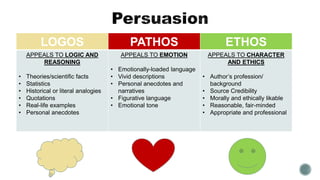
This document outlines elements of argumentation and persuasion that will be covered in an English IV class, including logical appeals, ambiguity, rhetoric, and persuasive tactics. It defines key terms like persuasion, ambiguity, and rhetoric. It also explains the components of an effective argument, including establishing a claim, providing reasons and evidence to support the position, addressing counterarguments, and reaching a conclusion. Different types of logical, emotional, and ethical appeals are described.