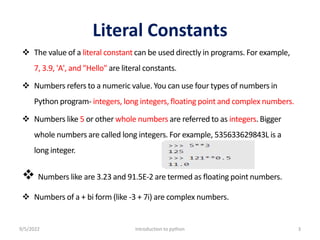
Values in Python can belong to different data types including numbers, strings, and lists. Numbers include integers, floating point numbers, and complex numbers. Strings are a sequence of characters that can be defined using single quotes, double quotes, or triple quotes. Common data types in Python include numbers, strings, lists, tuples, and dictionaries. Lists are mutable sequences while tuples are immutable sequences.






![• Boolean is another data type in Python.
• A variable of Boolean type can have one of the
two values- True or False.
List
• List is an ordered sequence of items. It is one of
the most used data type in Python and is very
flexible. All the items in a list do not need to be of
the same type.
• Lists are mutable. The elements in the list can be
modified.
• To declare a list in python, separate the items
using commas and enclose them within square
brackets [ ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-220905092332-980425c6/85/2-Values-and-Data-types-in-Python-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![>>> a = [1, 2.2, 'python'] The slicing operator [ ] is
used to extract an item or a range of items from a
list. Index starts form 0 in Python.
Example:
>>>a = [5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40]
>>>a[2]
15
>>>print("a[0:3] = ", a[0:3])
[5,10,15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-220905092332-980425c6/85/2-Values-and-Data-types-in-Python-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![Example:
>>> t = (5,'program', 1+3j)
print("t[1] = ", t[1])
print("t[0:3] = ", t[0:3])
Output:
t[1] = program
t[0:3] = (5, 'program', (1+3j))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-220905092332-980425c6/85/2-Values-and-Data-types-in-Python-pptx-11-320.jpg)

![Example:
s = 'Hello world!'
print("s[4] = ", s[4]) # s[4] = 'o'
print("s[6:11] = ", s[6:11]) # s[6:11] = 'world'
Output:
s[4] = o
s[6:11] = world](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-220905092332-980425c6/85/2-Values-and-Data-types-in-Python-pptx-13-320.jpg)