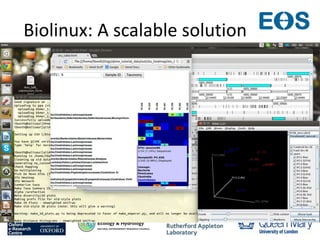
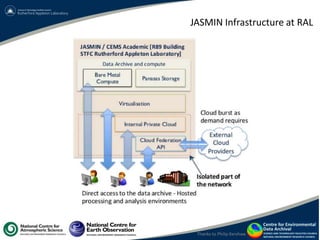
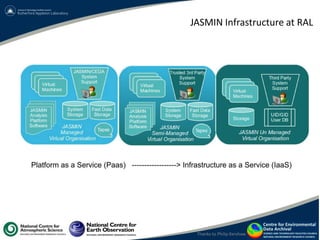
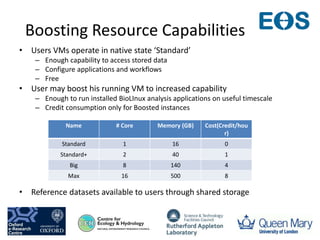
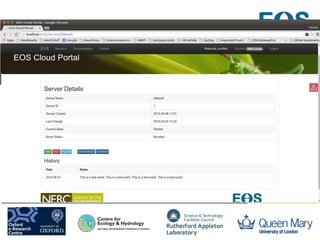
This document summarizes a desktop as a service solution called EOSCloud that provides scalable bioinformatics tools on the cloud. EOSCloud is a NERC Big Data project that gives researchers virtual machines with preinstalled bioinformatics software like Biolinux. Researchers are given two VMs - one with Biolinux and one Ubuntu Docker host. The VMs can be boosted to higher capabilities for more intensive tasks, consuming credits only for the boosted time. EOSCloud aims to make infrastructure more efficient and lower barriers to entry for researchers compared to traditional HPC or grid computing. A pilot launch is scheduled for March 31st, 2015 to test with early user communities.