The document outlines the use of DatagramSockets in Java for network communication via UDP, highlighting its advantages in applications like live TV coverage and online gaming where speed is prioritized over reliability. It details the steps for creating DatagramSockets and DatagramPackets, and provides sample server and client code implementations for both unicast and multicast communication. Additionally, it includes references for further learning through YouTube and GitHub.




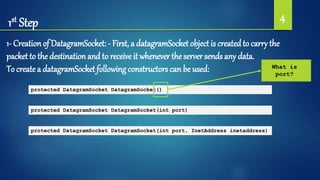
![2nd Step 5
2 - Creation of DatagramPacket: In this step, the packet for sending/receiving data via a
datagramSocket is created.
Constructor to senddata:
DatagramPacket(byte buf[], int length, InetAddress inetaddress, int port)
Parameters:
buf - the packet data.
offset - the packet data offset.
length - the packet data length.
address - the destination socket address.
Constructs a DatagramPacket for sending data at specifiedaddress and specifiedport.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-6-320.jpg)
![2nd Step… 6
Constructor to receive the data:
DatagramPacket(byte buf[], int length)
Parameters:
buf - thepacket data.
length- the packet data length.
Constructs a DatagramPacket for receiving the data of lengthlengthin the byte array buf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-7-320.jpg)
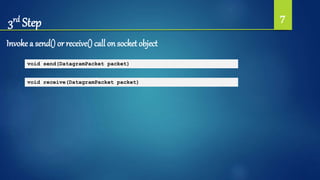

![9DatagramSocket socket = null;
byte[] receiverBuffer = null;
DatagramPacket receivePacket = null;
private void initializeVarible(){
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(Constants.PORT);
receiverBuffer = new byte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
} catch (SocketException ex) {
log("initializeVarible : " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
private String receiveData(){
String line = "";
try {
receivePacket = new
DatagramPacket(receiverBuffer,receiverBuffer.length);
socket.receive(receivePacket);
line = new
String(receivePacket.getData(),0,receivePacket.getLength());
} catch (IOException ex) {
log("receiveData : " + ex.getMessage());
}
return line;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-10-320.jpg)
![10
public static void main(String[] args){
Server server = new Server();
server.initializeVarible();
server.connecting();
}
private void connecting(){
while(true){
String data = receiveData();
log("Client : " + data);
if(data.equals(Constants.STOP)){
log("Client say bye...Exiting");
break;
}
receiverBuffer = new byte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-11-320.jpg)

![12Scanner scan = null;
DatagramSocket socket = null;
byte[] buffer = null;
private void initializeVarible(){
try {
scan = new Scanner(System.in);
socket = new DatagramSocket();
} catch (SocketException ex) {
log("initializeVarible : " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
private void send(String message){
try {
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
buffer = message.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packetSend = new
DatagramPacket(buffer,buffer.length,ip,Constants.PORT);
socket.send(packetSend);
} catch (IOException ex) {
log("send : " + ex.getMessage());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-13-320.jpg)
![13
private void connecting(){
while(true){
String line = readFromKeyboard();
send(line);
if(line.equals(Constants.STOP)){
break;
}
}
}
private String readFromKeyboard(){
String line = scan.nextLine();
return line;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Client client = new Client();
client.initializeVarible();
client.connecting();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-14-320.jpg)

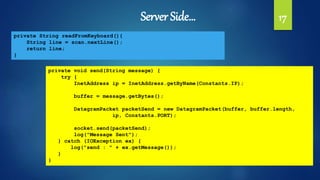
![Server Side 16
MulticastSocket socket = null;
byte[] buffer = null;
DatagramPacket receivePacket = null;
Scanner scan = null;
private void initializeVarible() {
try {
socket = new MulticastSocket();
buffer = new byte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
scan = new Scanner(System.in);
log("Server Running...");
} catch (SocketException ex) {
log("initializeVarible : " + ex.getMessage());
} catch (IOException ex) {
log("initializeVarible : " + ex.getMessage());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-17-320.jpg)
![Server Side… 18
private void connecting() {
while (true) {
String data = readFromKeyboard();
send(data);
buffer = new byte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server();
server.initializeVarible();
server.connecting();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-19-320.jpg)
![Client Side 19
MulticastSocket socket = null;
byte[] buffer = null;
DatagramPacket packet = null;
InetAddress ip = null;
private void initializeVarible() {
try {
socket = new MulticastSocket(Constants.PORT);
ip = InetAddress.getByName(Constants.IP);
buffer = new byte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
} catch (SocketException ex) {
log("initializeVarible : " + ex.getMessage());
} catch (IOException ex) {
log("initializeVarible : " + ex.getMessage());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-20-320.jpg)
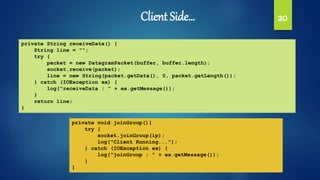
![Client Side… 21
private void connecting(){
joinGroup();
while(true){
String line = receiveData();
log("Client Received : " + line);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Client client = new Client();
client.initializeVarible();
client.connecting();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-2udp-190508220036/85/2-UDP-22-320.jpg)


