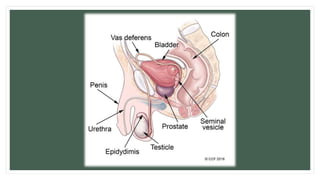
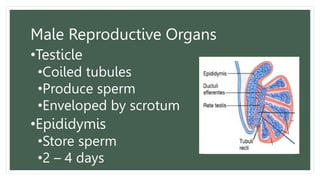
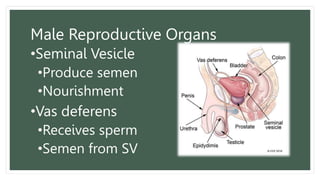
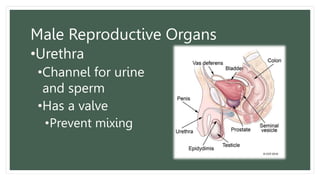
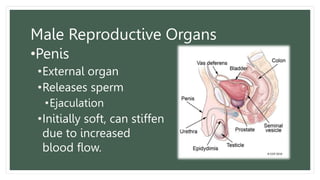
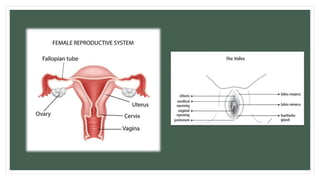
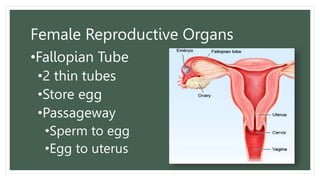
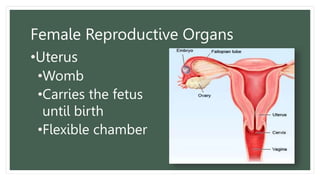
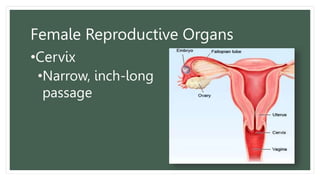
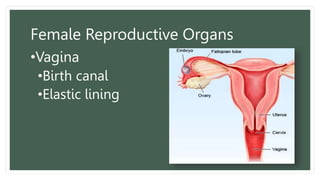
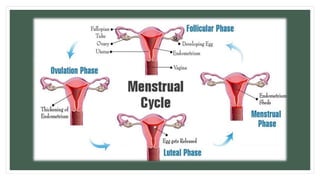
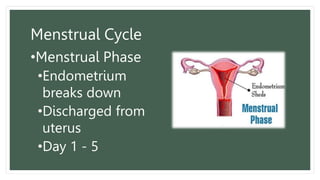
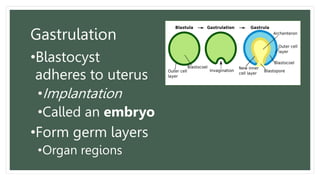
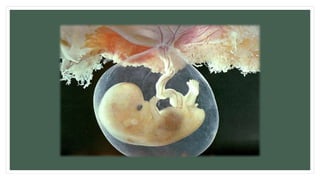
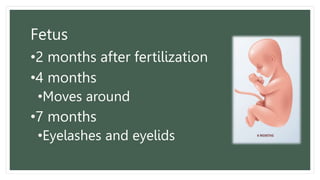
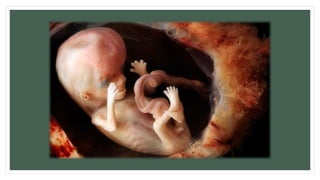
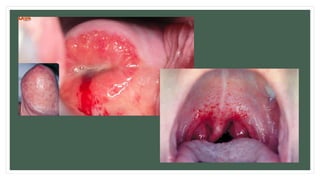
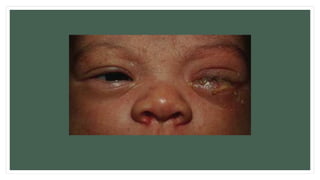
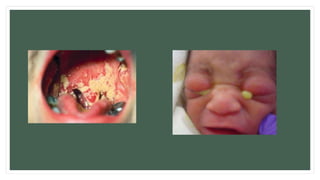
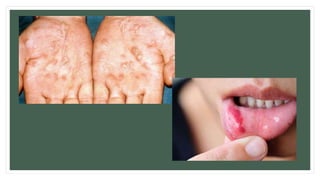
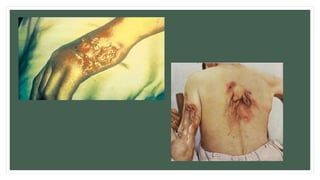
The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems and their organs, stages of embryonic development from fertilization through growth, and diseases of the reproductive system including STDs like chlamydia, genital herpes, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Key organs of the male system include the testicles, penis, and seminal vesicles. Key female organs include the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina. Embryonic development proceeds through cleavage, gastrulation, organogenesis, and specialization. STDs are transmitted sexually and can cause infections without treatment.