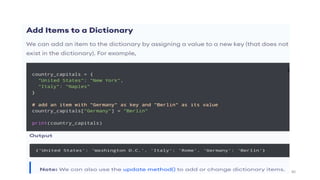
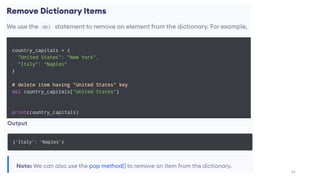
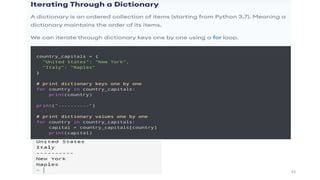
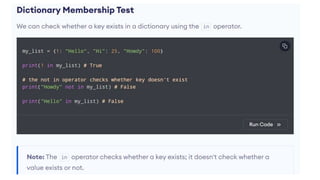
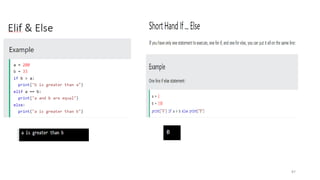
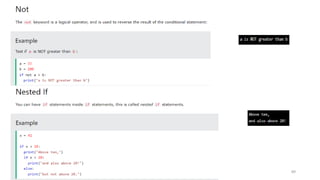
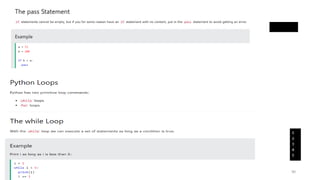
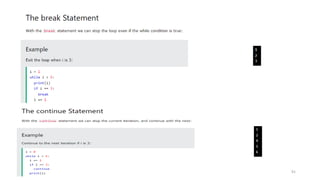
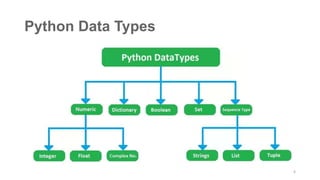
Python can be used for a variety of applications including web development, scientific computing, education, desktop GUIs, and software development. It is commonly used to build web applications using frameworks like Django and Flask, for scientific computing tasks using libraries like NumPy and SciPy, and for general software development tasks like build automation and testing. Python supports a range of data types including integers, floats, complex numbers, lists, dictionaries, sets, and strings. It can be used to write functions and programs to solve problems across many domains.
























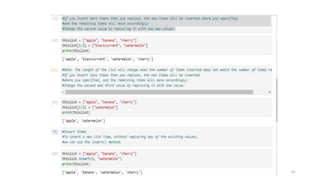
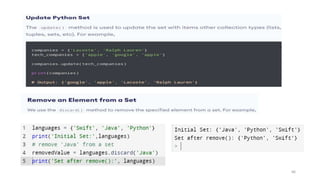
![Python Lists
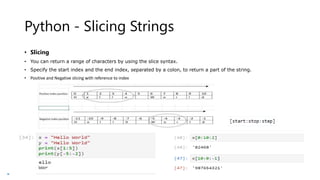
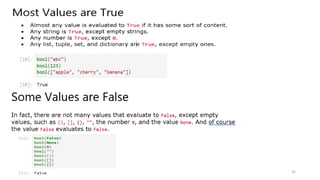
• mylist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
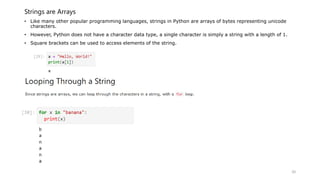
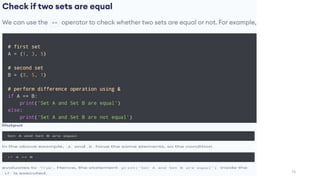
• Lists are used to store multiple items in a single variable.
• Lists are one of 4 built-in data types in Python used to store collections of data, the other 3 are Tuple, Set,
and Dictionary, all with different qualities and usage. Lists are created using square brackets:
37
List Items
List items are ordered, changeable, and allow duplicate values.
List items are indexed, the first item has index [0], the second item has index [1] etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-basics-230802055322-d45a48d7/85/Python-Basics-pptx-37-320.jpg)

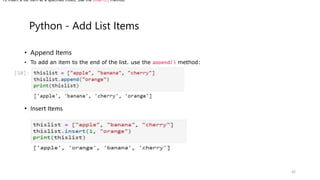
























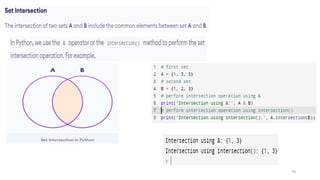

![Python Dictionaries
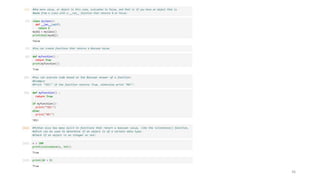
Dictionaries are used to store data values in key:value pairs.
A dictionary is a collection which is ordered*, changeable and do not allow duplicates.
Dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and have keys and values:
thisdict = {"brand":"Ford","model":"Mustang","year":1964}
print(thisdict)
Output : {"brand":"Ford","model":"Mustang","year":1964}
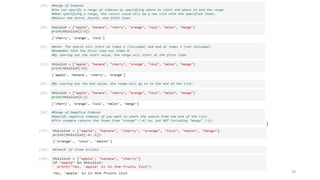
Print the "brand" value of the dictionary:
print(thisdict["brand"])
Output:Ford
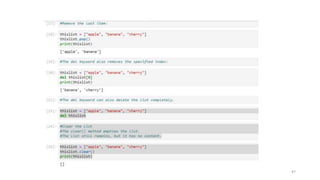
Ordered or Unordered?
When we say that dictionaries are ordered, it means that the items have a defined order, and that order will not change.
Unordered means that the items does not have a defined order, you cannot refer to an item by using an index.
Changeable
Dictionaries are changeable, meaning that we can change, add or remove items after the dictionary has been created.
Duplicates Not Allowed
Duplicate values will overwrite existing values:
thisdict = {"brand":"Ford","model":"Mustang","year":1964,"year":1968}
print(thisdict)
Output: {"brand":"Ford","model":"Mustang","year":1968}
75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-basics-230802055322-d45a48d7/85/Python-Basics-pptx-75-320.jpg)
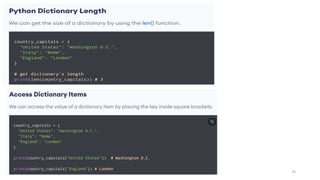
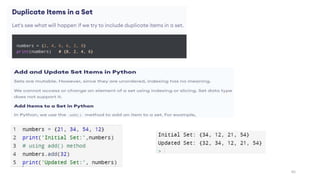
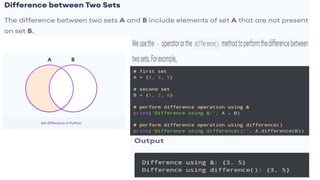
![Python - Access Dictionary Items
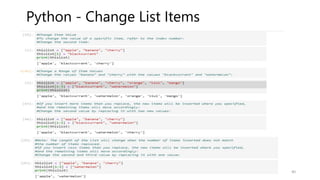
• Accessing Items
• You can access the items of a dictionary by referring to its key name, inside square brackets:
• Get the value of the "model" key:
• thisdict = {"brand":"Ford","model":"Mustang","year":1964}
• x = thisdict["model"]
• print(x)
• Output: Mustang
• There is also a method called get() that will give you the same result:
• Get the value of the "model" key:
• x = thisdict.get("model")
• print(x)
• Output: Mustang
77](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-basics-230802055322-d45a48d7/85/Python-Basics-pptx-77-320.jpg)