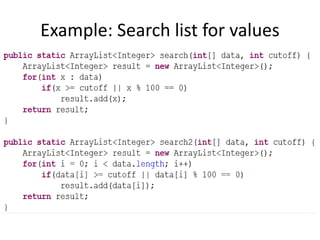
This document provides an overview of the CS324e course which teaches graphics and visualization using Java. It introduces Java after students have learned Python in previous courses. The first couple lectures and assignments focus on reviewing Java by looking at common techniques in Python and their Java equivalents. Java is an object-oriented language that uses braces, strong typing, and requires all code to be part of a class. The document defines Java identifiers, basic program structure, variables, arrays versus lists, and provides examples for calculating sums of squares, counting characters, and searching lists.





![Basic Program
public class Hello {
/**
* Where the program starts
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!!");
System.out.println("This is a Java program.");
}
}
• {} for code blocks
• main is called when program run
• ; at the end of statements
• System.out.println is standard output
– analogous to print statement in Python
• comments, /* stuff */ or // stuff](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15pythontojava-220912025446-68607417/85/1_5_Python_to_Java-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![Variables
Python
i = 10
j = 20
k = i * j + i / j
x = 1.7526
name = "Olivia"
list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
blank = [0] * 10
Java
int i = 10;
int j = 20;
int k = i * j + i / j;
double x = 1.7526;
String name = "Olivia";
int[] list = [1, 2, 3, 4];
int[] blank = new int[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15pythontojava-220912025446-68607417/85/1_5_Python_to_Java-pptx-7-320.jpg)