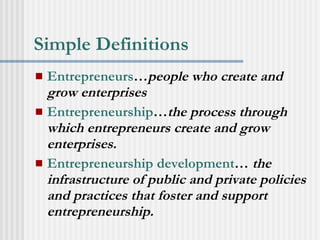
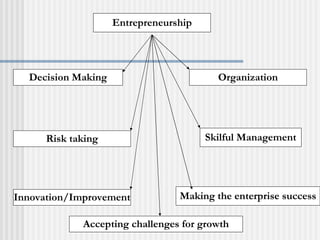
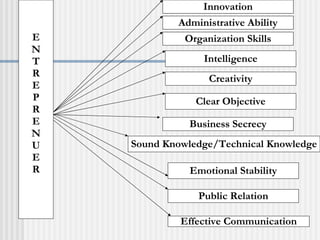
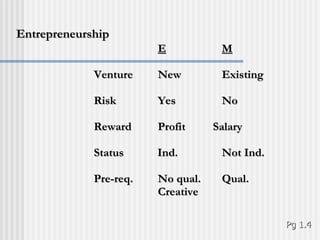
Ratan Tata is recognized as an accomplished entrepreneur who led the Tata Group's acquisition of Corus, creating the world's fifth largest steel company. As the chairman of Tata Sons, he helped expand the company's global presence through strategic acquisitions. Entrepreneurship involves recognizing opportunities, pursuing them through innovation and risk-taking despite limited resources, and having the flexibility and resilience to adapt to challenges. Successful entrepreneurs demonstrate traits like passion, creativity, self-reliance, leadership, and a willingness to take risks.