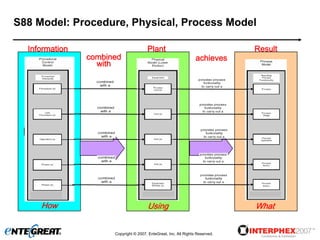
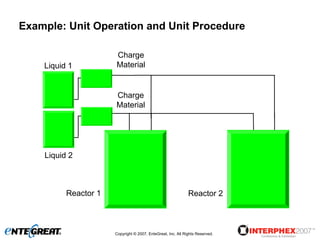
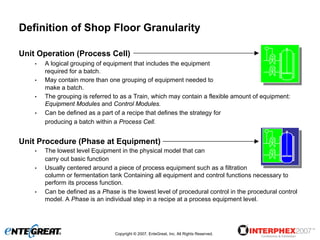
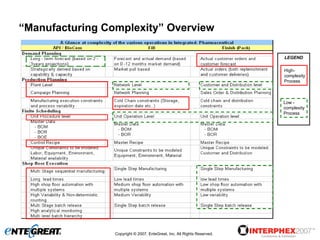
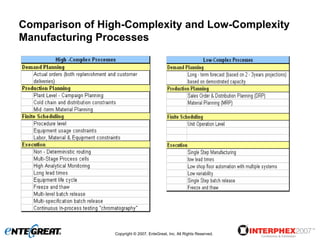
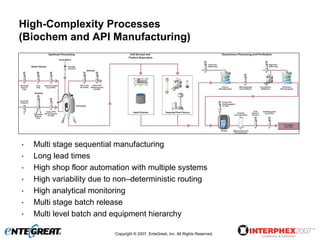
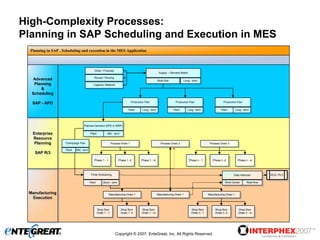
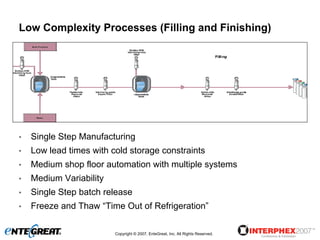
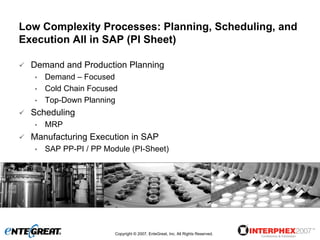
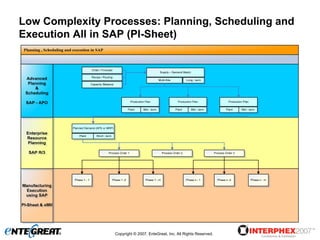
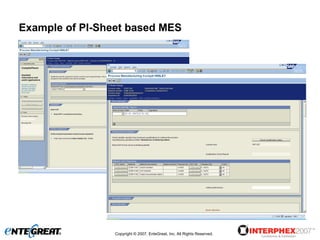
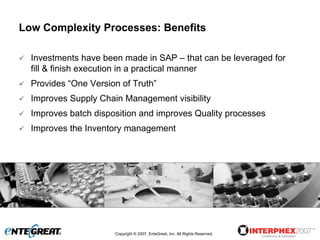
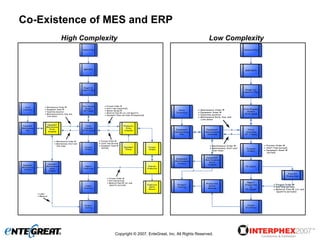
The document discusses a hybrid approach for leveraging ERP (SAP) and MES functionality within integrated biopharmaceutical manufacturing environments. It proposes planning in SAP and scheduling and execution in MES for high-complexity biologics manufacturing. For lower complexity filling and finishing, it suggests planning, scheduling and execution can all be handled in SAP using PI sheets. The approach aims to improve control, visibility and response times while leveraging existing SAP investments.