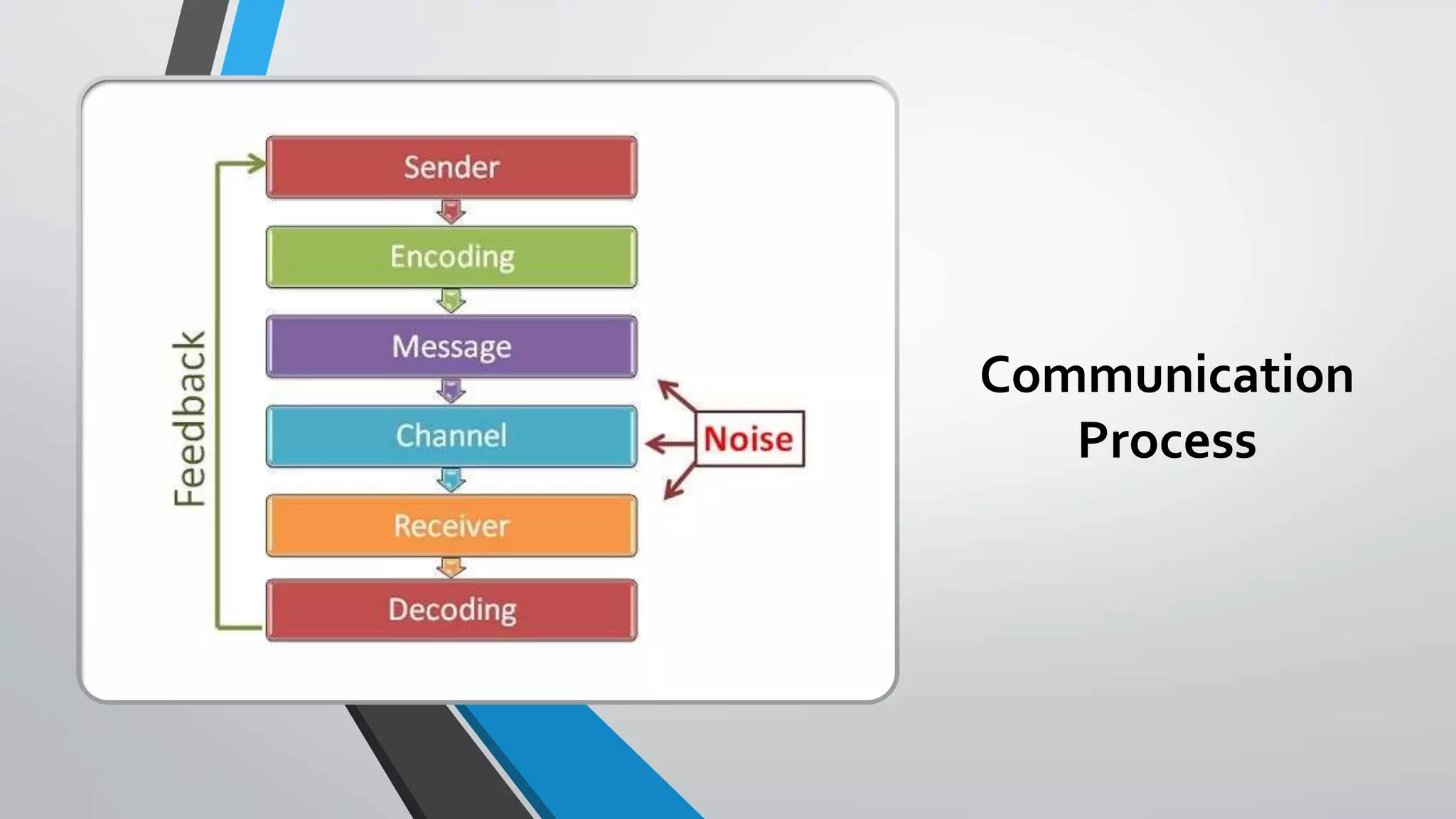
This document defines communication and describes the communication process. Communication is the exchange of information between two or more people through various channels or mediums. The communication process involves a sender encoding a message, transmitting it through a channel, which is received and decoded by the receiver. There may then be feedback from the receiver to the sender. The document also outlines different types of communication, forms of communication, and potential barriers to effective communication.