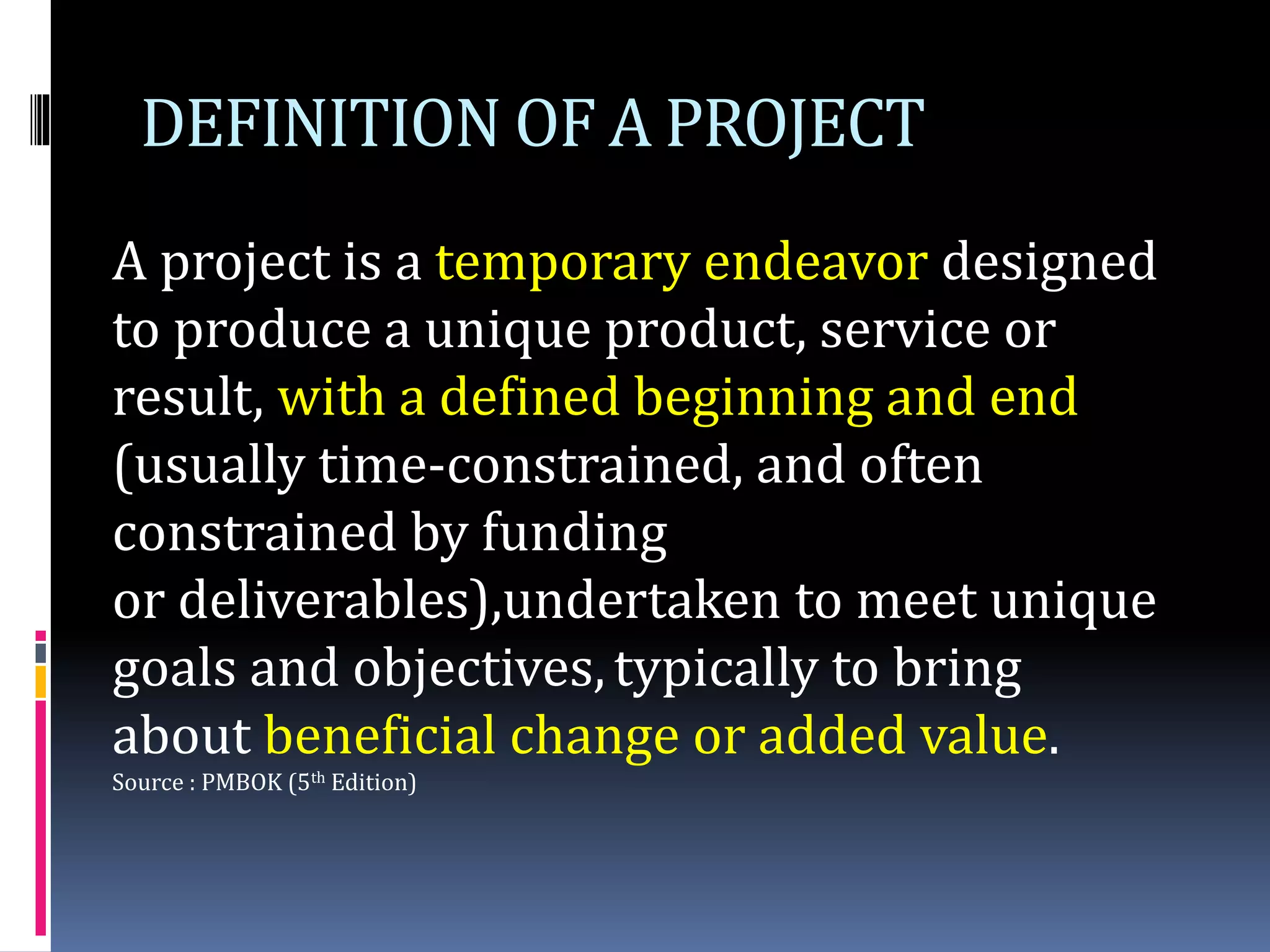
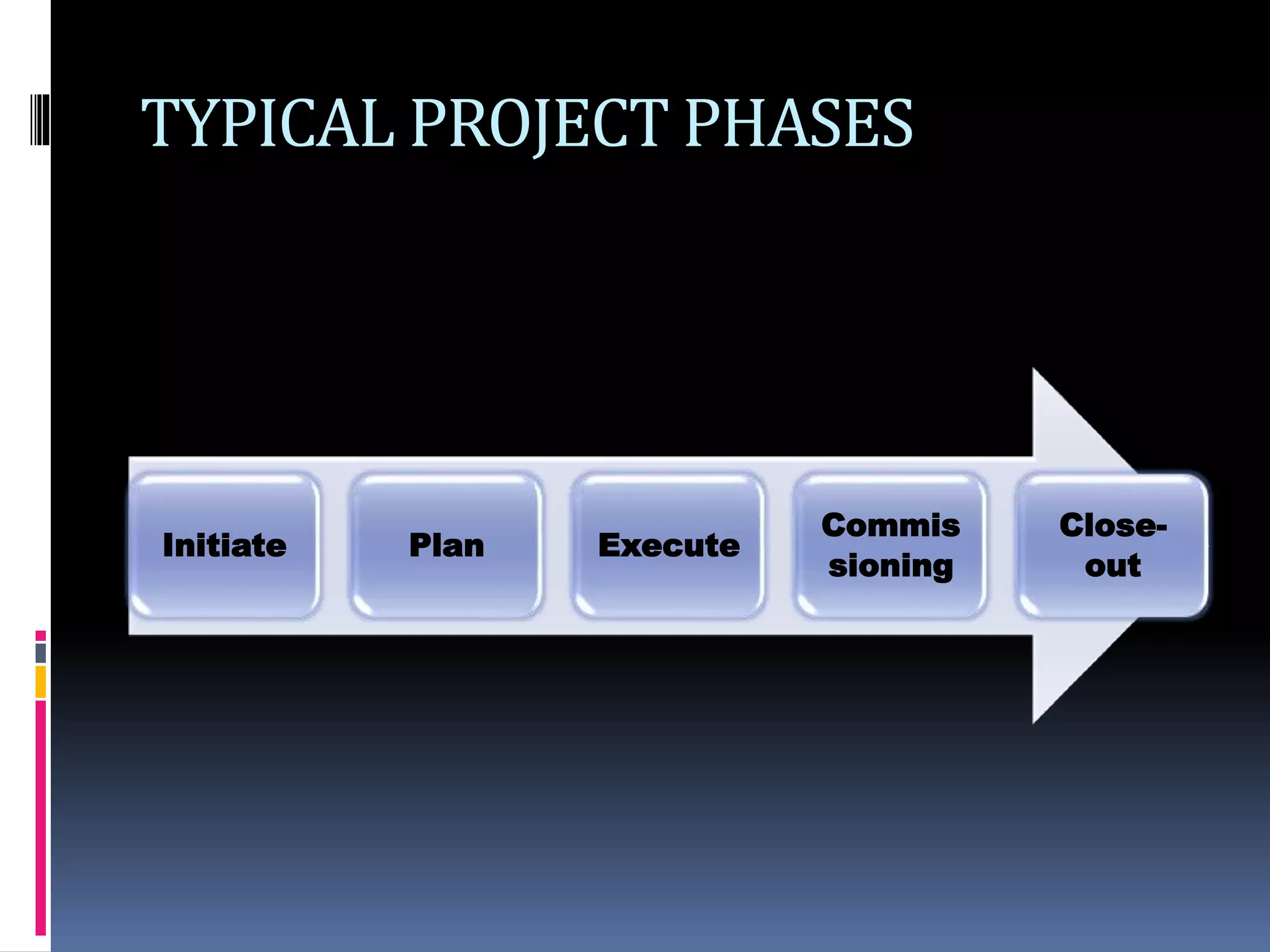
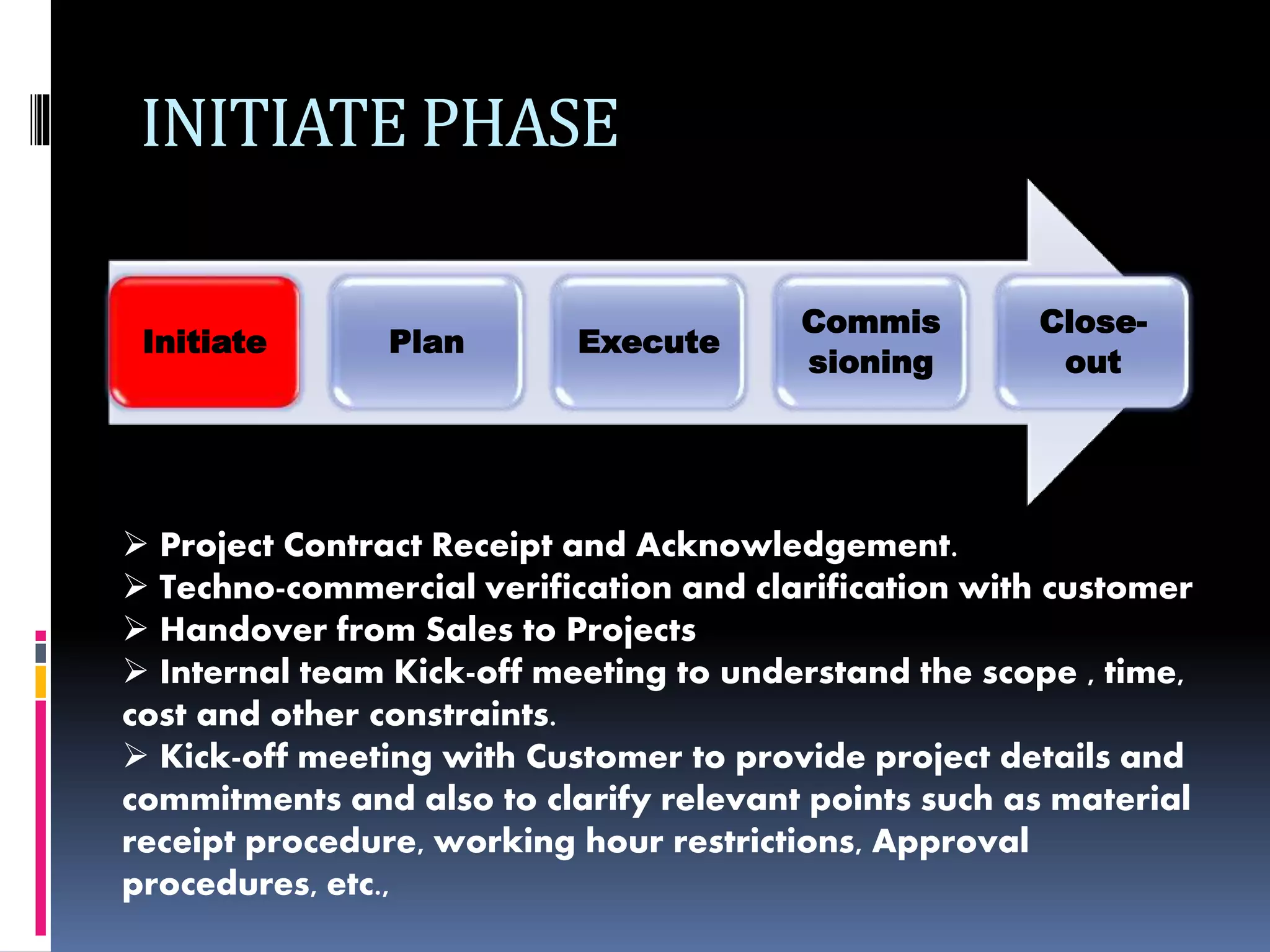
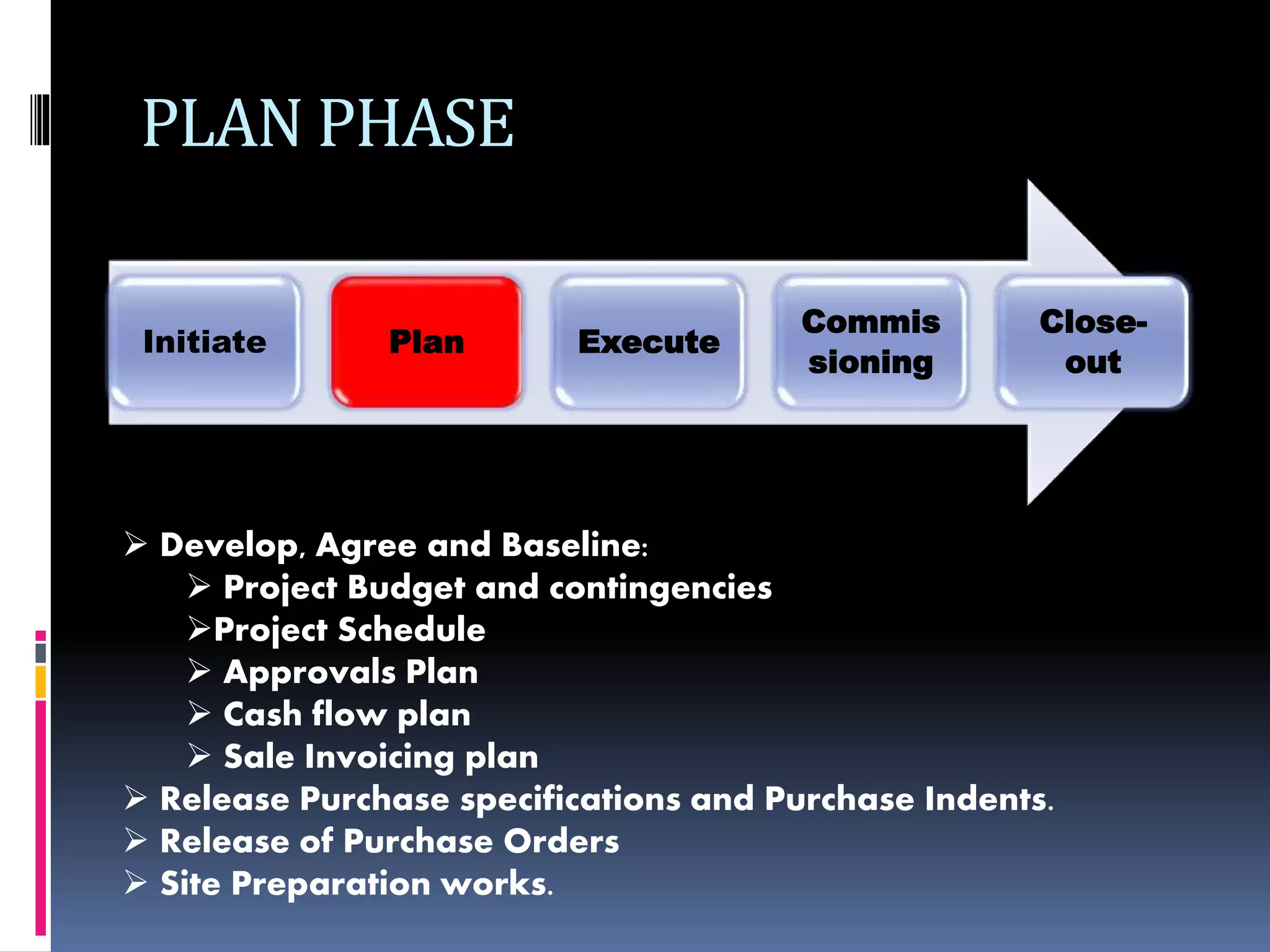
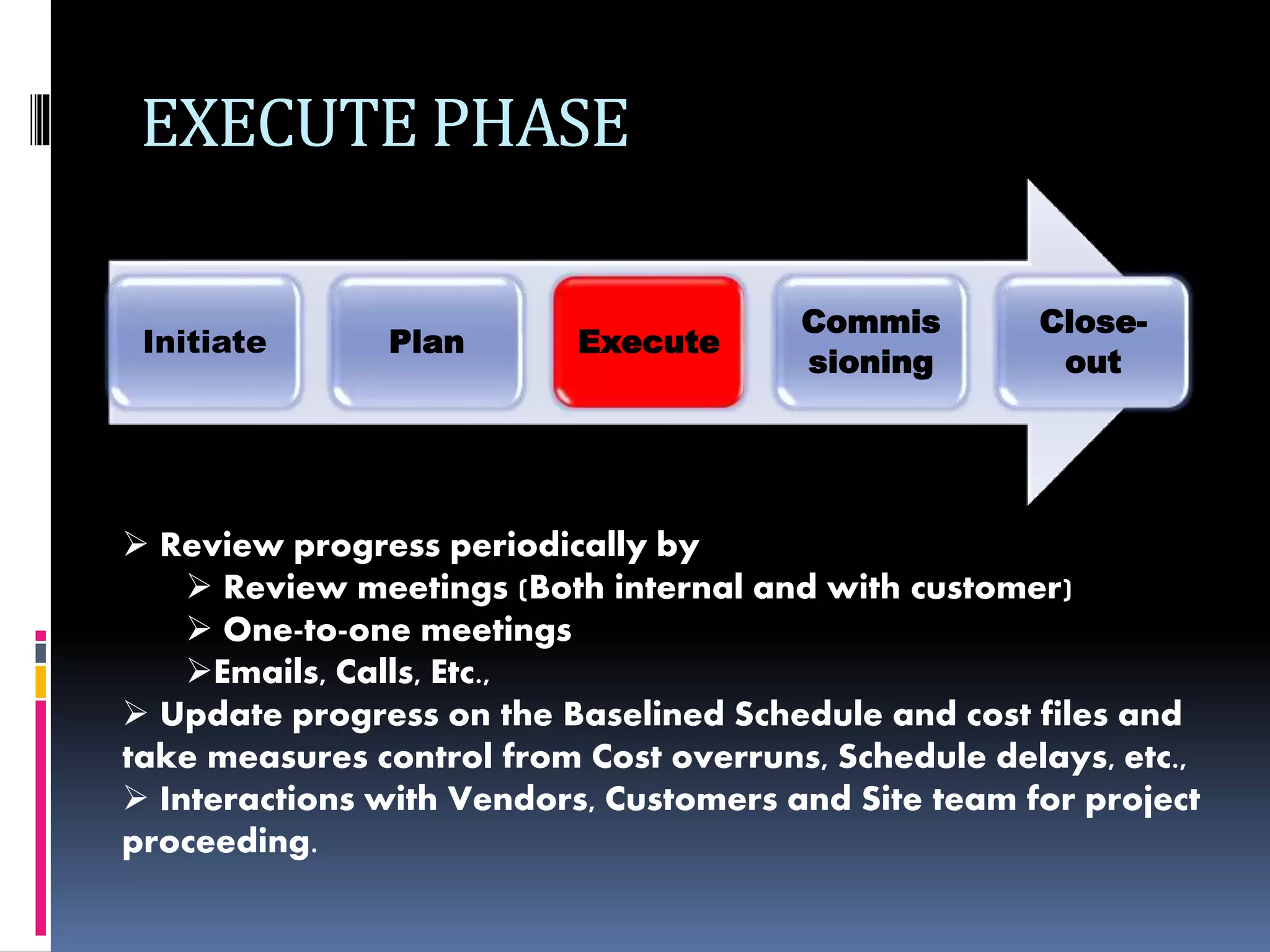
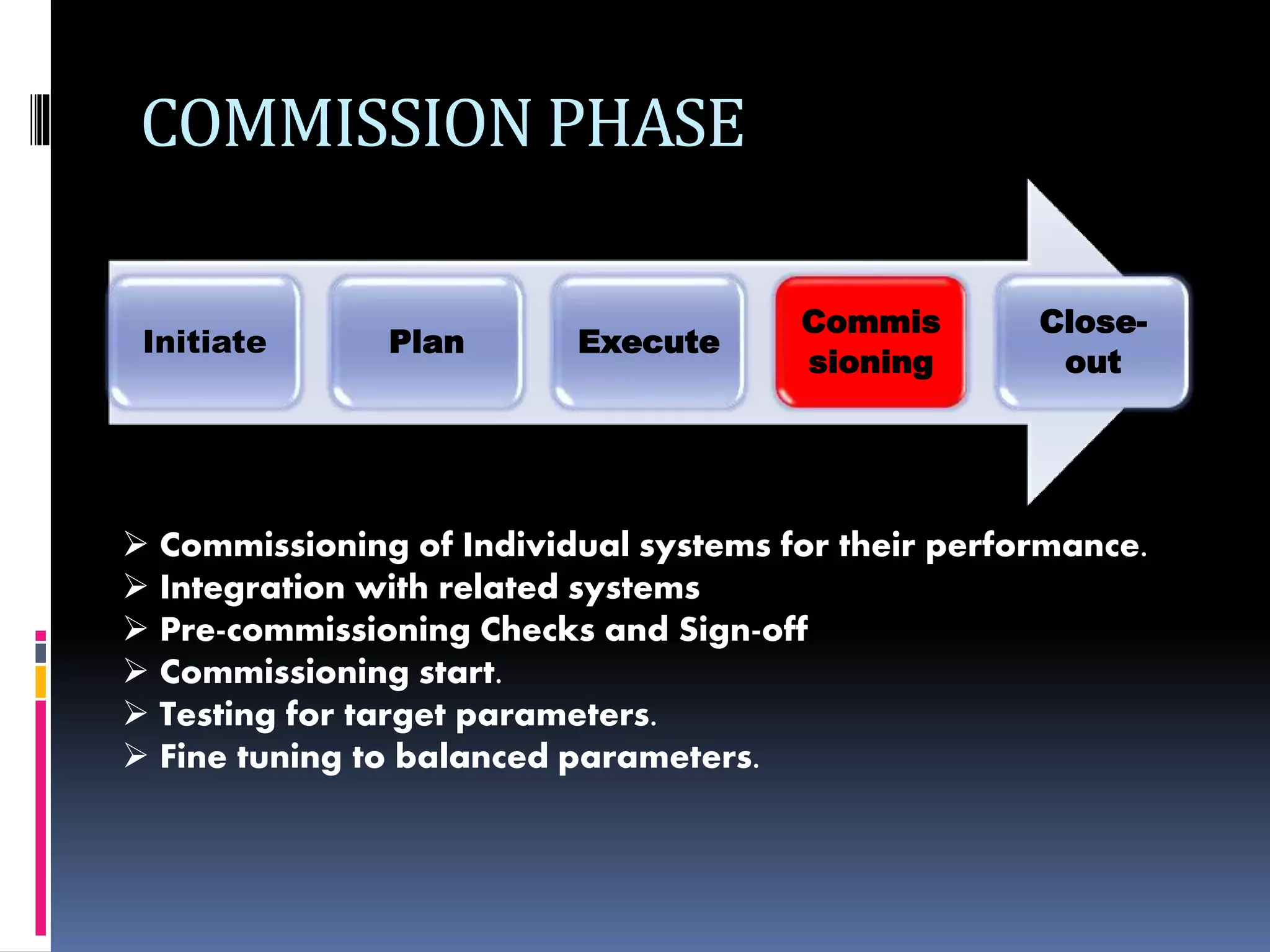
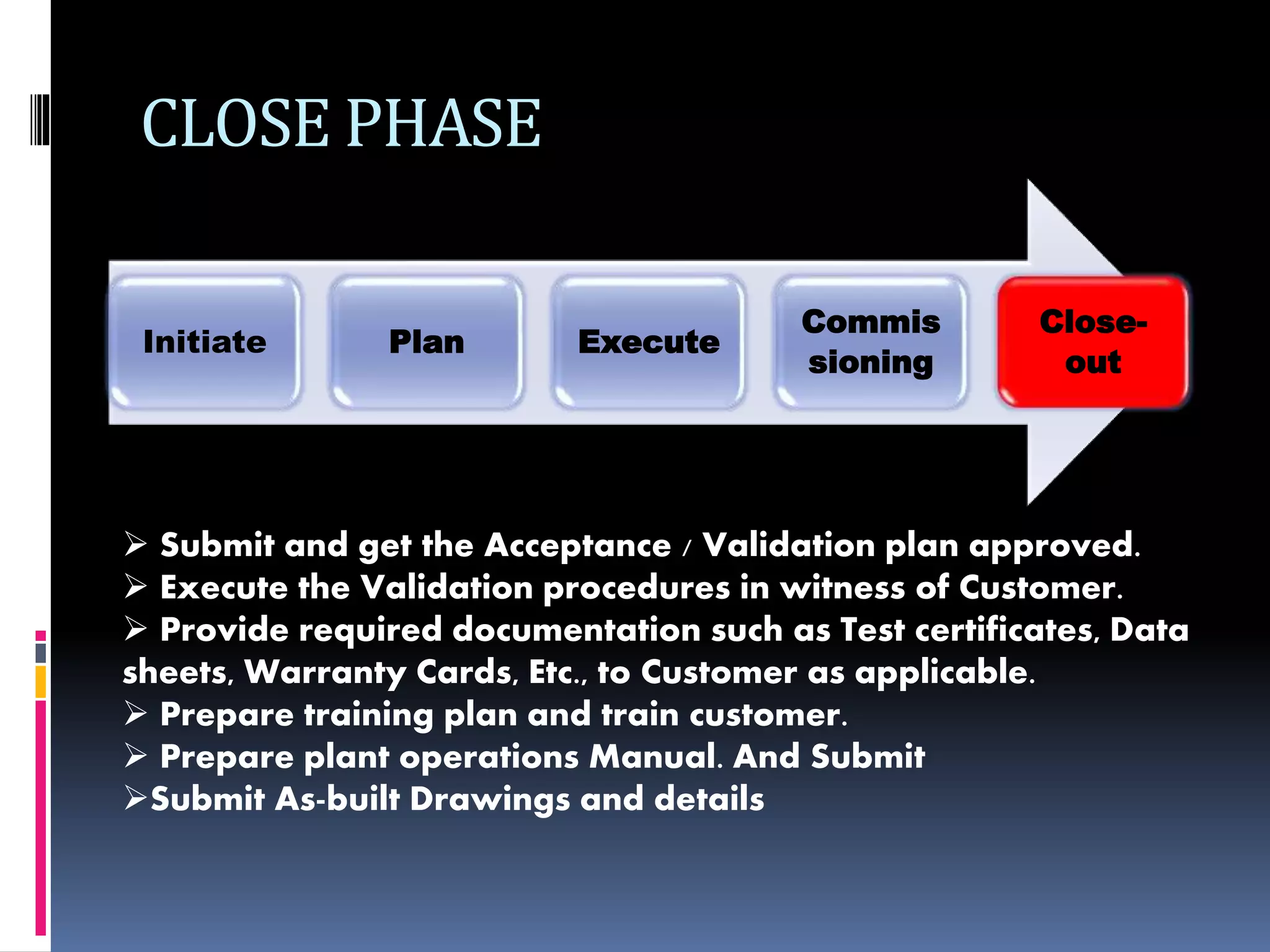
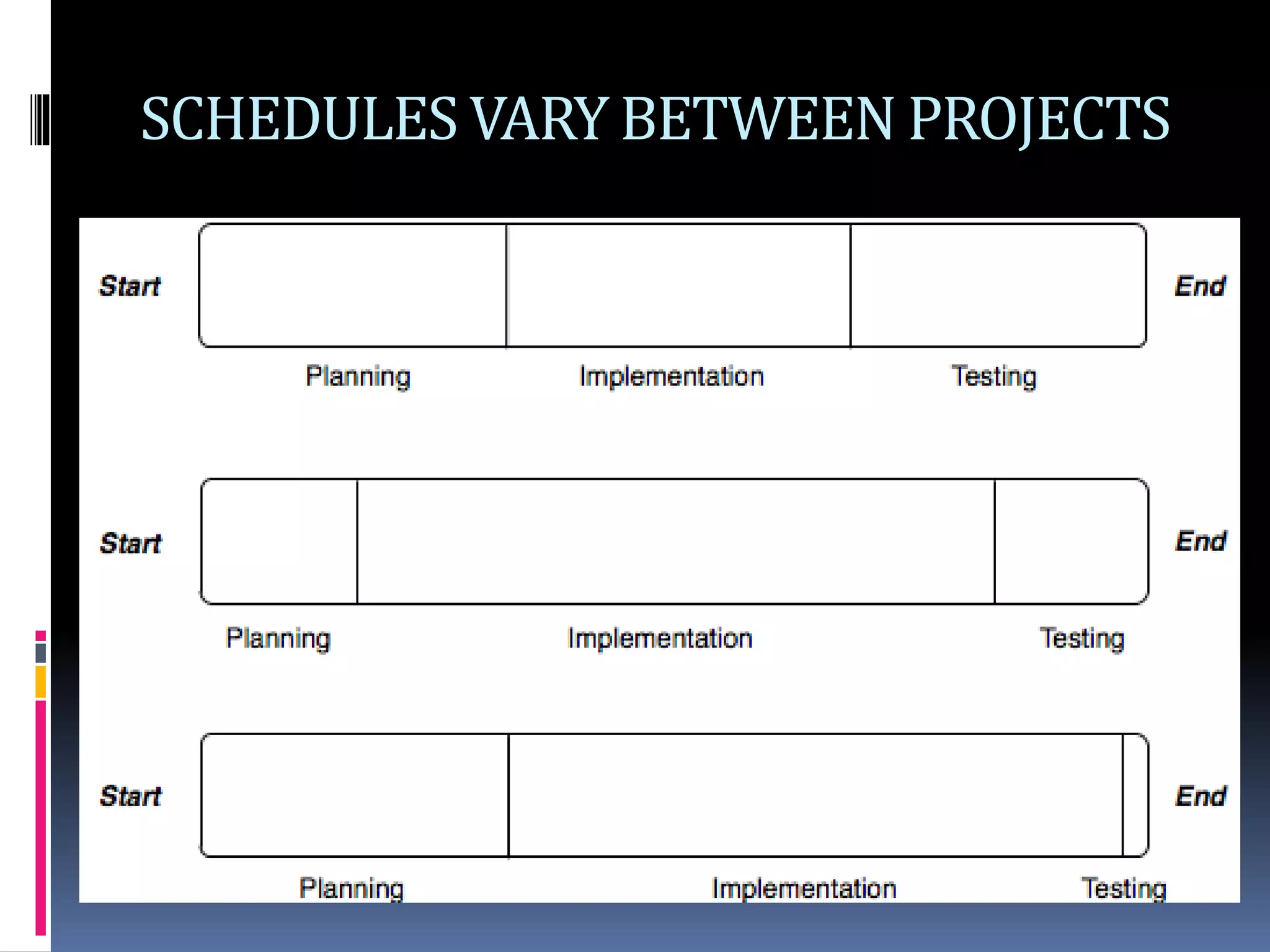
The document discusses project planning and management. It defines what a project is and what project management entails. It describes the typical phases of a project as initiate, plan, execute, commissioning, and close-out. It provides details on each phase. It also discusses project planning in more depth, describing the major deliverables of a project plan such as the project schedule, cost and budget documents, scope of works statement, quality plan, and risk matrix. Finally, it covers some common tools and techniques used for project planning, including Microsoft Office, Microsoft Project, schedule and cost monitoring sheets, earned value management, and project dashboards.