Embed presentation
Downloaded 30 times




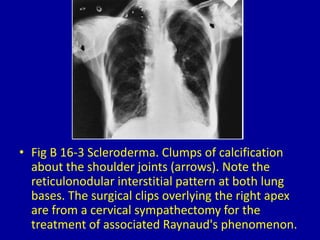
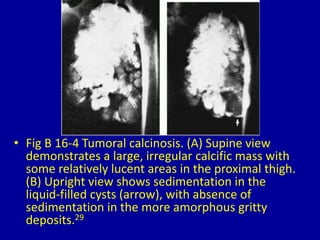
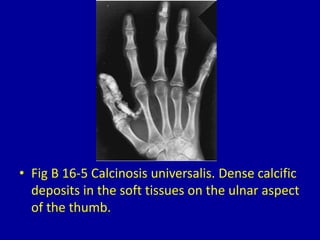
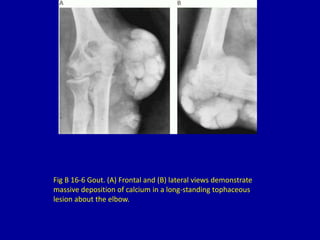




This document discusses various types of periarticular calcification seen on clinical imaging: 1) Calcific tendinitis is seen as amorphous calcium deposits in the supraspinatus tendon on shoulder imaging. 2) Hyperparathyroidism can cause dense masses of tumoral calcification in joint capsules and soft tissues, as seen in the foot of a patient with renal osteodystrophy. 3) Scleroderma is associated with clumps of calcification around shoulder joints, along with reticulonodular lung patterns and surgical clips from treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon.










