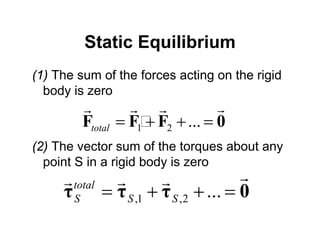
(1) Static equilibrium requires the sum of the forces on a rigid body to be zero and the sum of the torques about any point to be zero.
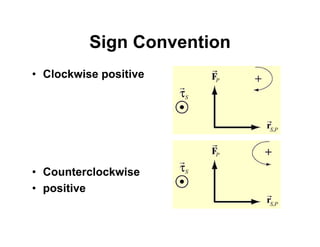
(2) To solve static equilibrium problems, first draw a free body diagram and identify the system. Write equations for the force and torque. Choose a point to analyze torque, and determine sign convention.
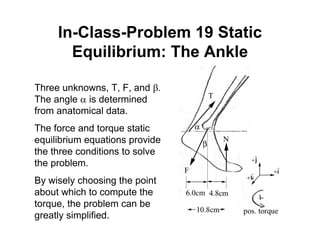
(3) Examples provided demonstrate solving for unknown forces in static systems like a forearm, suspended beam, and forces at the ankle joint. Choosing the reference point for torque calculations simplifies solving the problem.