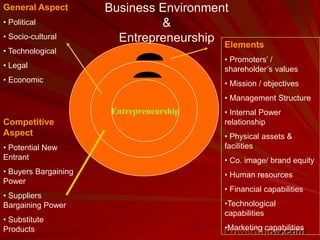
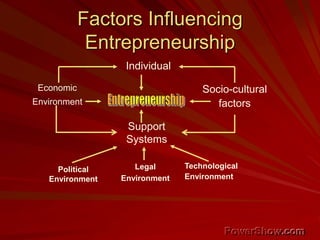
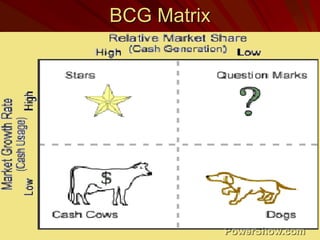
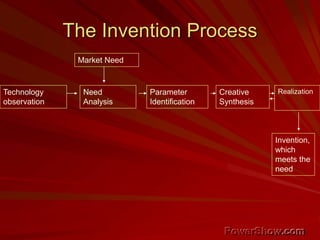
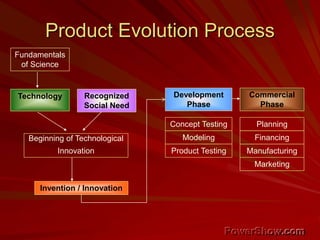
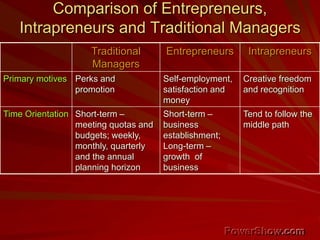
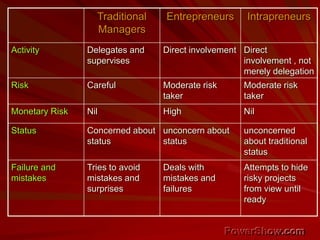
This document explores the concept of entrepreneurship, defining entrepreneurs as individuals who undertake business ventures with associated risks for potential profit. It discusses various entrepreneurship theories throughout history, the characteristics of successful entrepreneurs, and the role of innovation and planning in business success. Additionally, it highlights the impact of entrepreneurship on economic development and the importance of management education in fostering entrepreneurial skills.