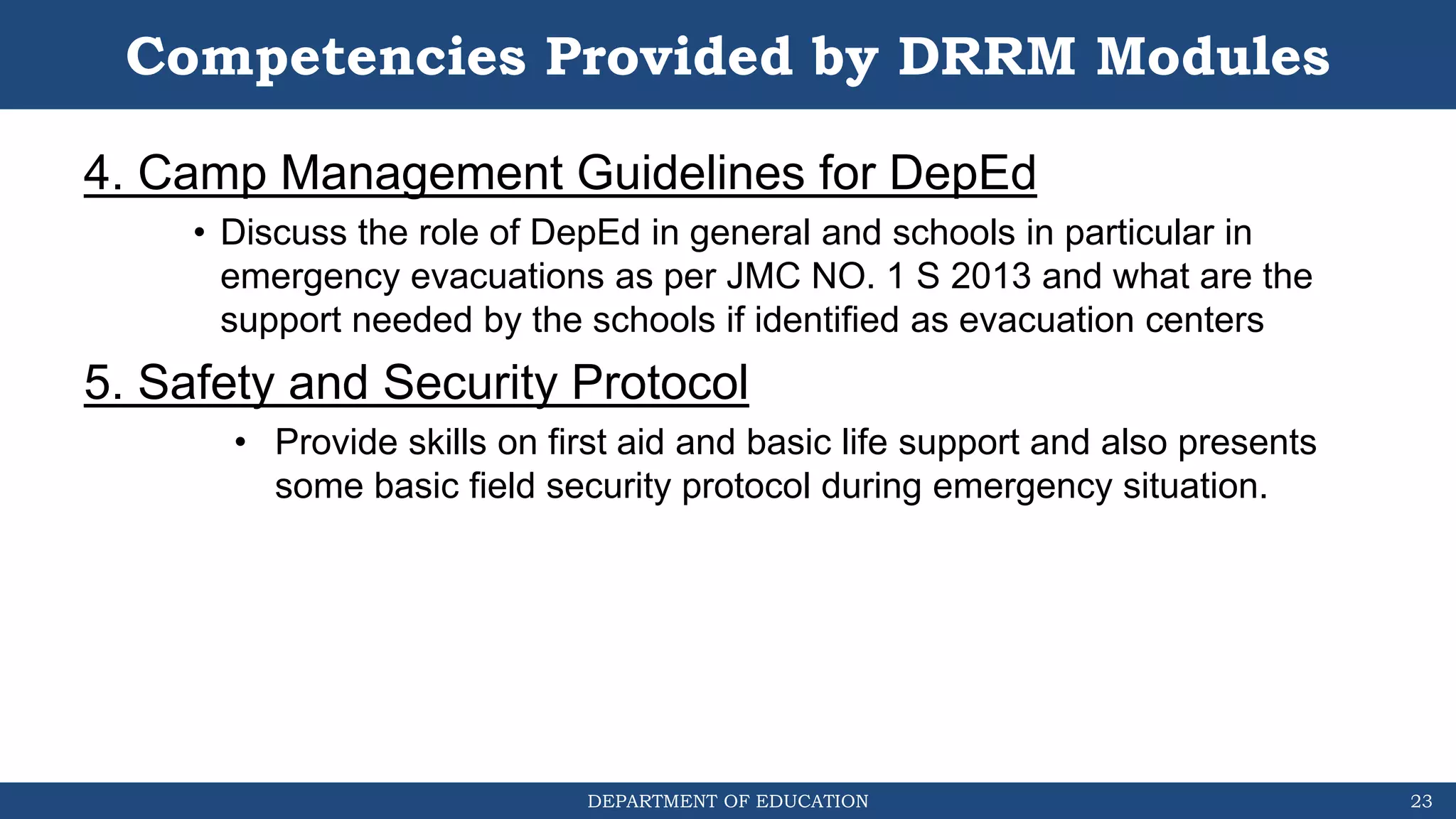
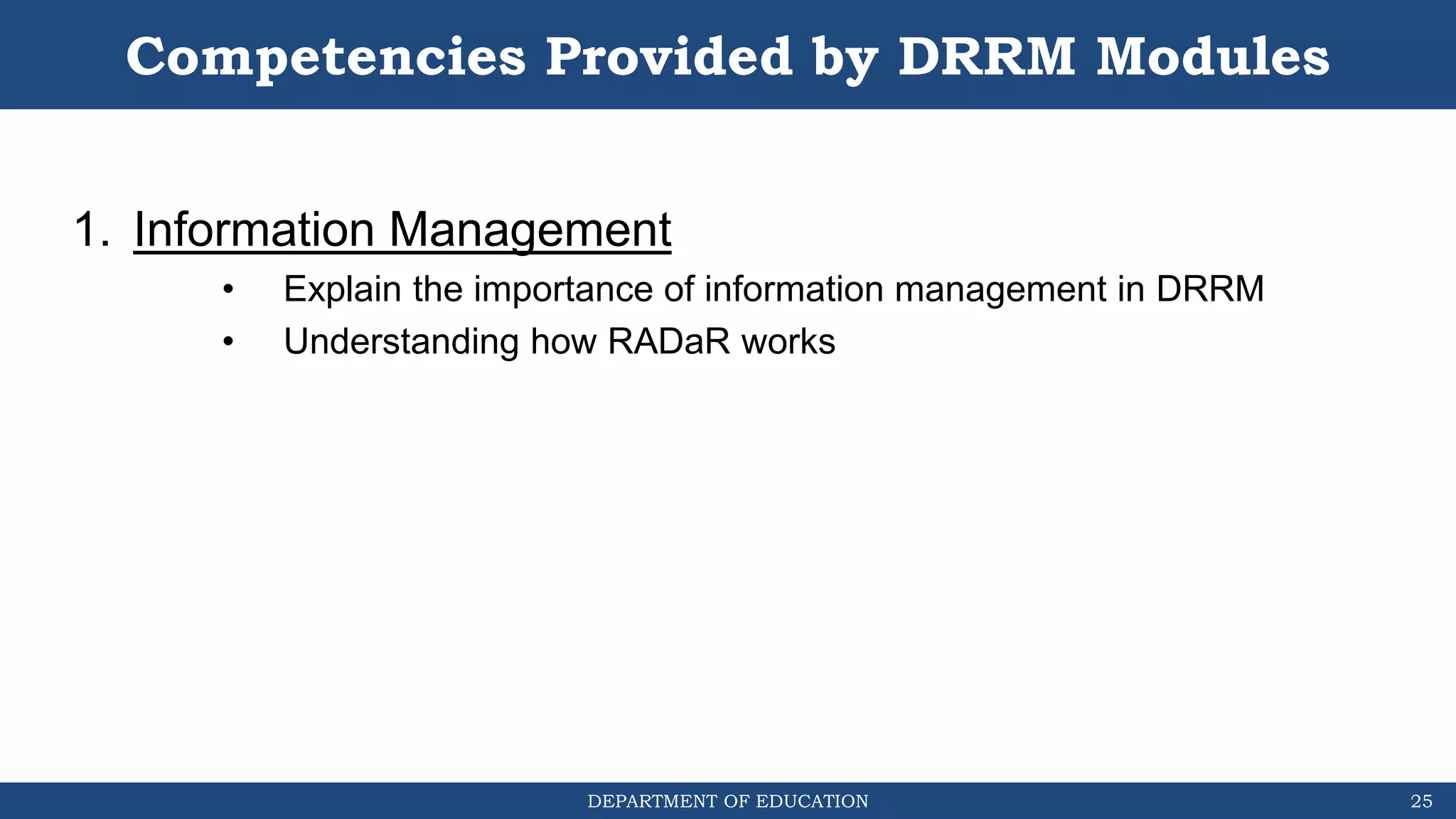
The document discusses how the DRRM Modules supplement the School Disaster Risk Reduction Management (SDRRM) Manual. The modules provide competencies to support schools in implementing the 4 steps of DRRM: 1) Assess, 2) Plan, 3) Implement Plan, and 4) Monitor, Evaluate, and Report. Some competencies include understanding hazards, mainstreaming DRRM into planning, and using alternative delivery modes. The overall goal is to build capacity of DRRM Coordinators to help schools accomplish international, national, and local DRRM frameworks and standards.