This document discusses crisis management and provides an overview of key topics including:
- The nature of crises, how they are defined for different organizations, and common features of crises.
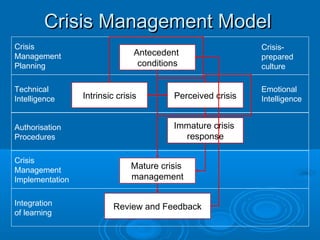
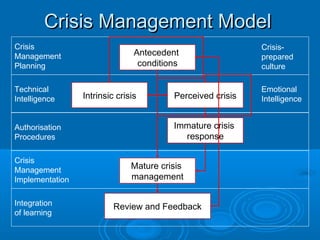
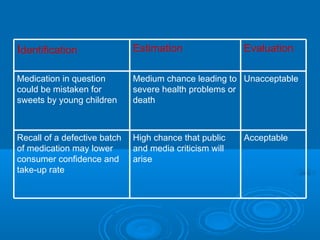
- A crisis management model involving antecedent conditions, the intrinsic and perceived crisis, immature and mature crisis responses, and review/feedback.
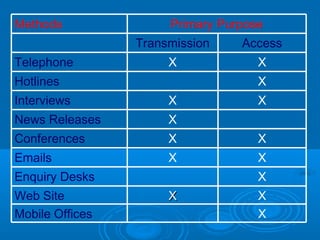
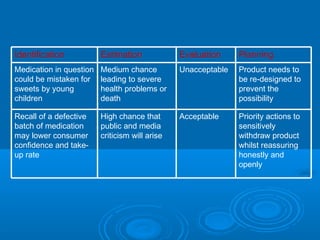
- Elements of crisis planning including gathering intelligence, assessing risks, risk management, and developing crisis communication plans.
- The importance of identifying audiences, communication methods, and messages as part of crisis communication planning.
The presentation provides guidance on building organizational capacity to effectively manage unforeseen crises through prevention, planning, and developing a crisis-prepared culture.










































![Message OptionsMessage Options [What?][What?]
1)1) Full apologyFull apology
2)2) Corrective actionCorrective action
3)3) IngratiationIngratiation
4)4) JustificationJustification
5)5) ExcuseExcuse
6)6) DenialDenial
7)7) Attack the attackerAttack the attacker](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/19bcrisismanagement-130604144315-phpapp01/85/19b-crisis-management-47-320.jpg)






![Media demandsMedia demands [How?][How?]
Accuracy and simplicityAccuracy and simplicity
Statistics which are explainedStatistics which are explained
Context of informationContext of information
Comments from highest authorityComments from highest authority
Some controversial elementsSome controversial elements
Both sides of the issueBoth sides of the issue
Speed, speed and speedSpeed, speed and speed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/19bcrisismanagement-130604144315-phpapp01/85/19b-crisis-management-54-320.jpg)