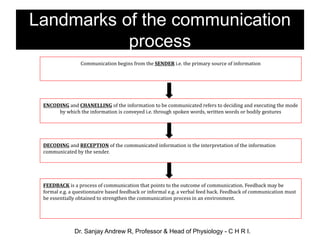
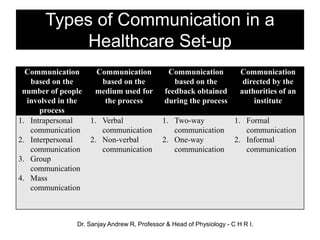
This document outlines the essential principles of communication for healthcare professionals. It defines communication as the meaningful exchange of information between individuals in the healthcare field, including doctors, patients, families, nurses, and administrators. The document discusses the importance of effective communication in achieving patient well-being and preventing conflicts. It also describes the key components of the communication process, types of communication, barriers to communication, and facilitators that can improve communication. The overall goal is to enhance healthcare professionals' ability to communicate with patients in a respectful, empathetic manner.