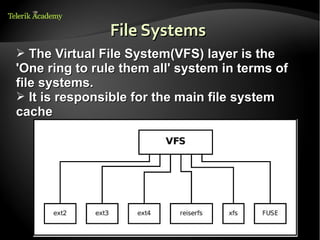
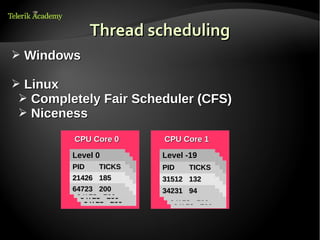
The document discusses operating systems and their core functions. It describes how operating systems manage hardware resources, provide common services to applications, and act as an intermediary between users and the computer system. It also outlines several key components of operating systems, including the kernel, memory management, interrupt handling, device drivers, file systems, and scheduling for CPUs, I/O, and networks. Finally, it briefly discusses different operating system types, architectures, and free trainings available through Telerik Academy.
![2 – Operating Systems
Marian Marinov Borislav Varadinov
CEO of 1H Ltd. System Administrator
mm@1h.com bobi [ at ] itp.bg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-operatingsystems-130307041413-phpapp02/75/2-operating-systems-1-2048.jpg)