This document provides an overview of different types of electrical machines:
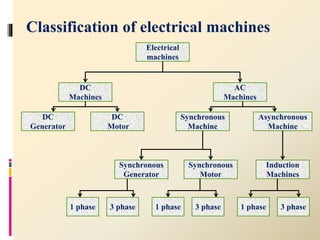
1. Electrical machines are classified as static machines like transformers or rotating machines like motors and generators.
2. Rotating machines are further divided into DC machines like DC generators and DC motors, and AC machines like asynchronous and synchronous machines.
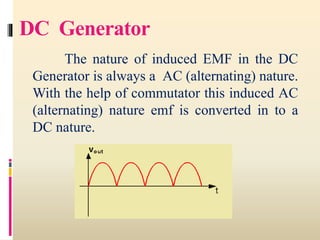
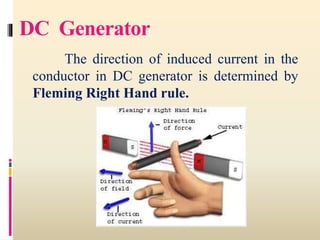
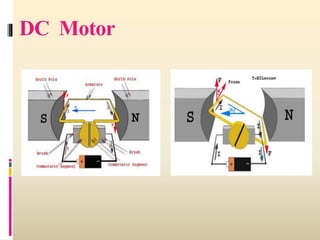
3. DC generators operate based on Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction, producing an alternating current that is converted to direct current via a commutator. DC motors use the interaction between a magnetic field and electric current to produce motion.