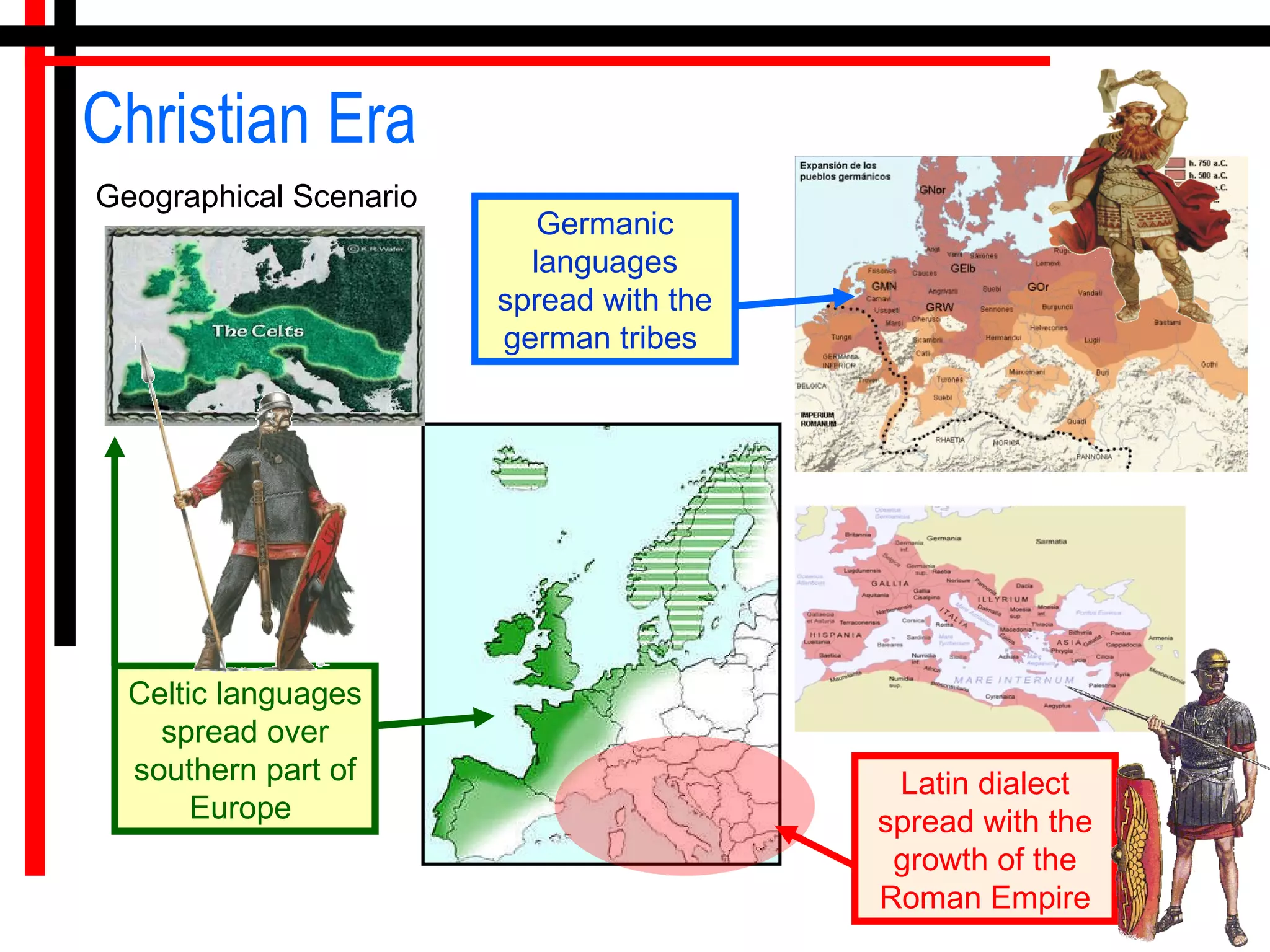
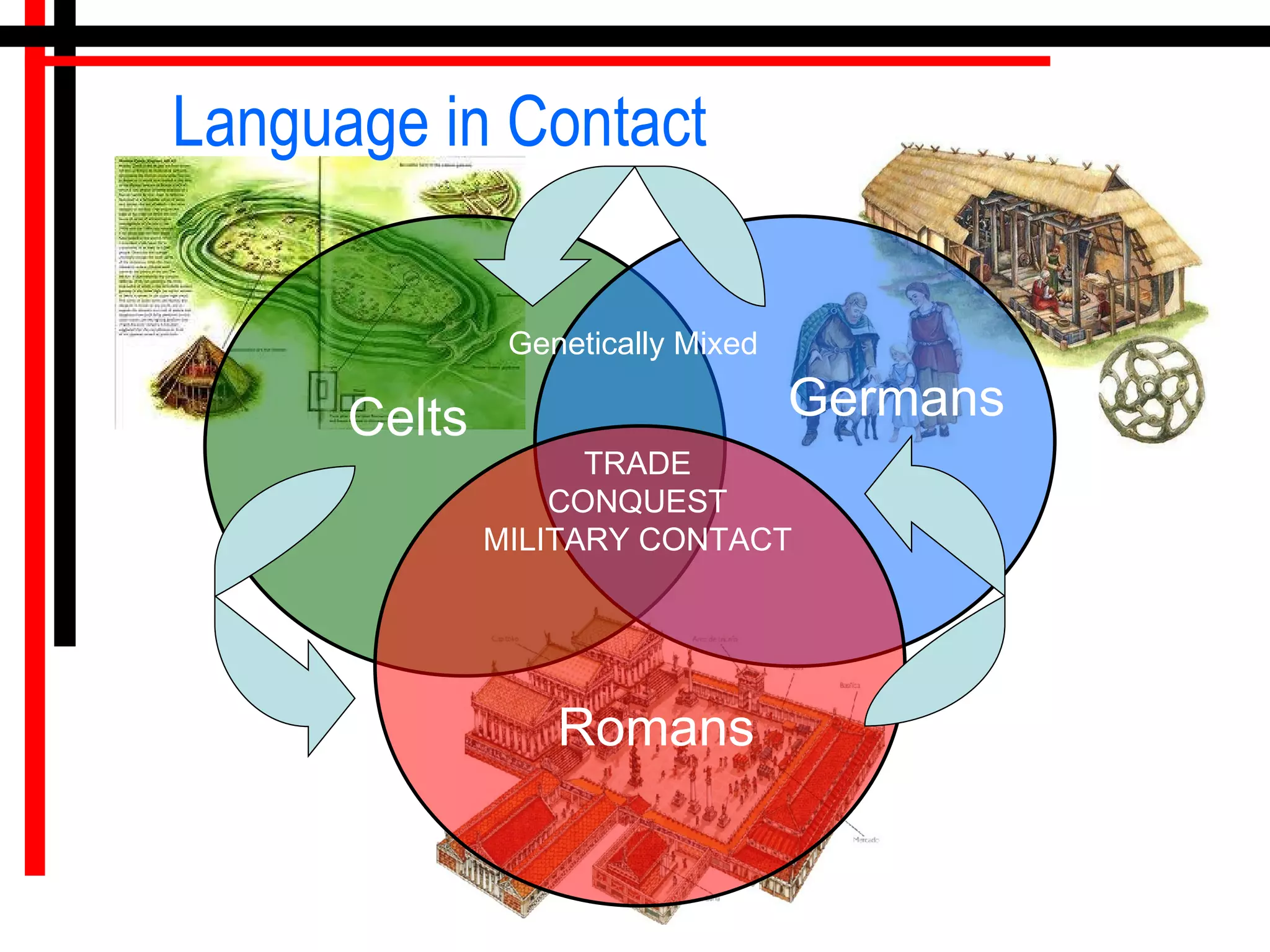
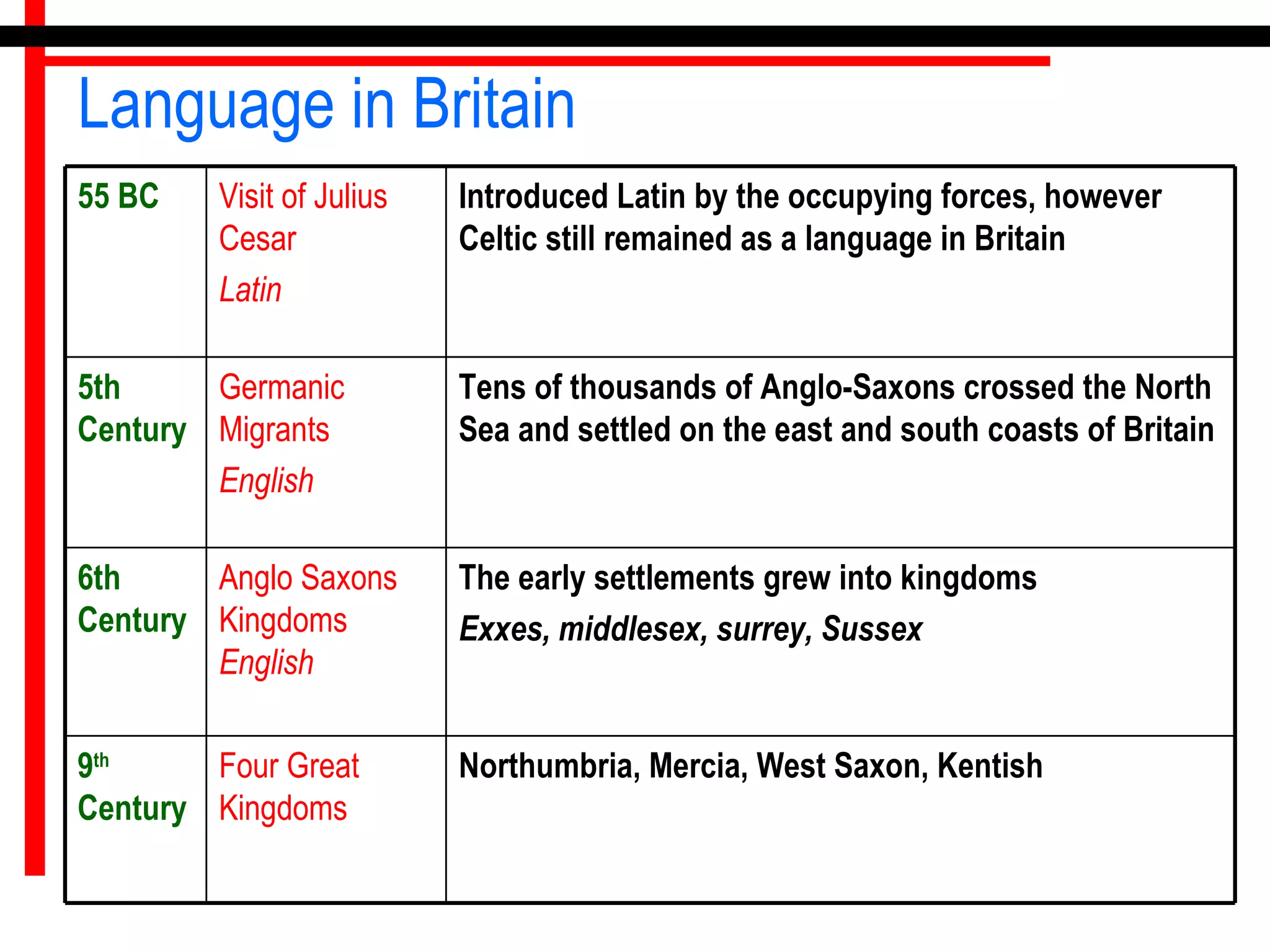
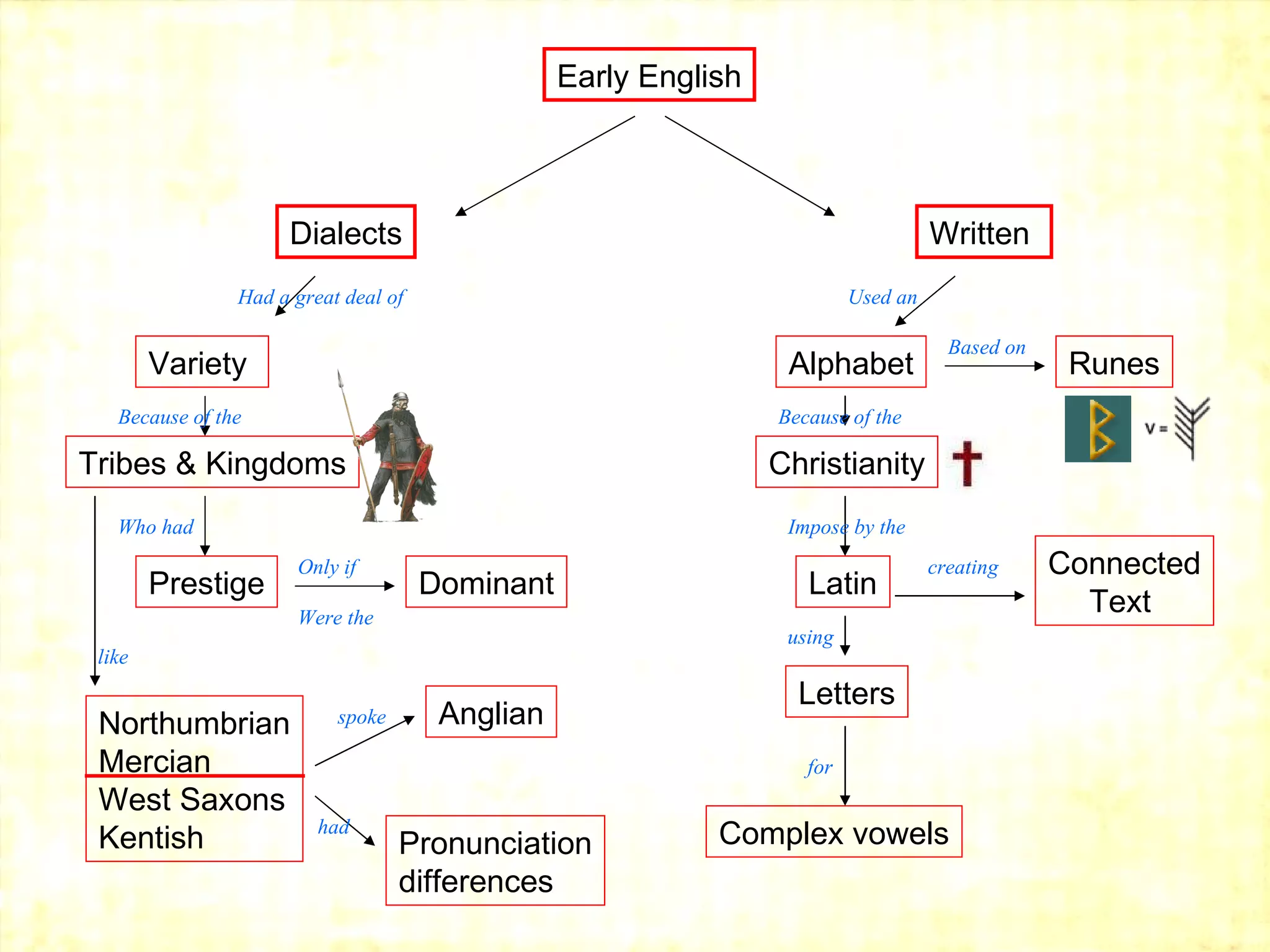
The origins of the English language can be traced back to the contact between Celtic, Latin, and Germanic languages in Britain. Celtic languages originally spread throughout Britain, but Latin was introduced when the Romans invaded in 55 BC. In the 5th century, Germanic tribes from northwest Germany invaded and settled eastern Britain, bringing their Germanic languages. The Celtic Britons were pushed westward, while the Germanic languages dominated in the east. Over centuries, English emerged as a distinct language through the blending and influence of Celtic, Latin, and Germanic languages in Britain.