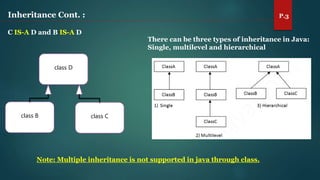
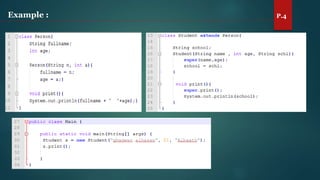
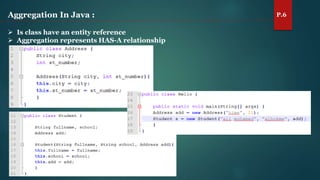
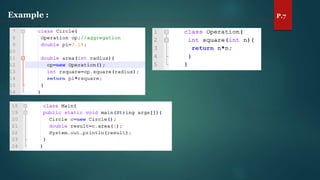
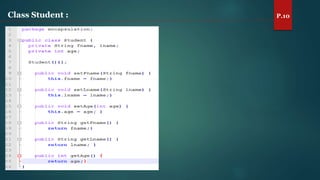
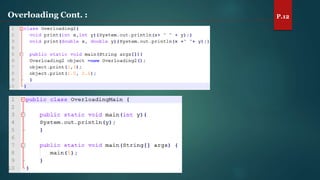
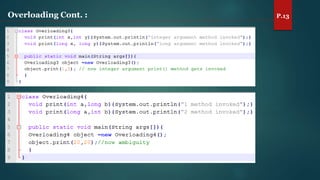
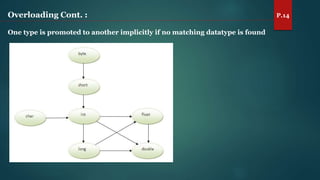
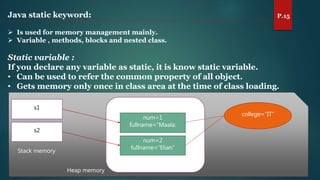
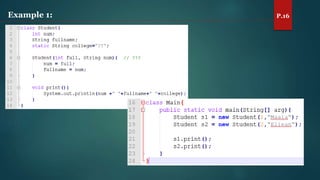
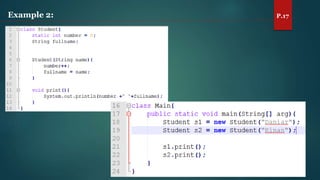
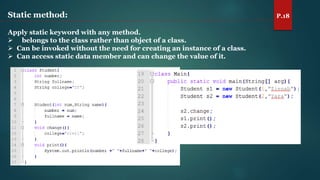
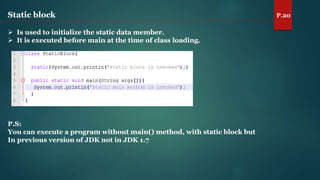
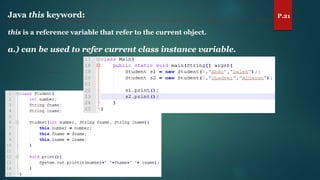
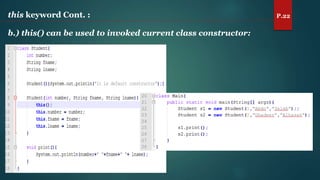
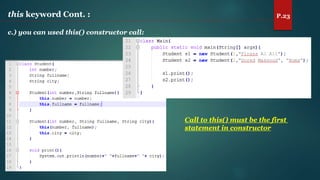
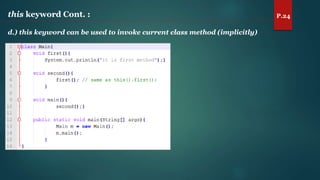
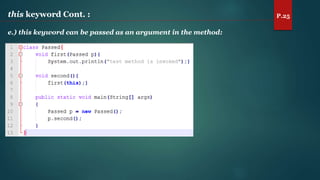
The document discusses key concepts of inheritance, aggregation, encapsulation, overloading, the static keyword, and the 'this' keyword in Java. It explains the mechanisms and relationships (is-a and has-a), the purpose of encapsulation, method overloading, static methods and variables, and the usage of the 'this' reference. Specific examples are provided to illustrate these concepts.