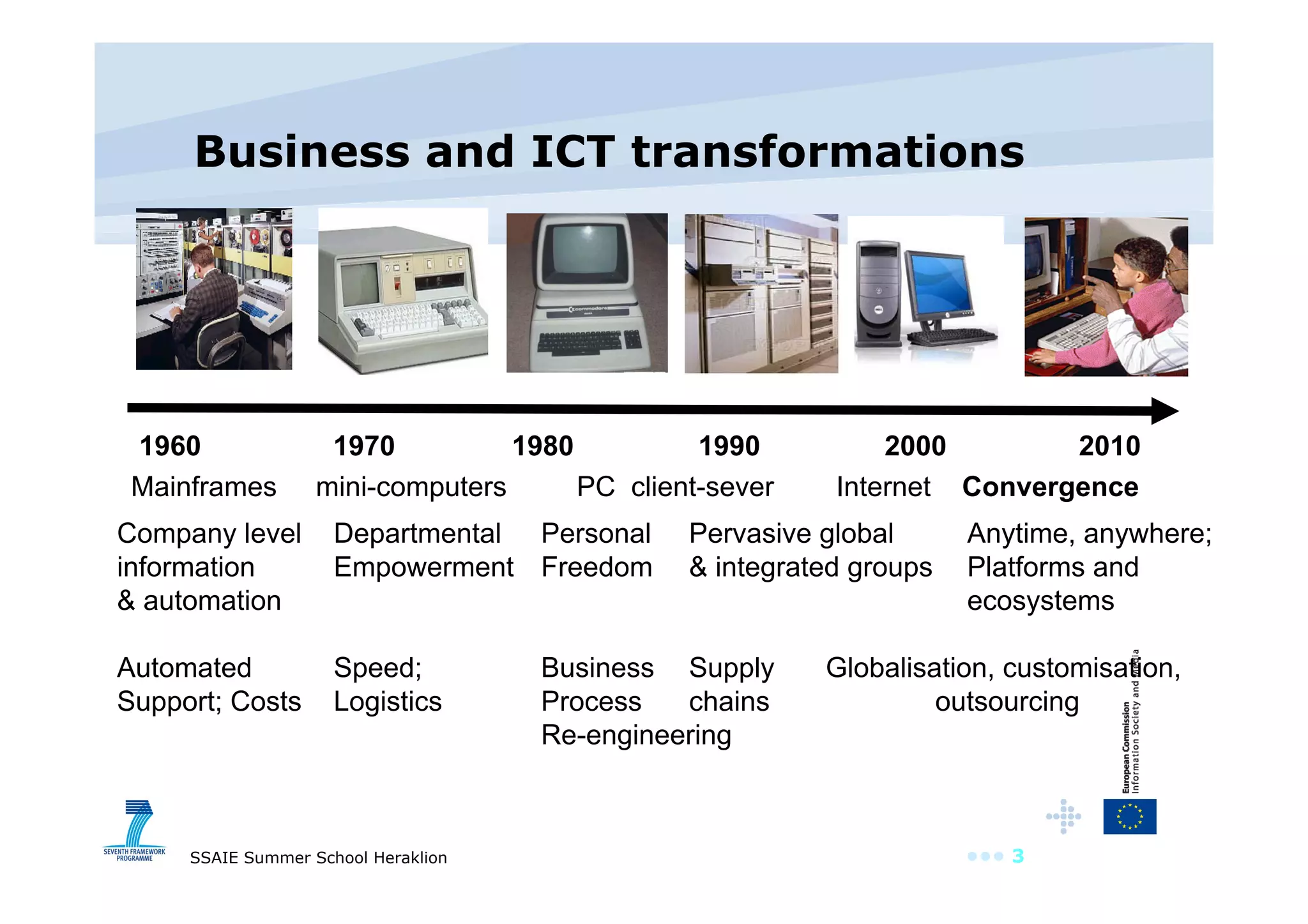
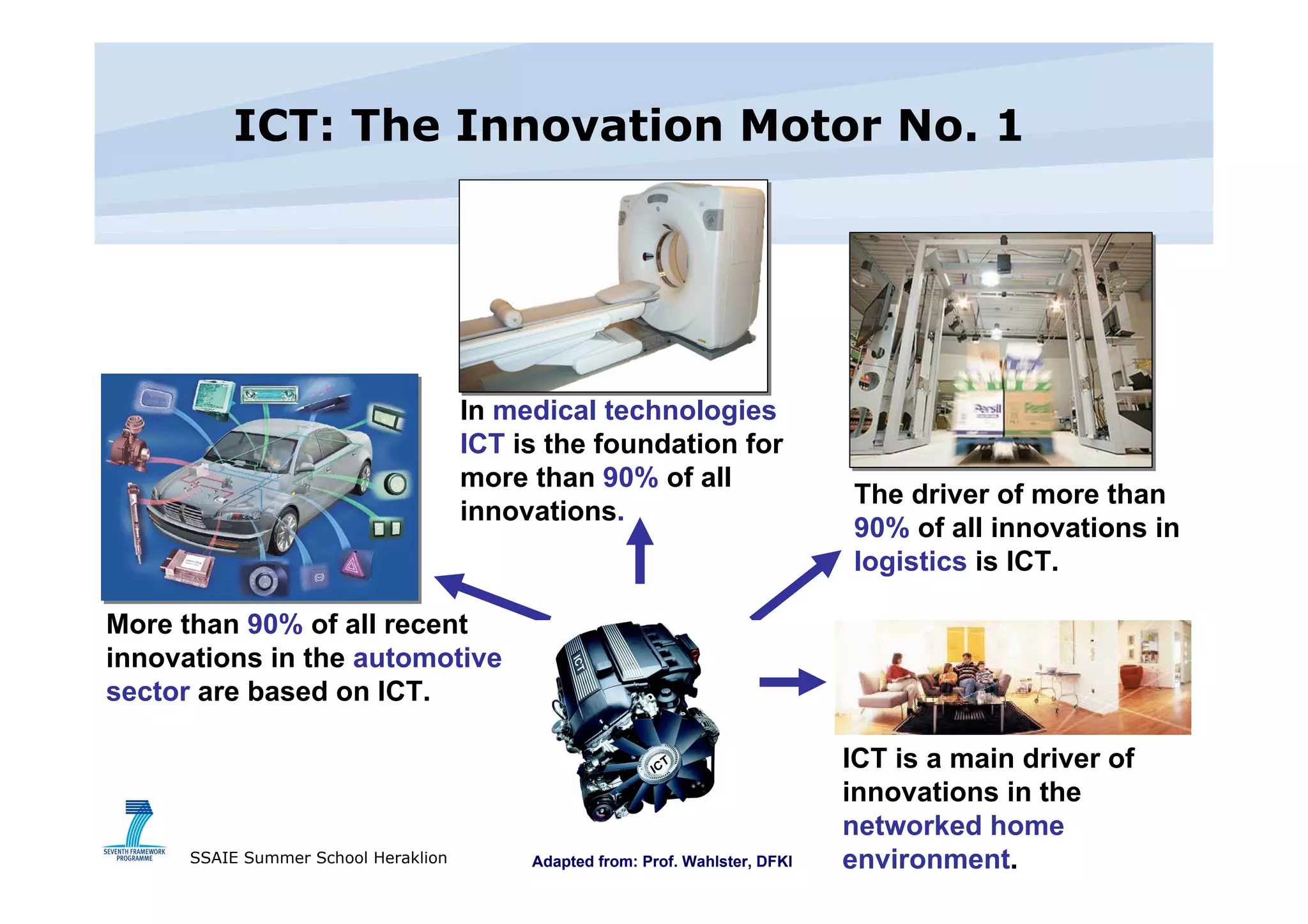
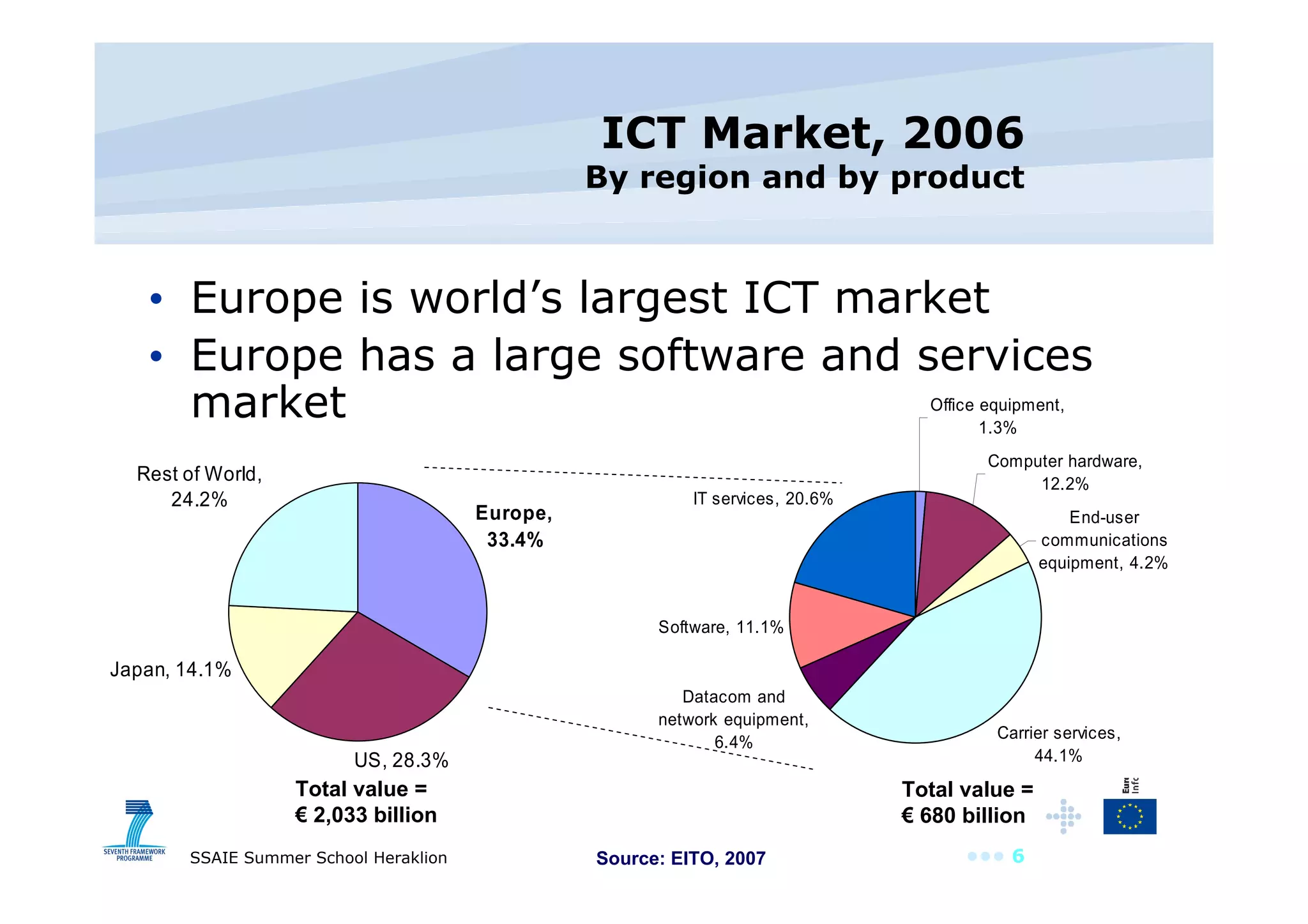
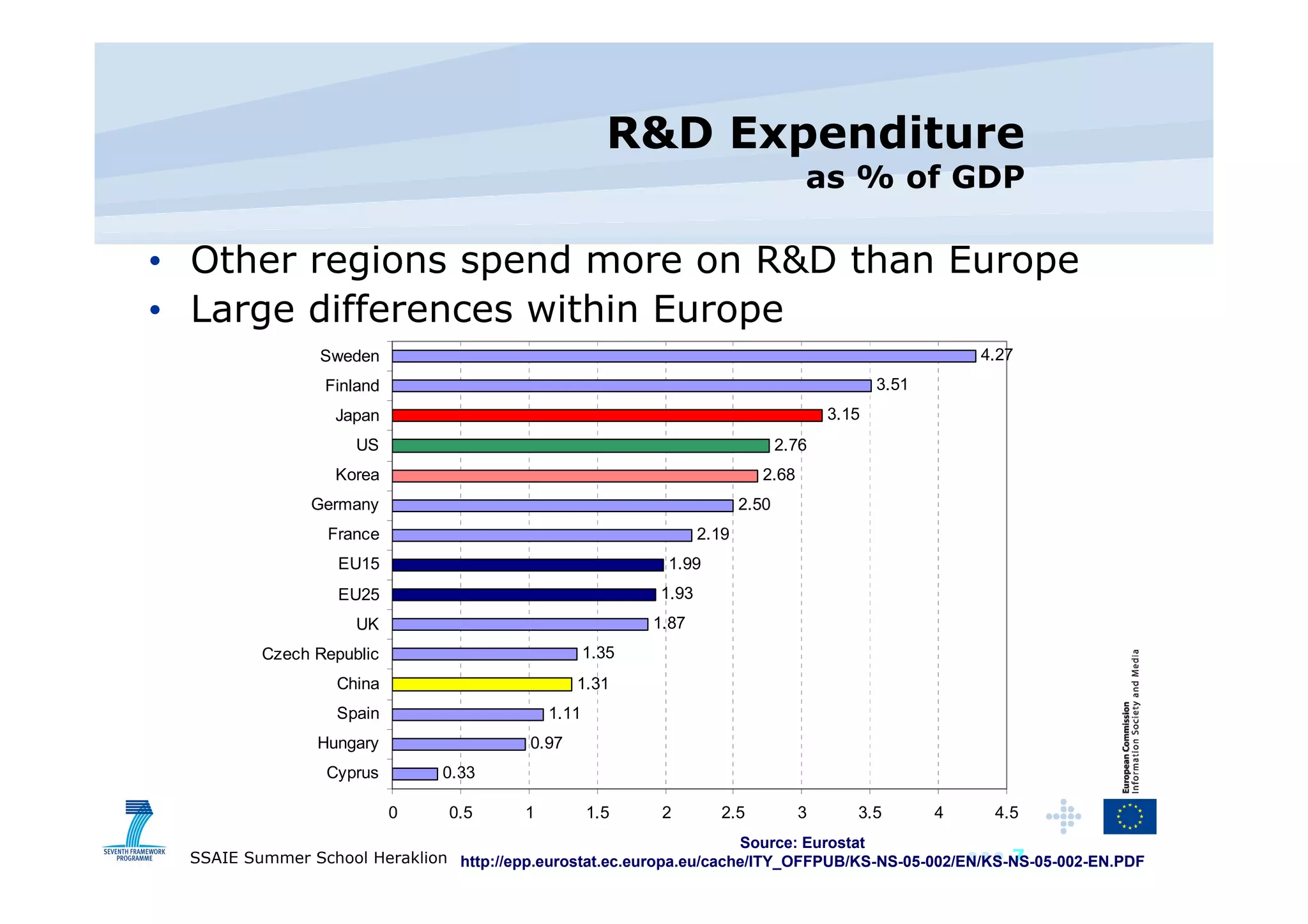
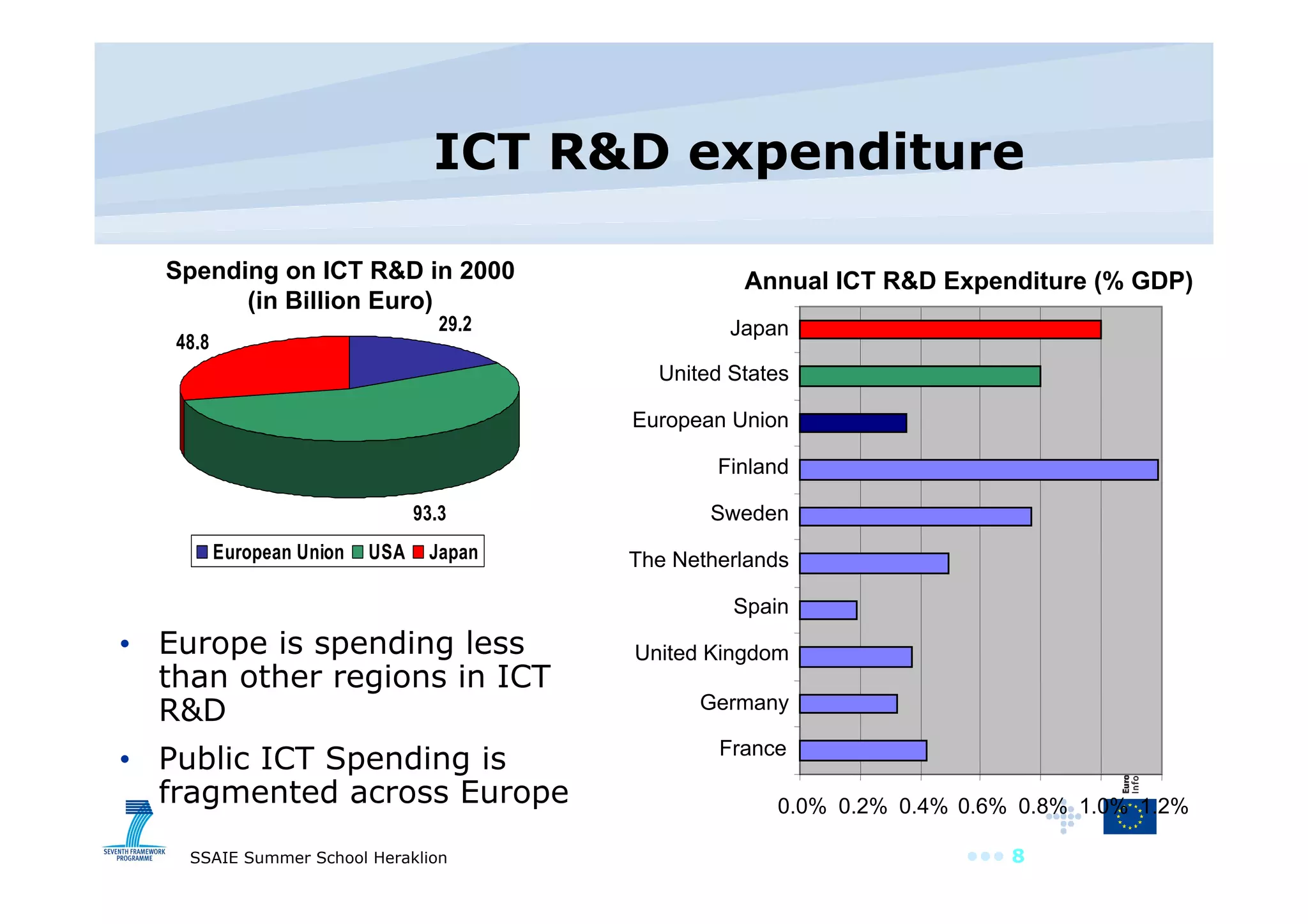
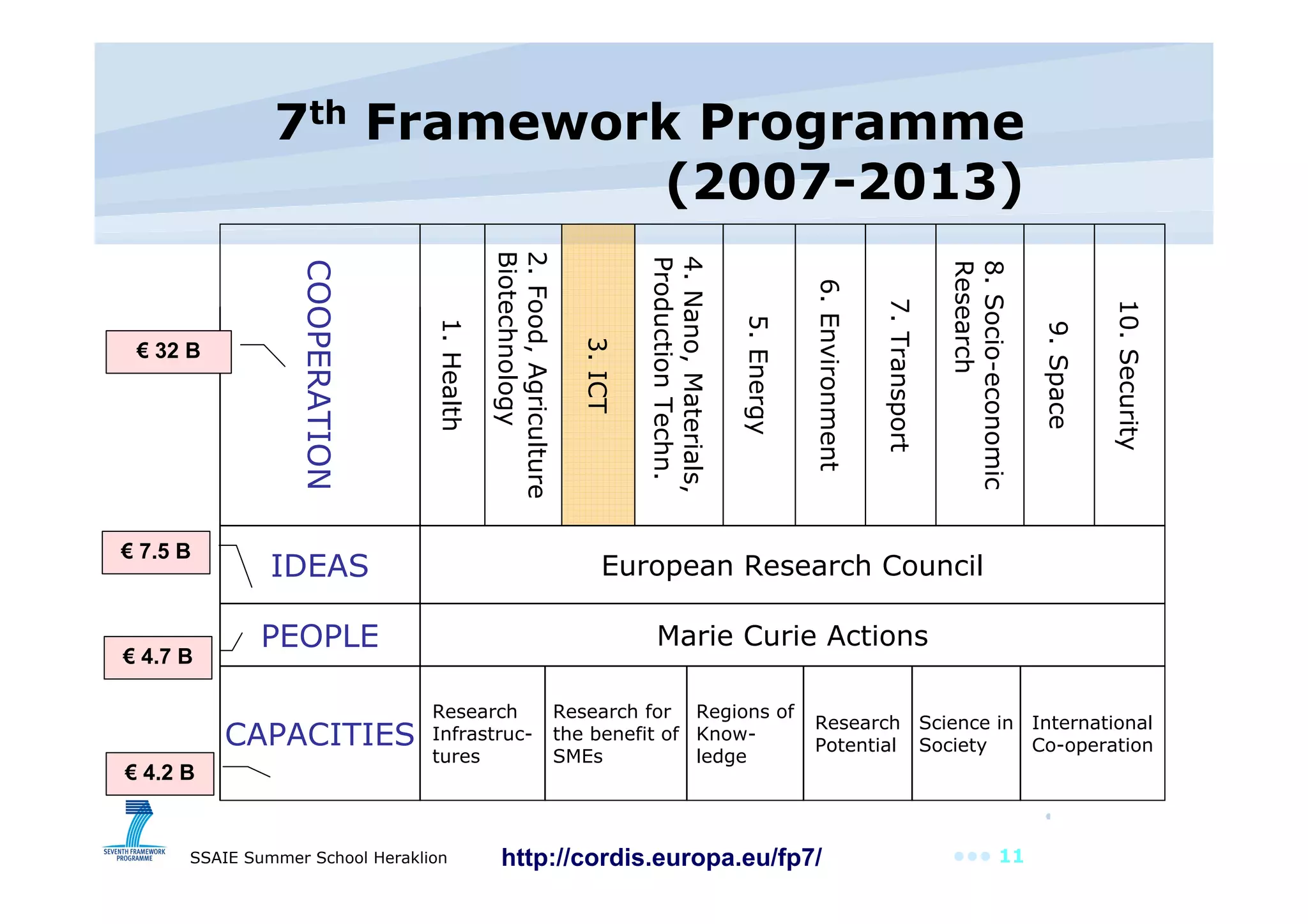
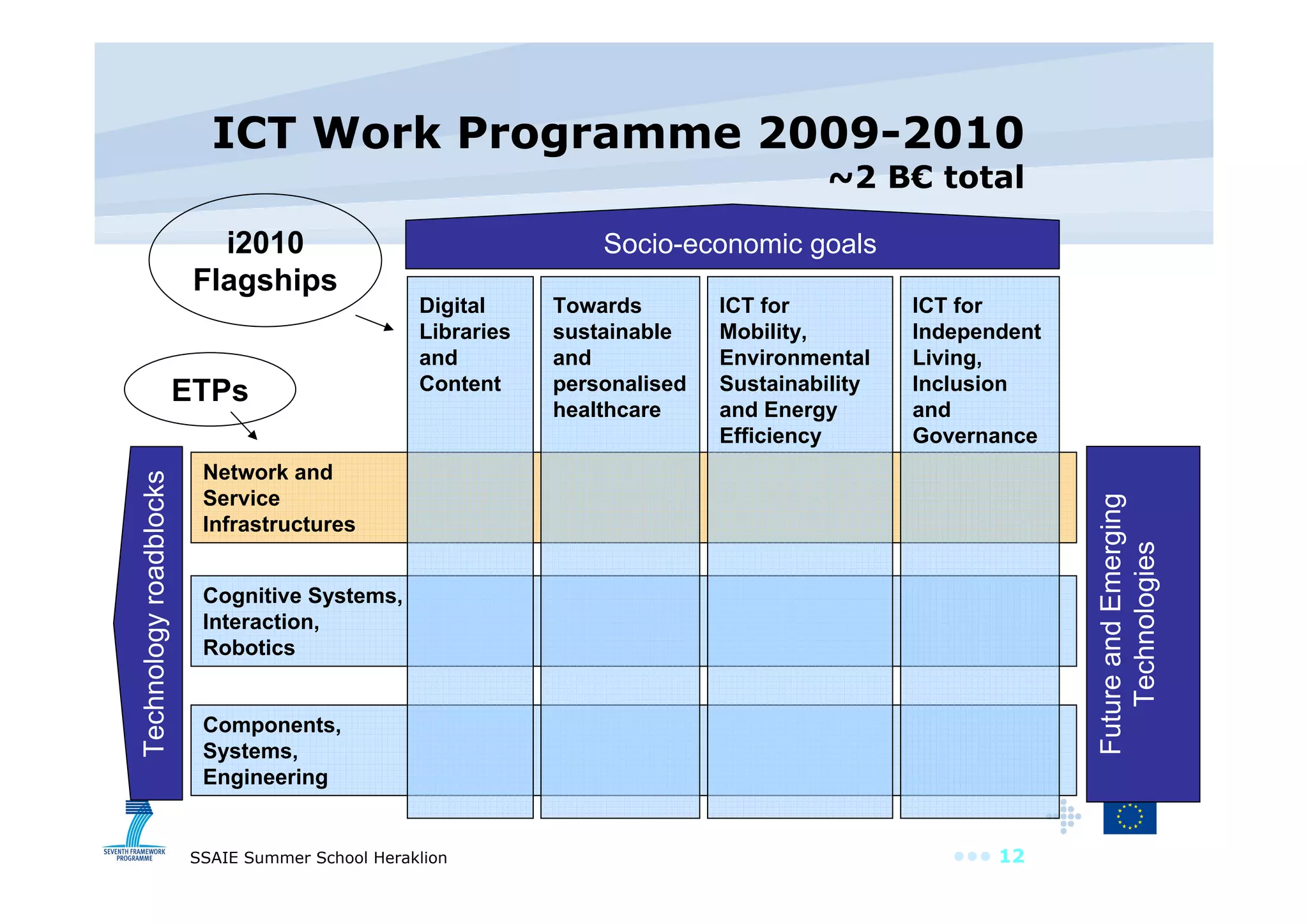
The document discusses the importance of investing in EU ICT research, highlighting its role as a driver of innovation across various sectors. It points out that Europe has a significant software and services market but spends less on ICT R&D compared to other regions. The text also outlines the objectives and outcomes of the ICT work program for 2009, emphasizing the need for innovative service engineering and cooperation in developing future internet services.










![For more information FP7 http://cordis.europa.eu/fp7/ http://cordis.europa.eu/fp7/ict/ Software & Service Architectures and Infrastructures http://cordis.europa.eu/software-services Future Internet http://ec.europa.eu/foi http://www.future-internet.eu/ E-mail [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090616heraklionsummerschool-final-090618055249-phpapp02/75/20090616-Investing-in-Software-Services-Research-24-2048.jpg)