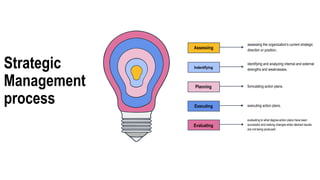
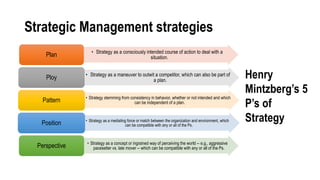
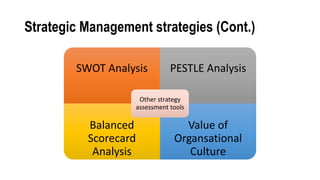
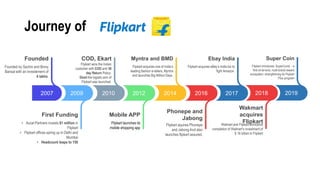
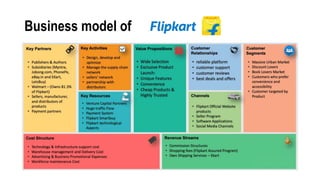
This document provides an overview of strategic management and its application to MSMEs (micro, small, and medium enterprises). It begins by defining strategic management and outlining the typical strategic management process of assessing, identifying, planning, executing, and evaluating. It then discusses why strategic management is important for organizations. The document also covers various strategic management tools and frameworks, the strategic management process for MSMEs, and provides an example of how strategic management has been applied at Flipkart, a major Indian e-commerce company.