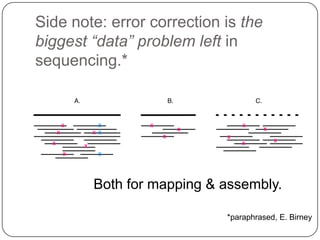
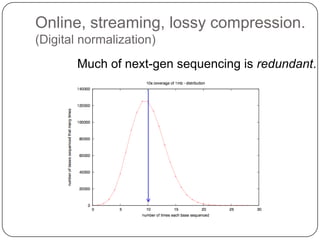
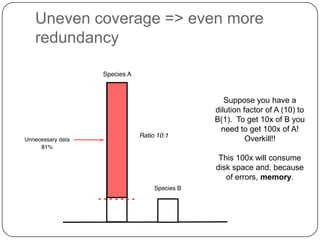
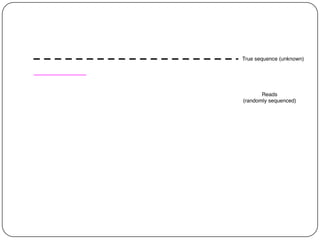
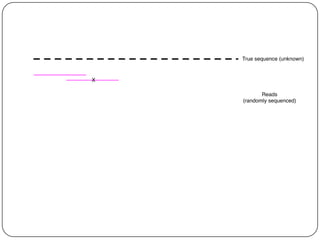
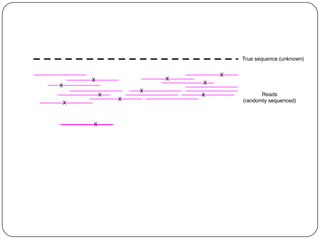
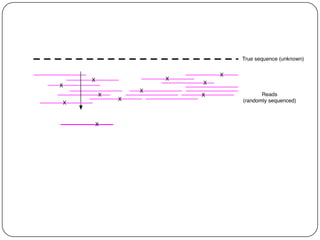
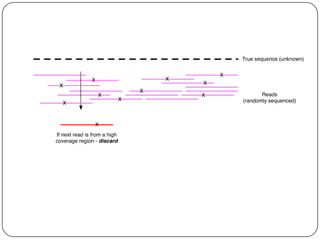
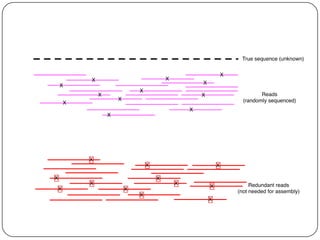
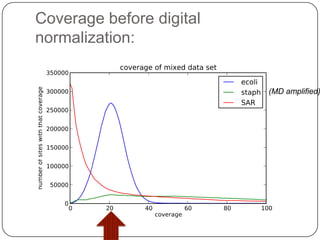
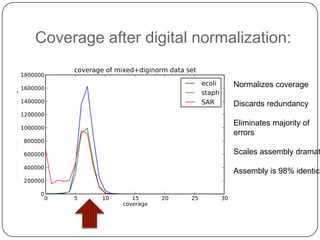
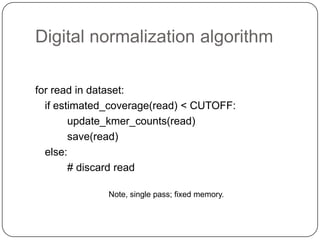
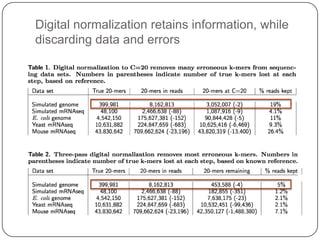
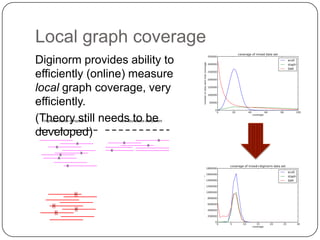
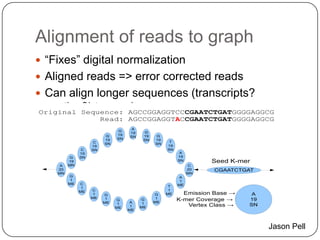
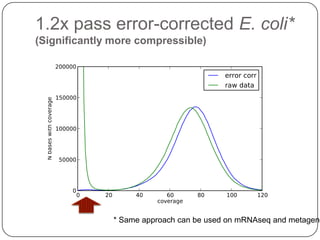
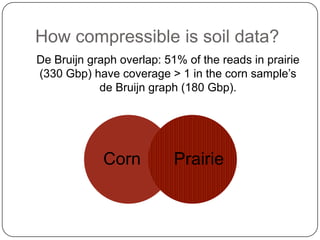
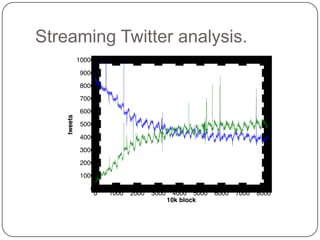
Digital normalization is a streaming approach to sequence data compression that reduces redundancy and errors. It works by normalizing coverage across reads and discarding redundant reads to dramatically reduce data size and memory needs while retaining 98% of the original assembly information. This approach enables online and streaming analysis of sequence data and has implications for scalable variant calling, sample categorization, and graph-based assembly and alignment.