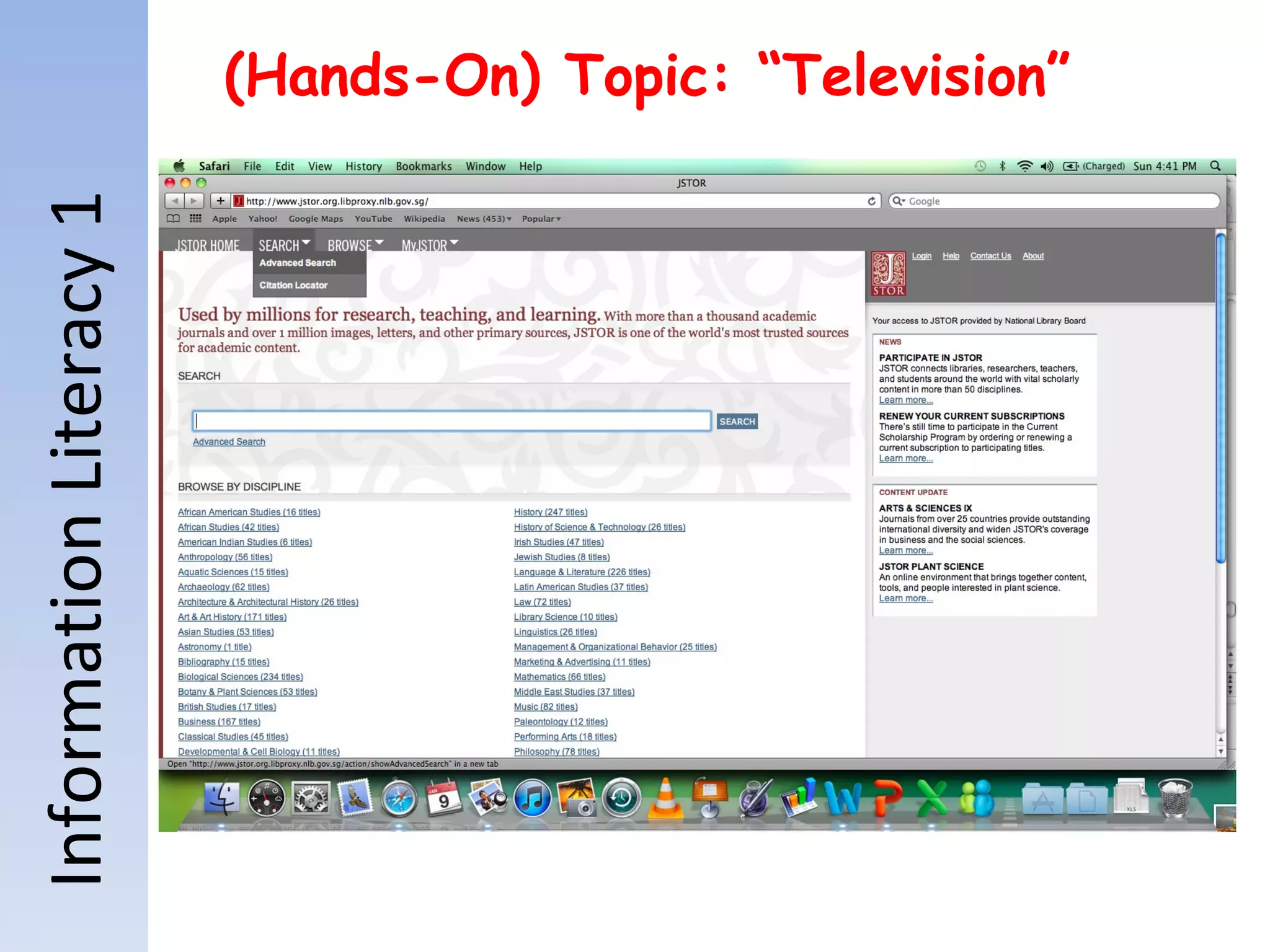
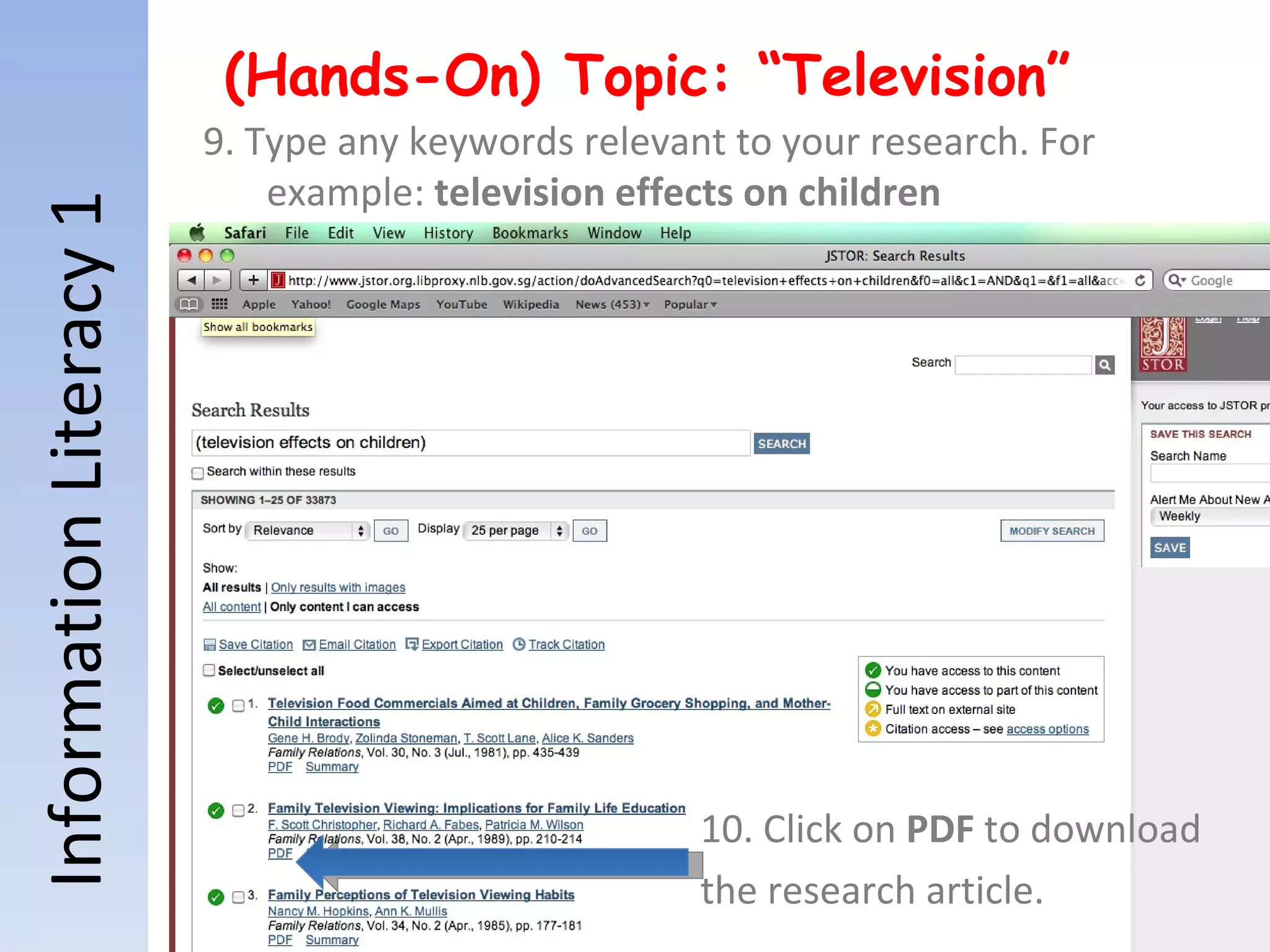
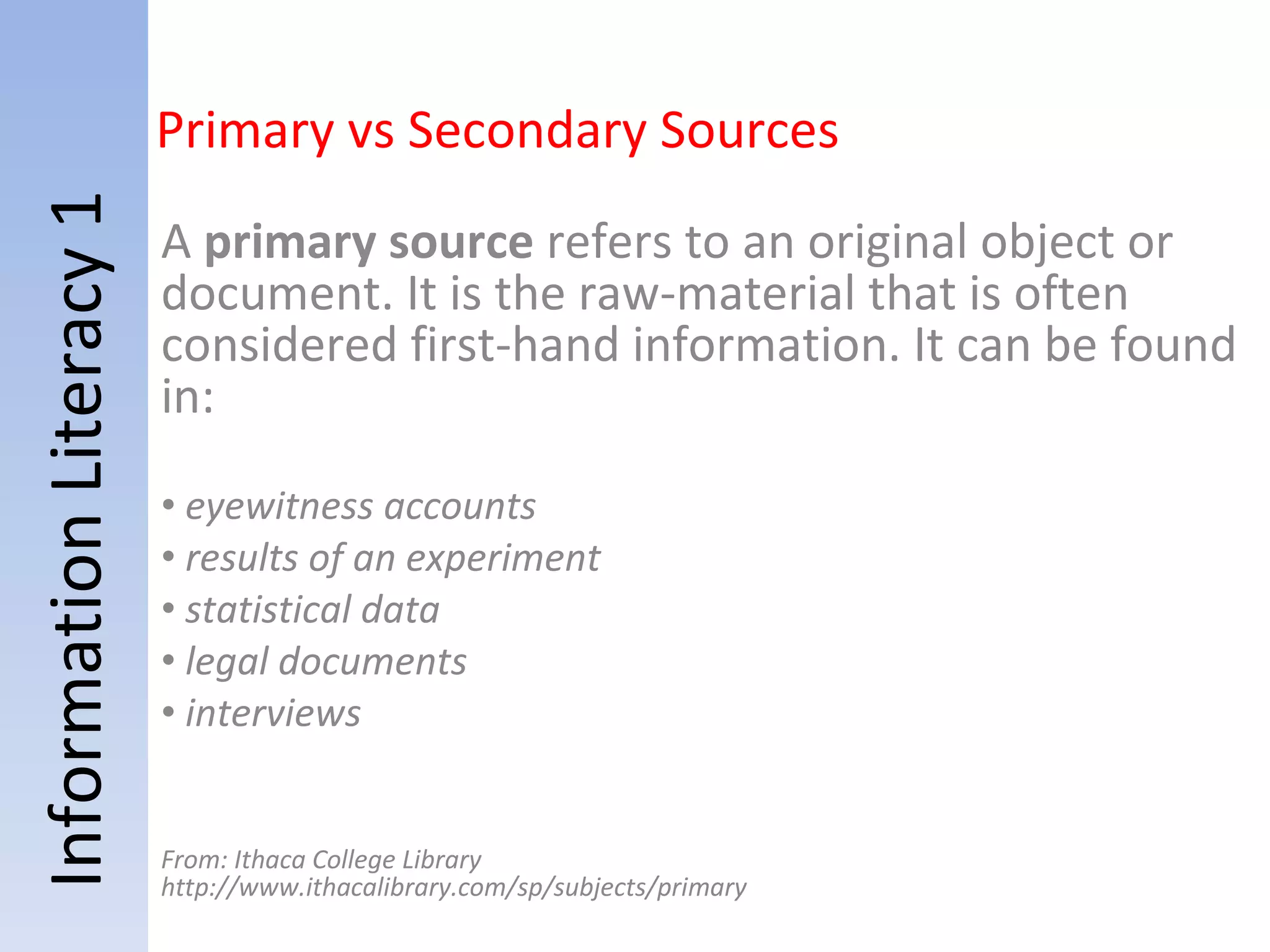
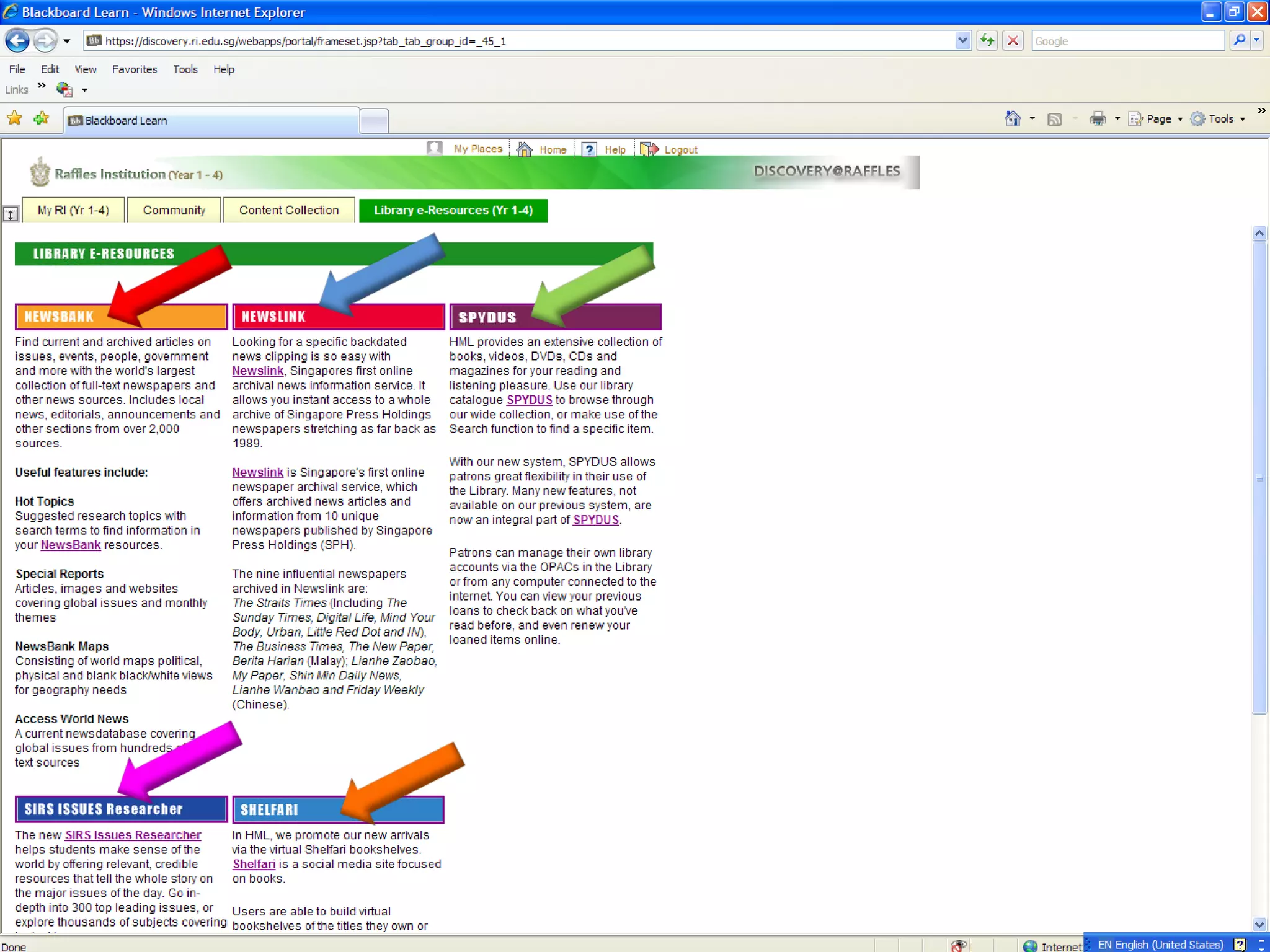
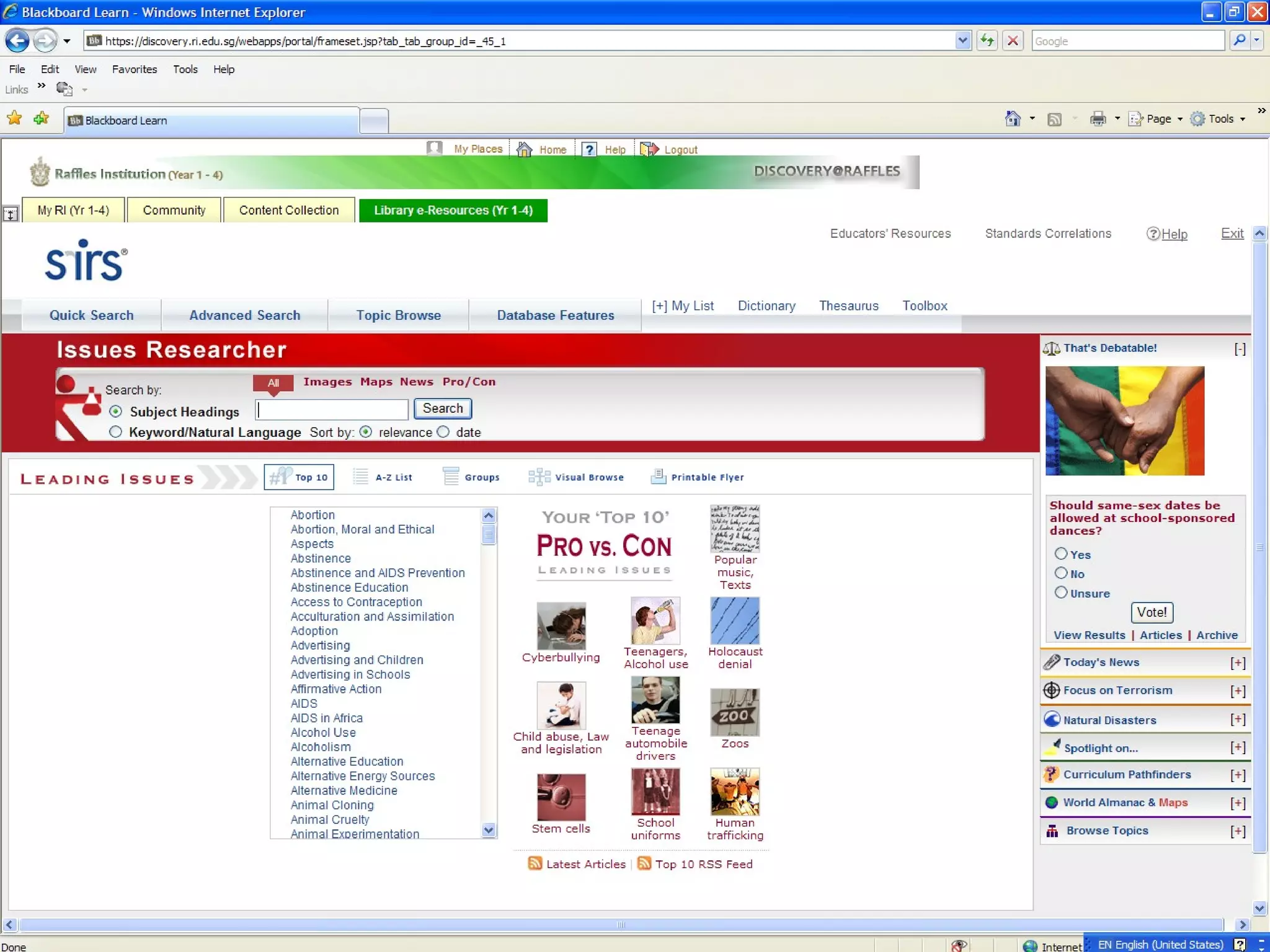
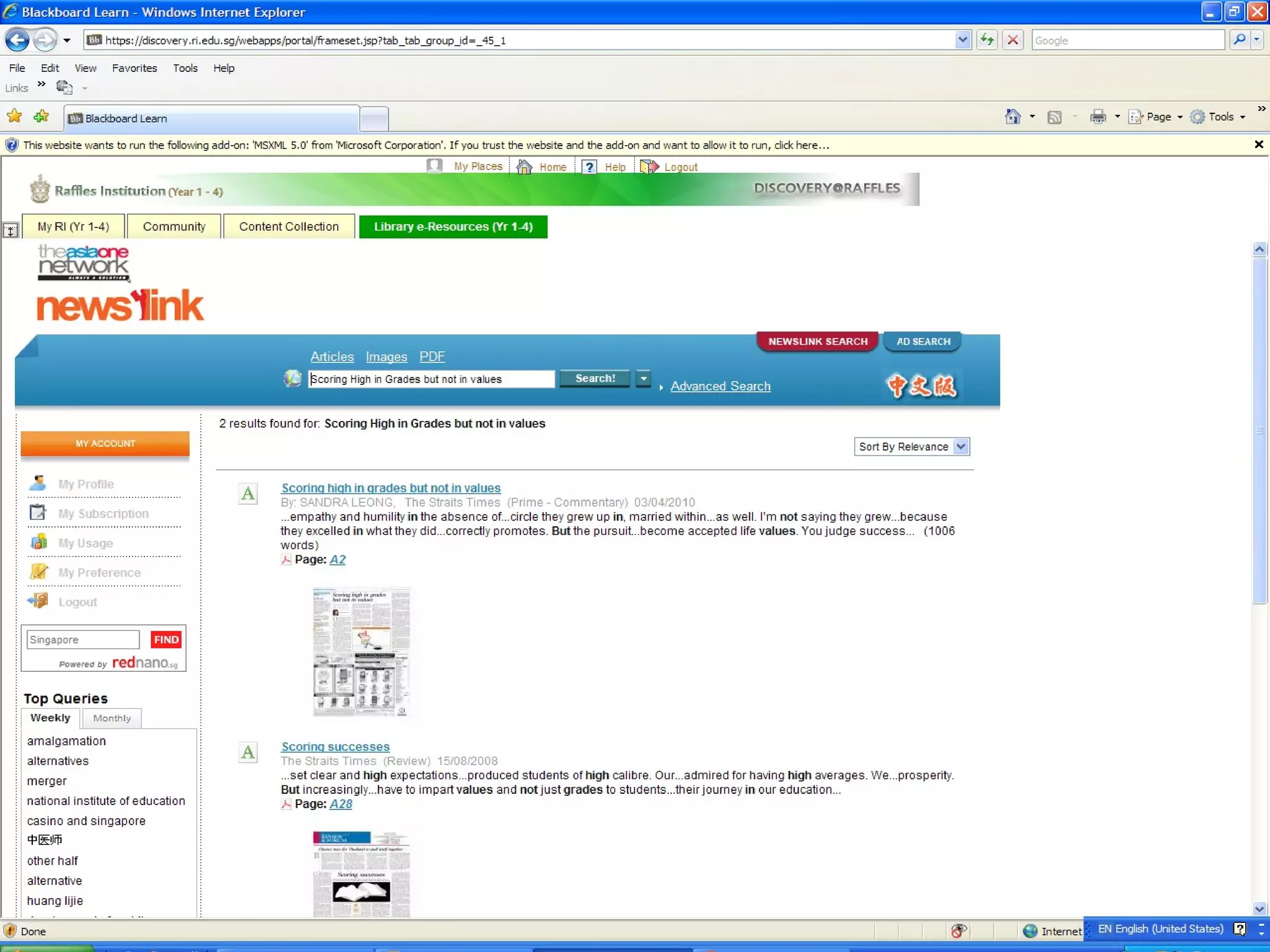
Information literacy is the ability to identify needed information, understand how information is organized, locate the best sources for a given need, evaluate sources critically, and share information. It involves knowing commonly used research techniques. Information literacy is important because it allows people to effectively sort through vast amounts of information from various sources that may differ in quality and reliability. Information can be organized by genre, subject, format, or how it is produced for popular versus scholarly audiences. Primary sources are original materials, while secondary sources discuss or interpret primary sources. The best resources for academic research are primary sources and scholarly sources because they are credible, useful, reliable, and relevant.


![Information Literacy 1 Information literacy is the ability to identify what information is needed; [WHAT] understand how the information is organized; [HOW] identify the best sources of information for a given need; [WHERE] locate those sources ; [WHERE] evaluate the sources critically ; [WHY/ HOW] and share that information . [FOR WHOM] It is the knowledge of commonly used research techniques. (From: the University of Idaho) http://www.webs.uidaho.edu/info_literacy/ Note: Information literacy is NOT computer skills. What is information literacy?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012informationliteracy1final-111231161704-phpapp01/75/2012-information-literacy-1-final-6-2048.jpg)











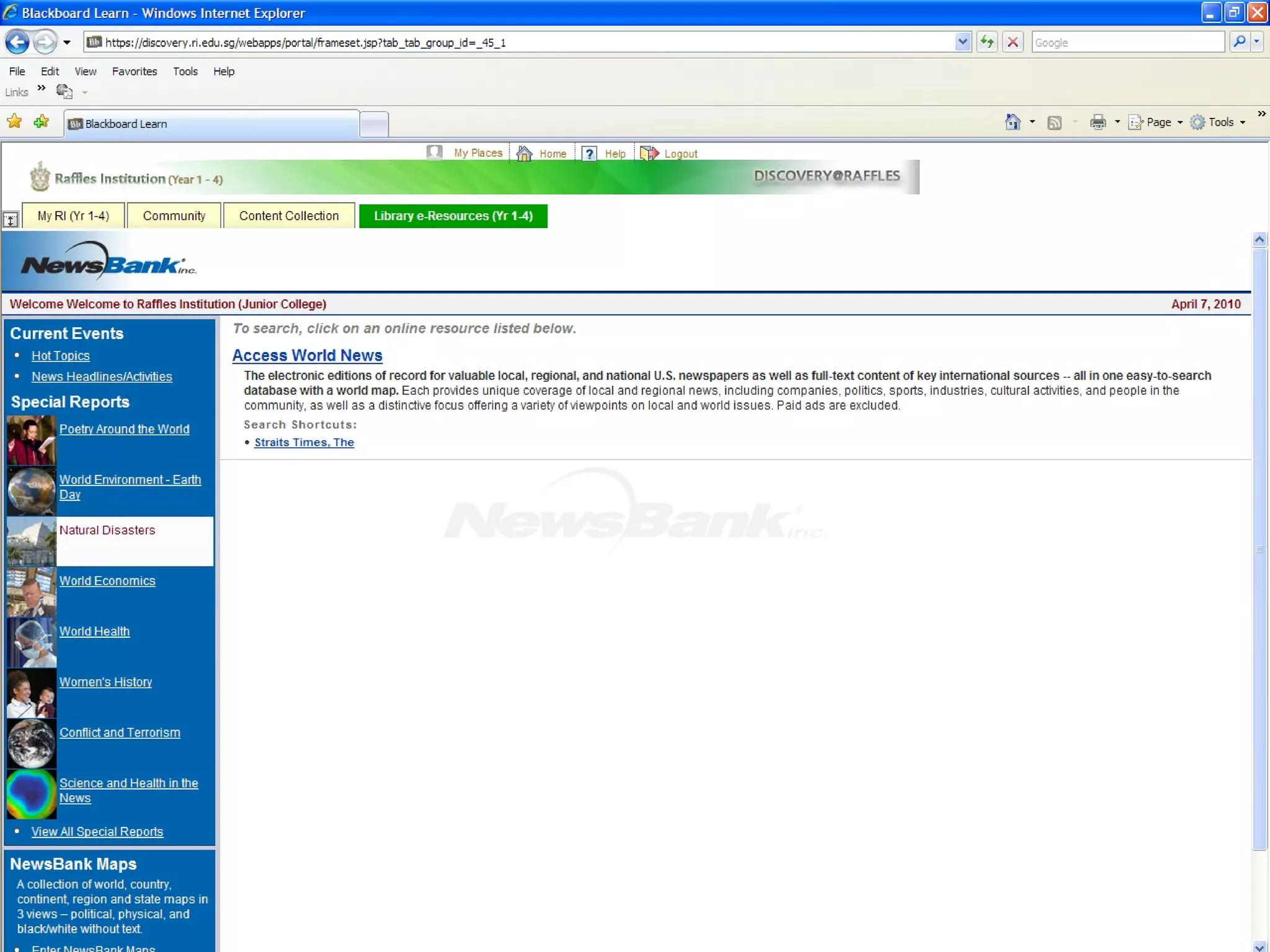

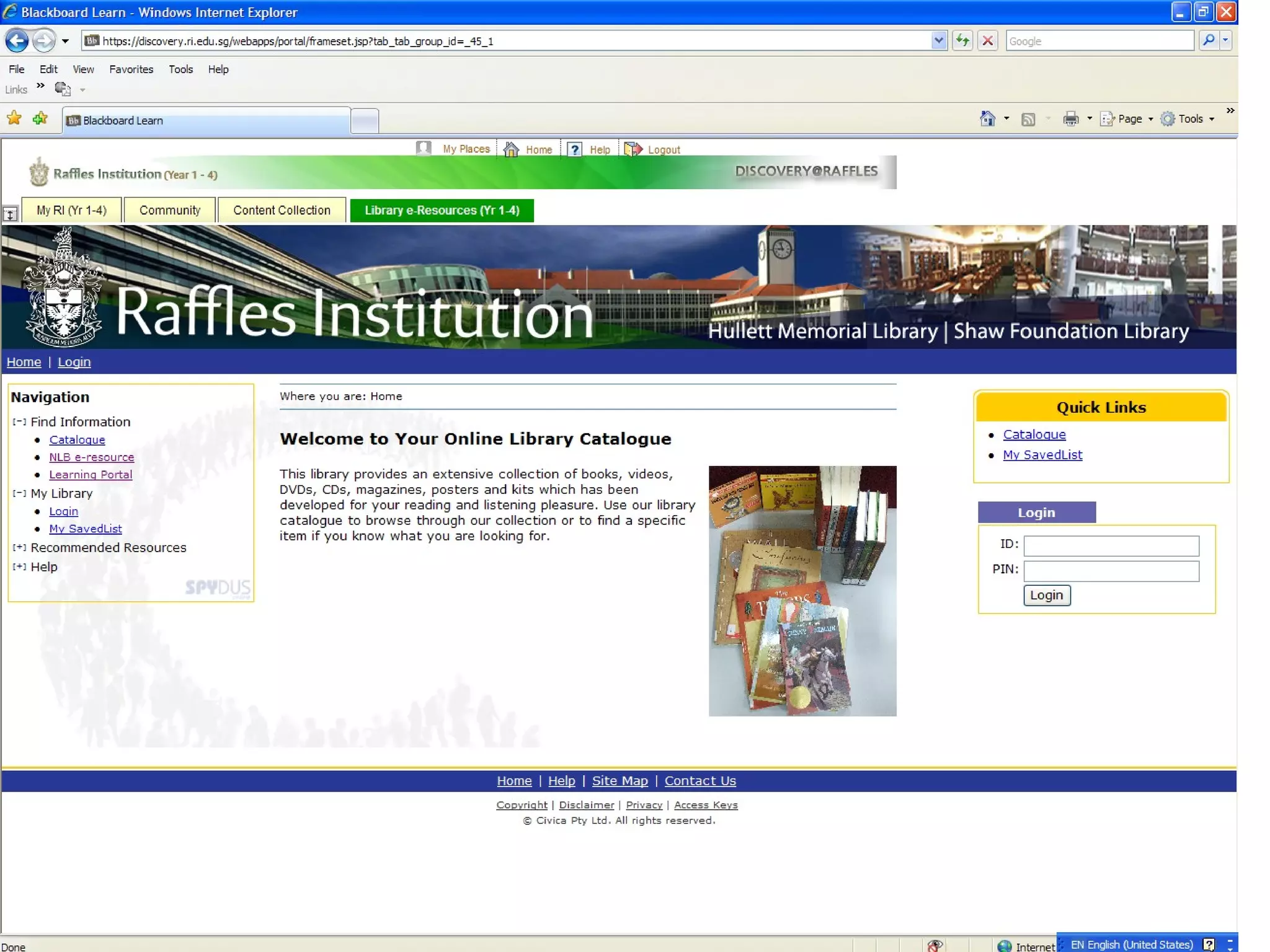

![Information Literacy 1 (Hands-On) Topic: “Television” 5. Read the first paragraph: Research into the media and violence examines whether a link between consuming media violence and subsequent aggressive and violent behavior exists. Although some social scientists support this link, [1] methodological and theoretical problems with the existing literature limit interpretation of findings in this area. There is concern among some scholars that media researchers may have exaggerated effects (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009; Freedman, 2002; Pinker 2002; Savage, 2004). Let’s analyse this short paragraph.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012informationliteracy1final-111231161704-phpapp01/75/2012-information-literacy-1-final-35-2048.jpg)
![Information Literacy 1 (Hands-On) Topic: “Television” 5. Read the first paragraph: Research into the media and violence examines whether a link between consuming media violence and subsequent aggressive and violent behavior exists. Although some social scientists support this link, [1] methodological and theoretical problems with the existing literature limit interpretation of findings in this area. There is concern among some scholars that media researchers may have exaggerated effects (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009; Freedman, 2002; Pinker 2002; Savage, 2004).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012informationliteracy1final-111231161704-phpapp01/75/2012-information-literacy-1-final-36-2048.jpg)
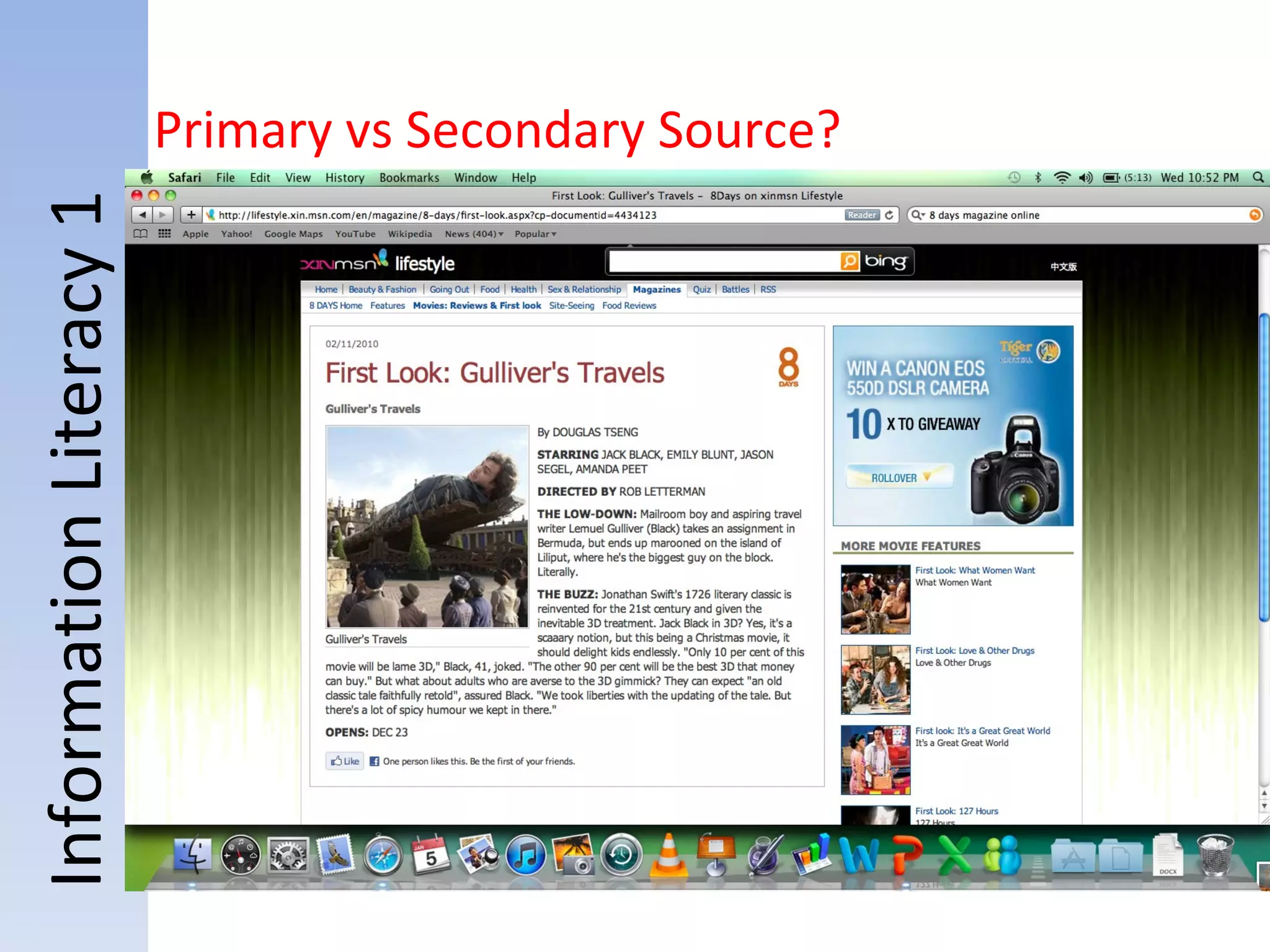
![Information Literacy 1 (Hands-On) Topic: “Television” 5. Read the first paragraph: Research into the media and violence examines whether a link between consuming media violence and subsequent aggressive and violent behavior exists. Although some social scientists support this link, [1] methodological and theoretical problems with the existing literature limit interpretation of findings in this area. There is concern among some scholars that media researchers may have exaggerated effects (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009; Freedman, 2002; Pinker 2002; Savage, 2004). Secondary source?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012informationliteracy1final-111231161704-phpapp01/75/2012-information-literacy-1-final-37-2048.jpg)
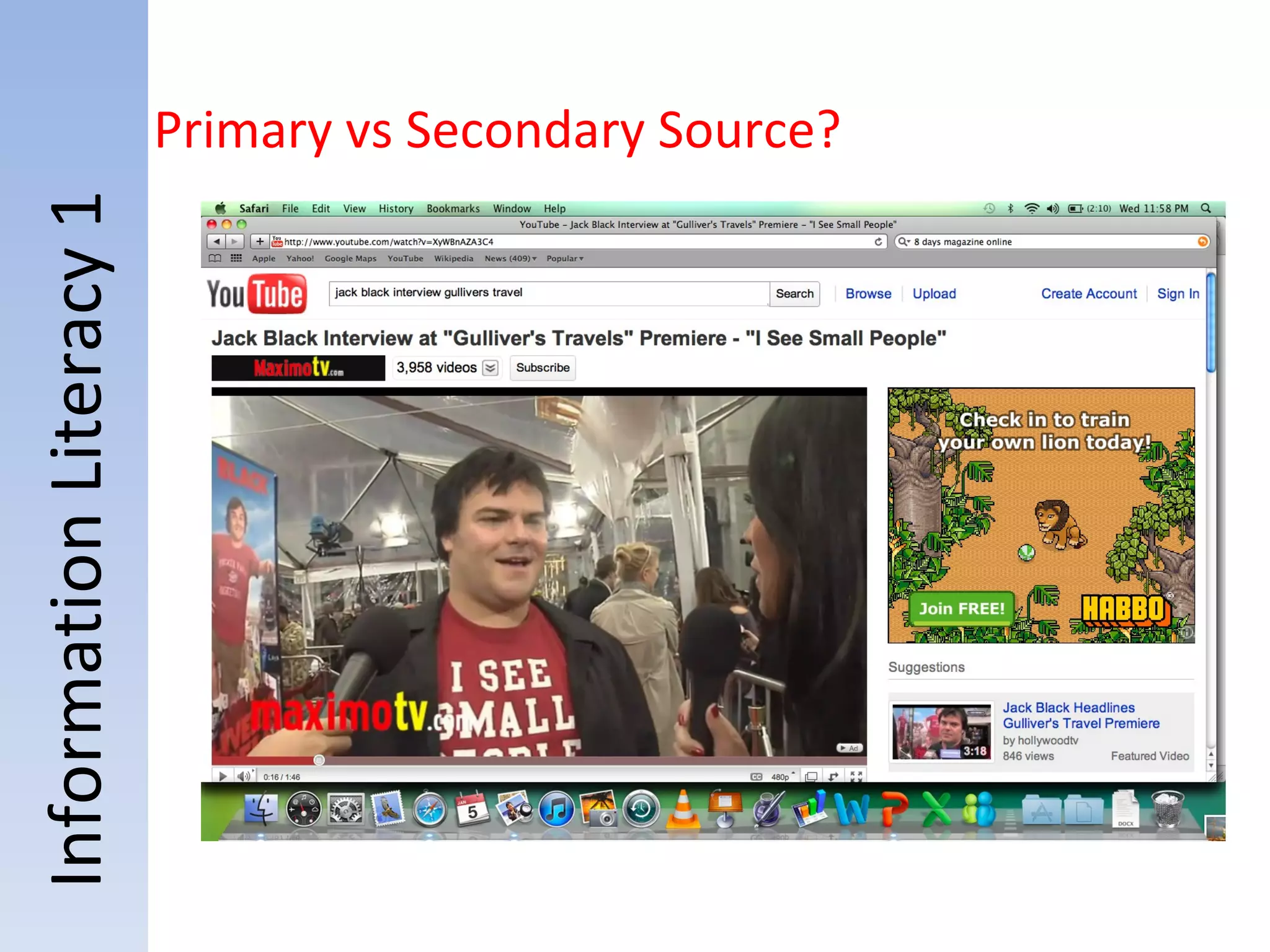
![Information Literacy 1 (Hands-On) Topic: “Television” 5. Read the first paragraph: Research into the media and violence examines whether a link between consuming media violence and subsequent aggressive and violent behavior exists. Although some social scientists support this link, [1] methodological and theoretical problems with the existing literature limit interpretation of findings in this area. There is concern among some scholars that media researchers may have exaggerated effects (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009; Freedman, 2002; Pinker 2002; Savage, 2004). Primary sources?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012informationliteracy1final-111231161704-phpapp01/75/2012-information-literacy-1-final-38-2048.jpg)
![Information Literacy 1 (Hands-On) Topic: “Television” 5. Read the first paragraph: Research into the media and violence examines whether a link between consuming media violence and subsequent aggressive and violent behavior exists. Although some social scientists support this link, [1] methodological and theoretical problems with the existing literature limit interpretation of findings in this area. There is concern among some scholars that media researchers may have exaggerated effects (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009; Freedman, 2002; Pinker 2002; Savage, 2004). Primary sources? Probably yes. But which are the more scholarly ones?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012informationliteracy1final-111231161704-phpapp01/75/2012-information-literacy-1-final-39-2048.jpg)