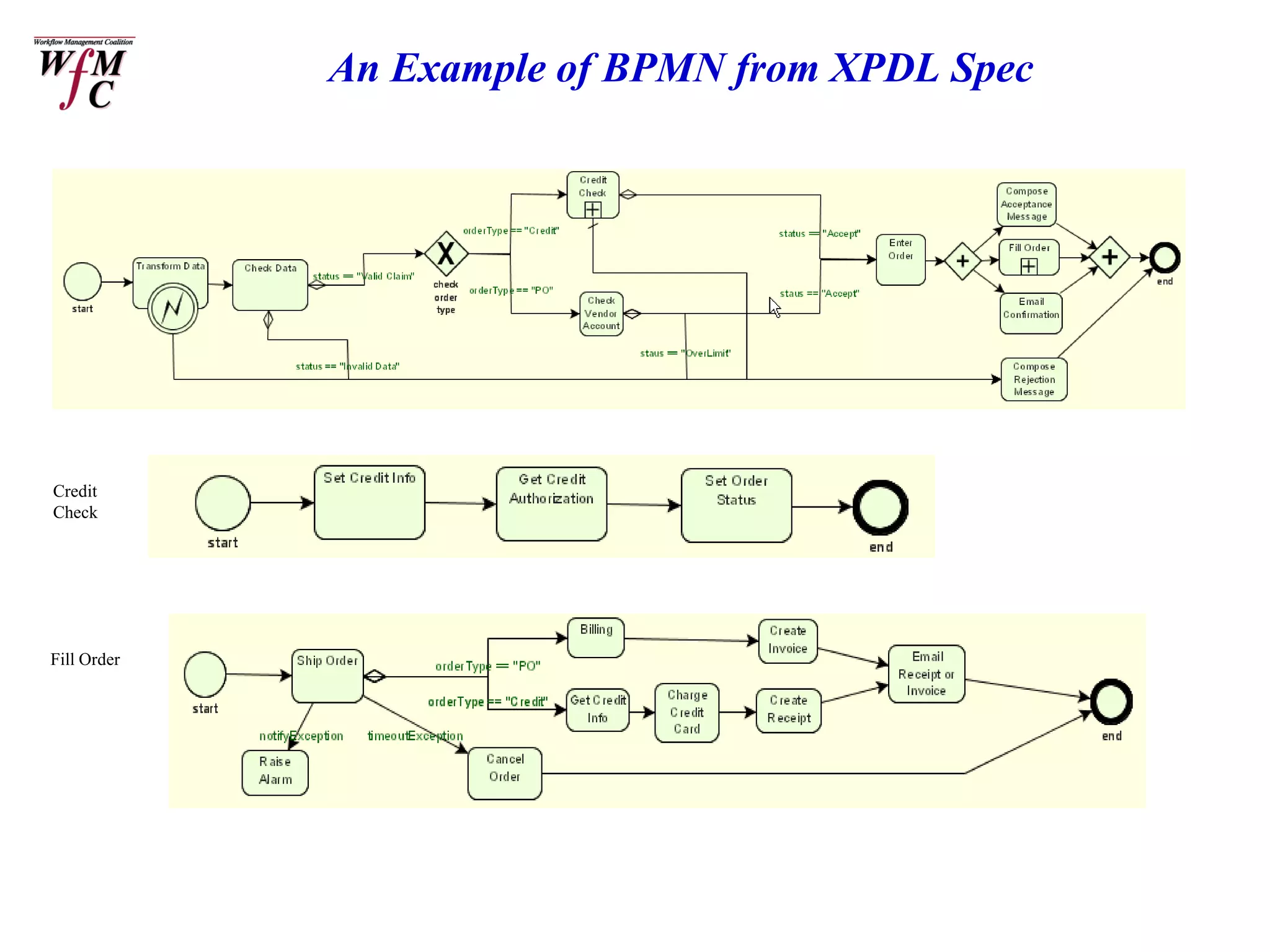
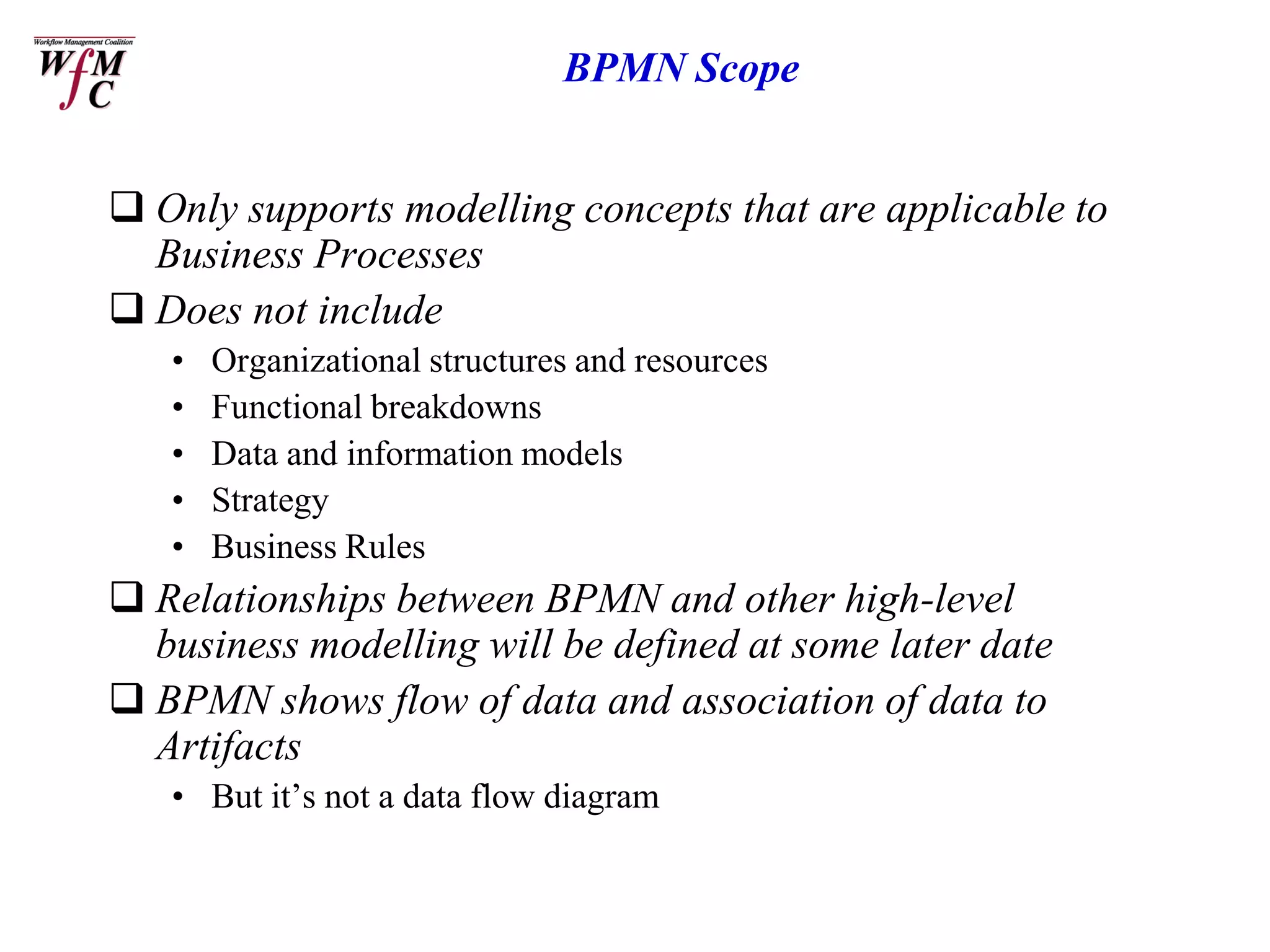
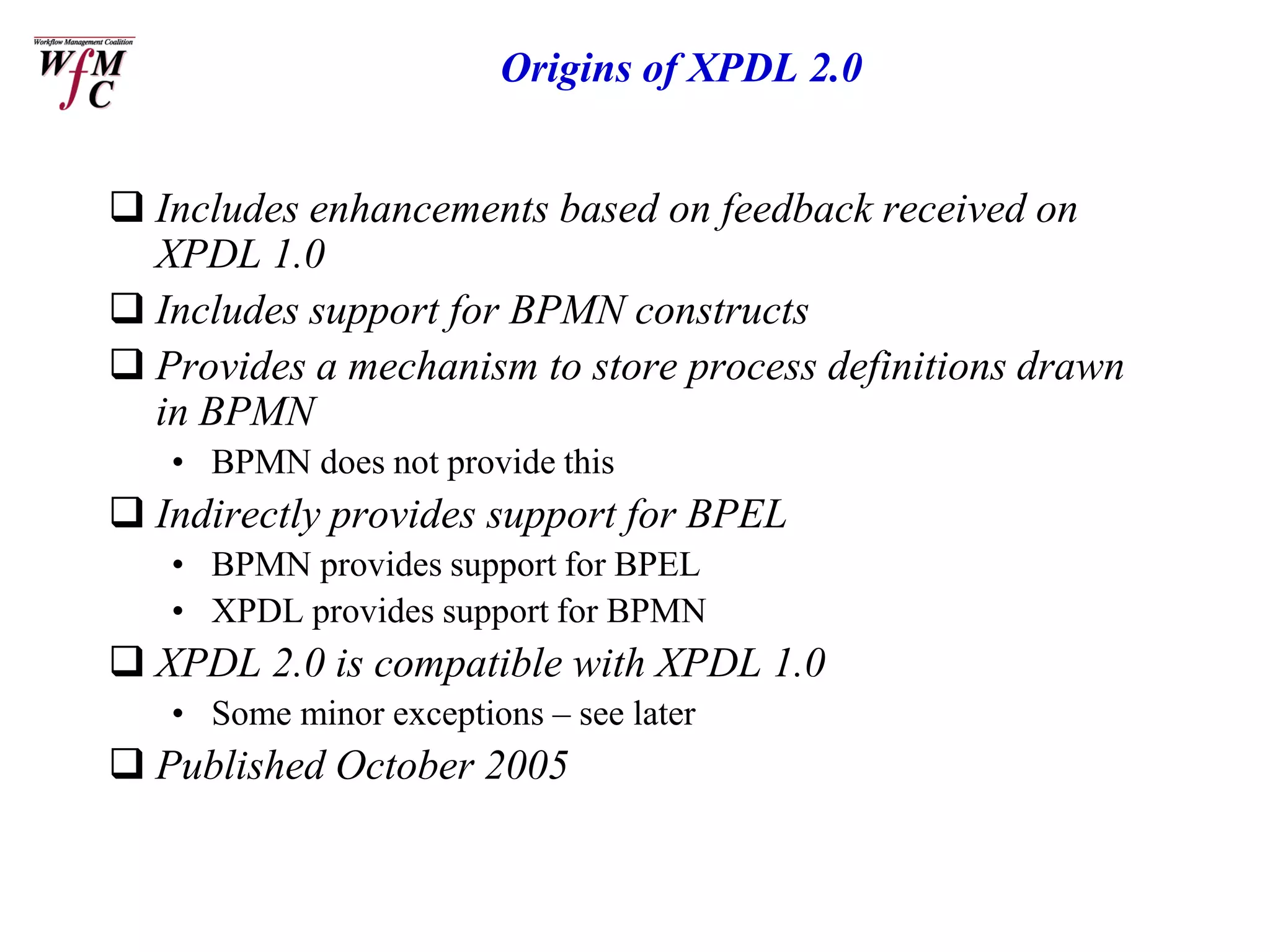
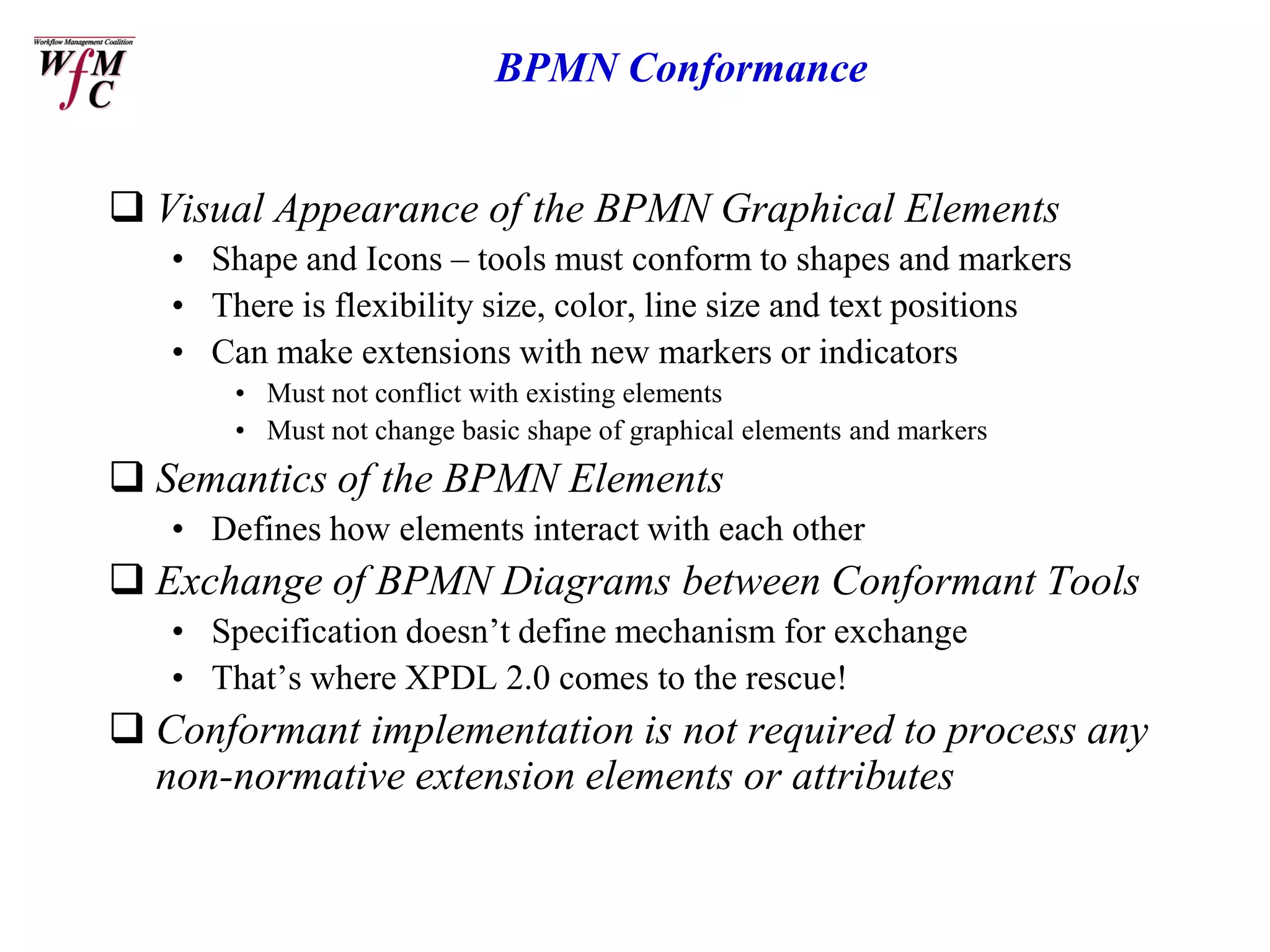
The document discusses the XPDL 2.0 and BPMN tutorial presented at the Business Process Management Summit in February 2006, outlining the roles of key speakers and the agenda topics. It explains the origins, uses, and enhancements of XPDL and BPMN, including conformance requirements for both languages. Additionally, it highlights the relationships between them and makes reference to various organizations supporting these standards.




![It’s All About Processes
WfMC defines a process as:
• “The representation of a business process in a form that supports
automated manipulation, such as modeling, or enactment by a
workflow [or business] management system. The process
definition consists of a network of activities and their relationships,
criteria to indicate the start and termination of the process, and
information about the individual activities, such as participants,
associated IT applications and data, etc.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2006mmksjbmiamiflorida-bpmsummitxpdltutorial-130219115950-phpapp02/75/2006-mm-ks-jb-miami-florida-bpm-summit-xpdl-tutorial-5-2048.jpg)