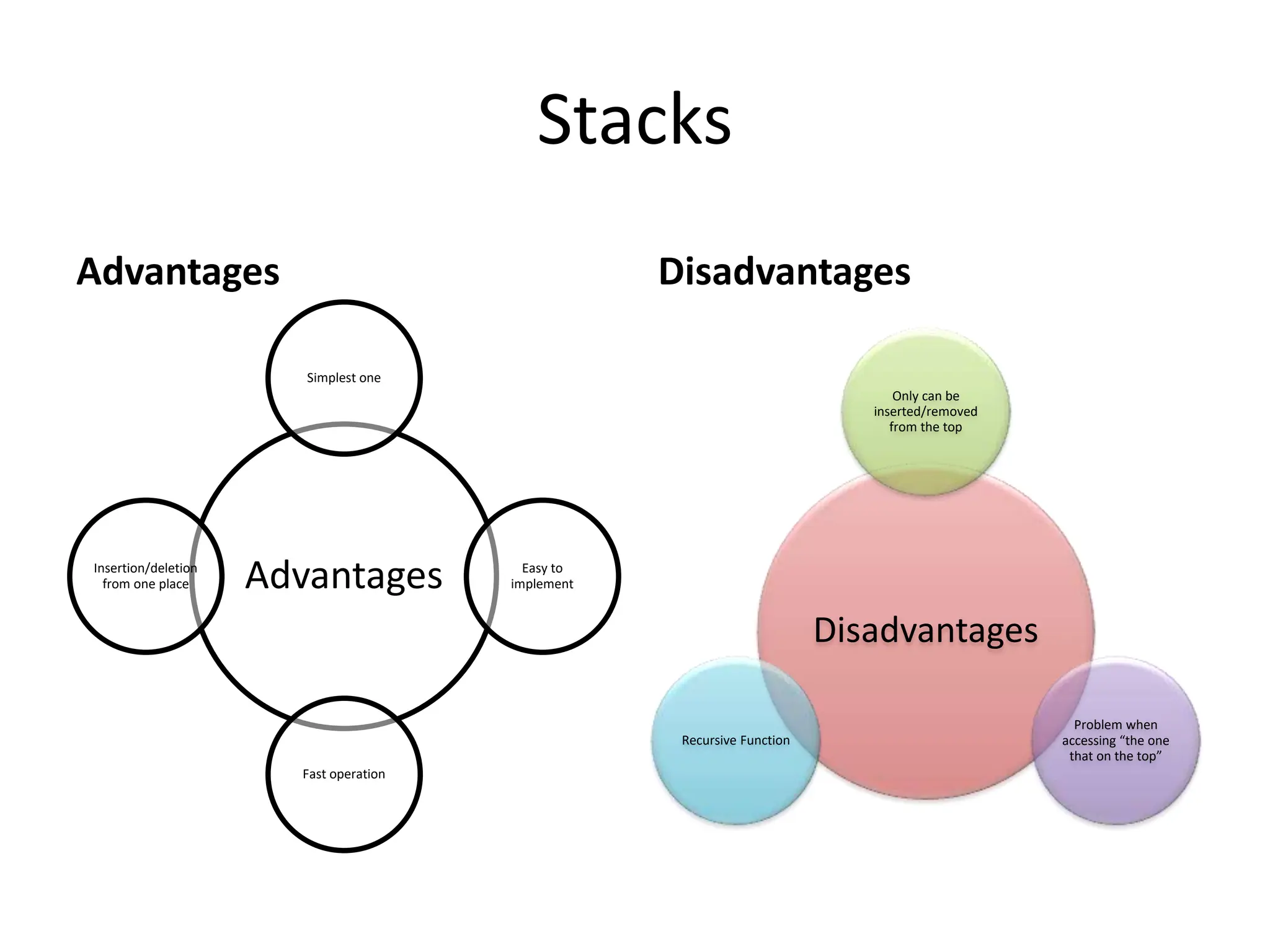
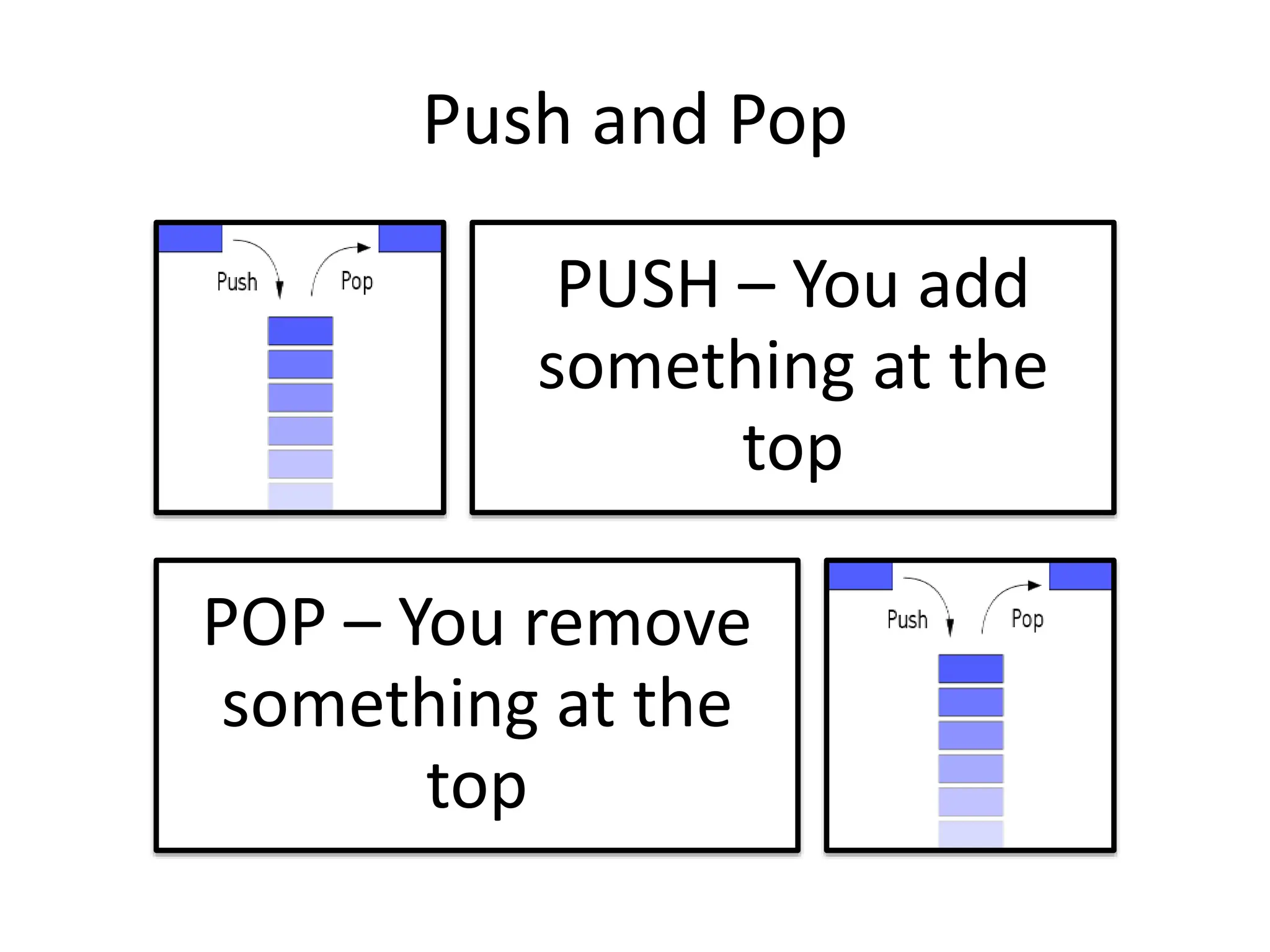
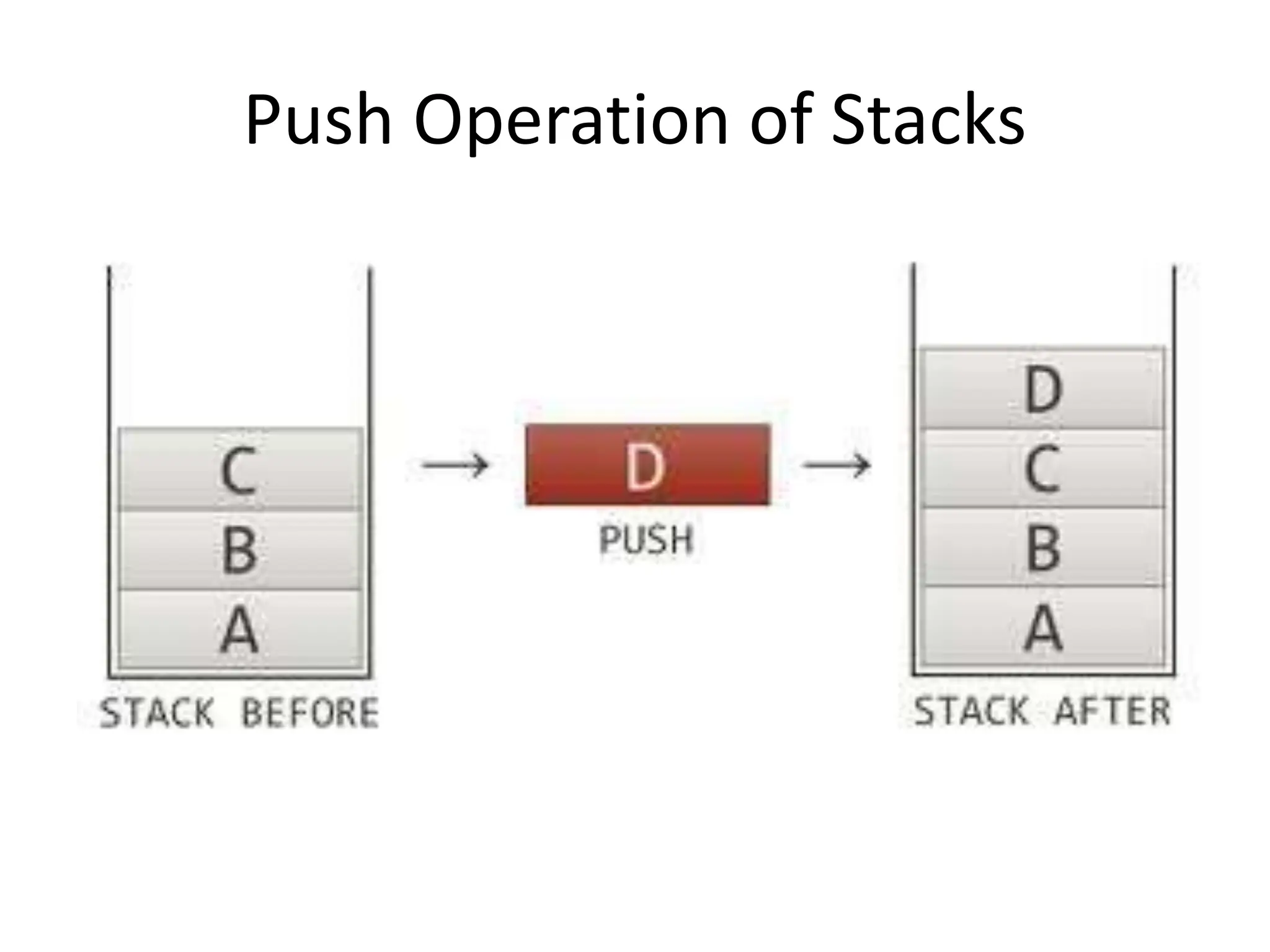
The document discusses stacks as a last in, first out (LIFO) data structure, outlining their advantages, basic operations, and usage in applications like undo/redo features and string reversal. It includes implementation examples, coding explanations for push and pop functions, and applications of stacks in converting decimal to binary, as well as infix to postfix notation. Additionally, it touches on the Towers of Hanoi problem as a stack-based application.










![Let us Implement Stacks
We declare a private inside “stack” class
- arr[MAX] : this is where we put all the data
- top : we assign our “leader” here.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-14-2048.jpg)




![Let us Implement Stacks
Then, we check whether top is still lower than MAX.
If the top still lower than MAX, we continue to insert
data at the position according to the top position
arr[0] = 40 (recall that top = 0).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-19-2048.jpg)


![Example push(40)
4
2
12
32
54
5
top = 6
if(top<MAX)
{
arr[top]=a;
}
- Yes, top is still lower than
MAX which is 10.
- So, arr[6] = 40
(since we receive a = 40)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-22-2048.jpg)


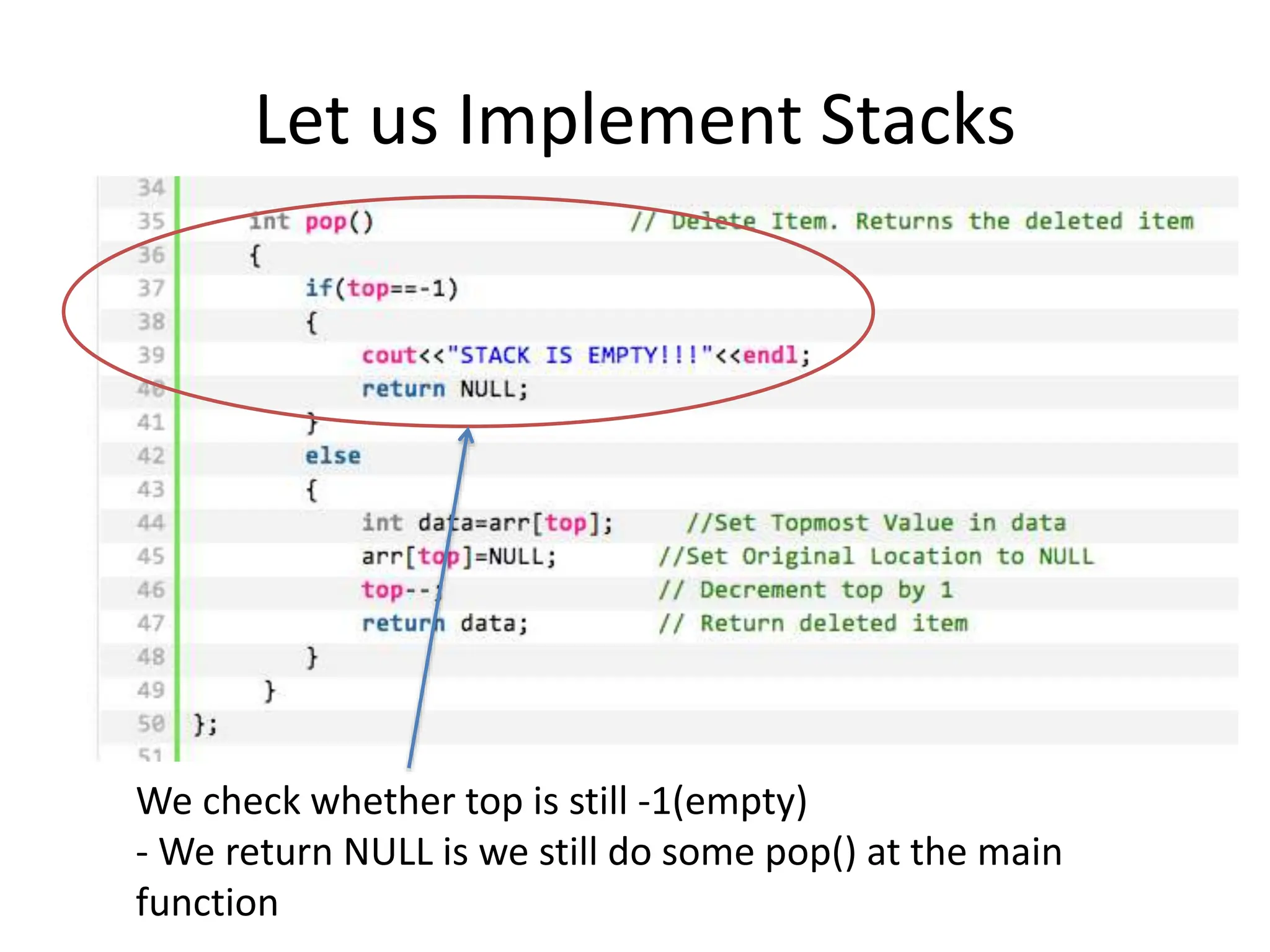
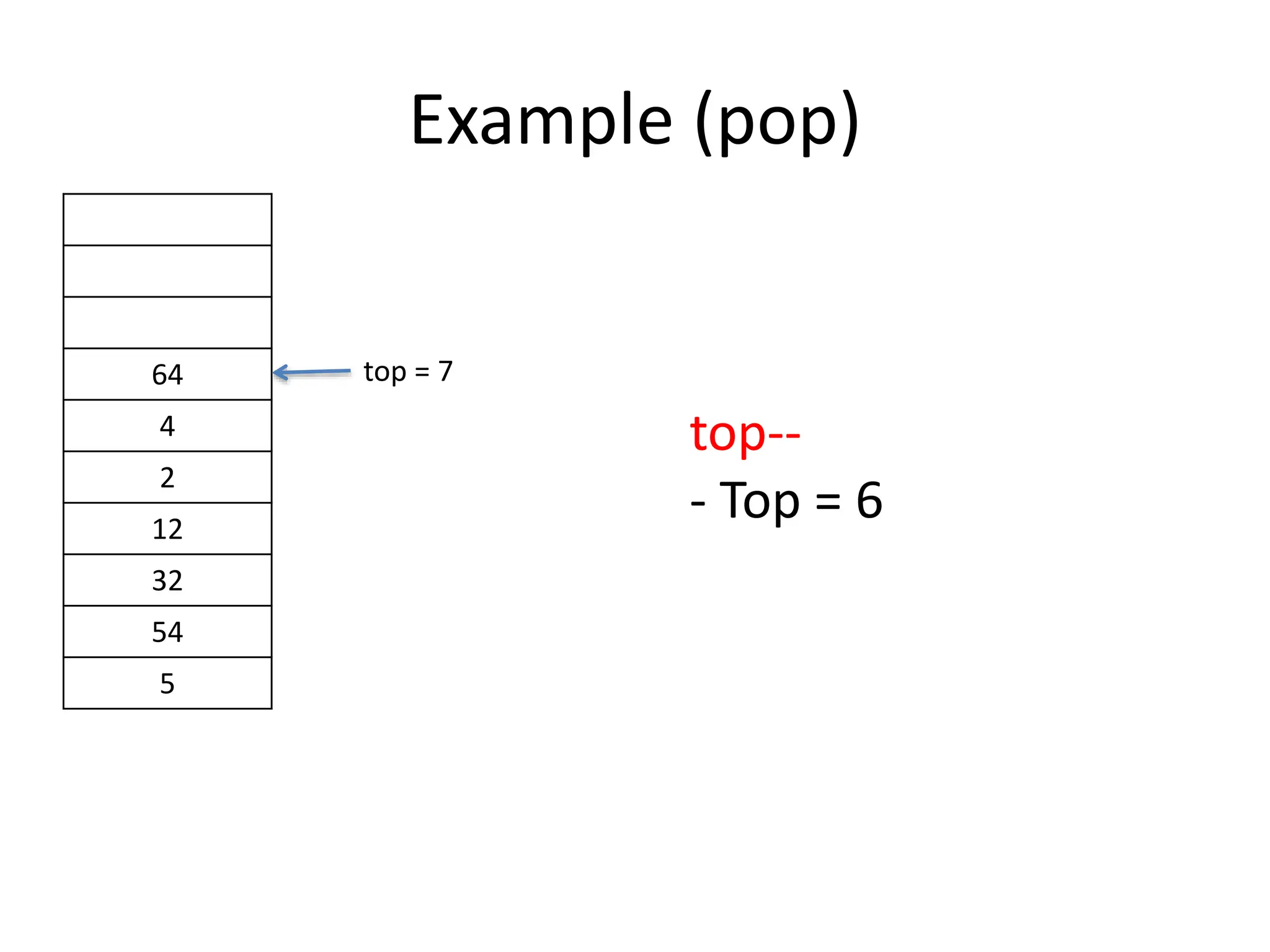
![Let us Implement Stacks
If it is not
- We give any topmost data inside arr[top] to local
variable int data
- Then, we set the arr[top] = NULL since we actually
remove the data
- We set back the top to top--. Example if top = 5, then
top now is 4.
- We will return the int data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-26-2048.jpg)
![Example (pop)
5
64
4
2
12
32
54
5
top = 7
int data = arr[top]
- int data = arr[7]=5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-27-2048.jpg)
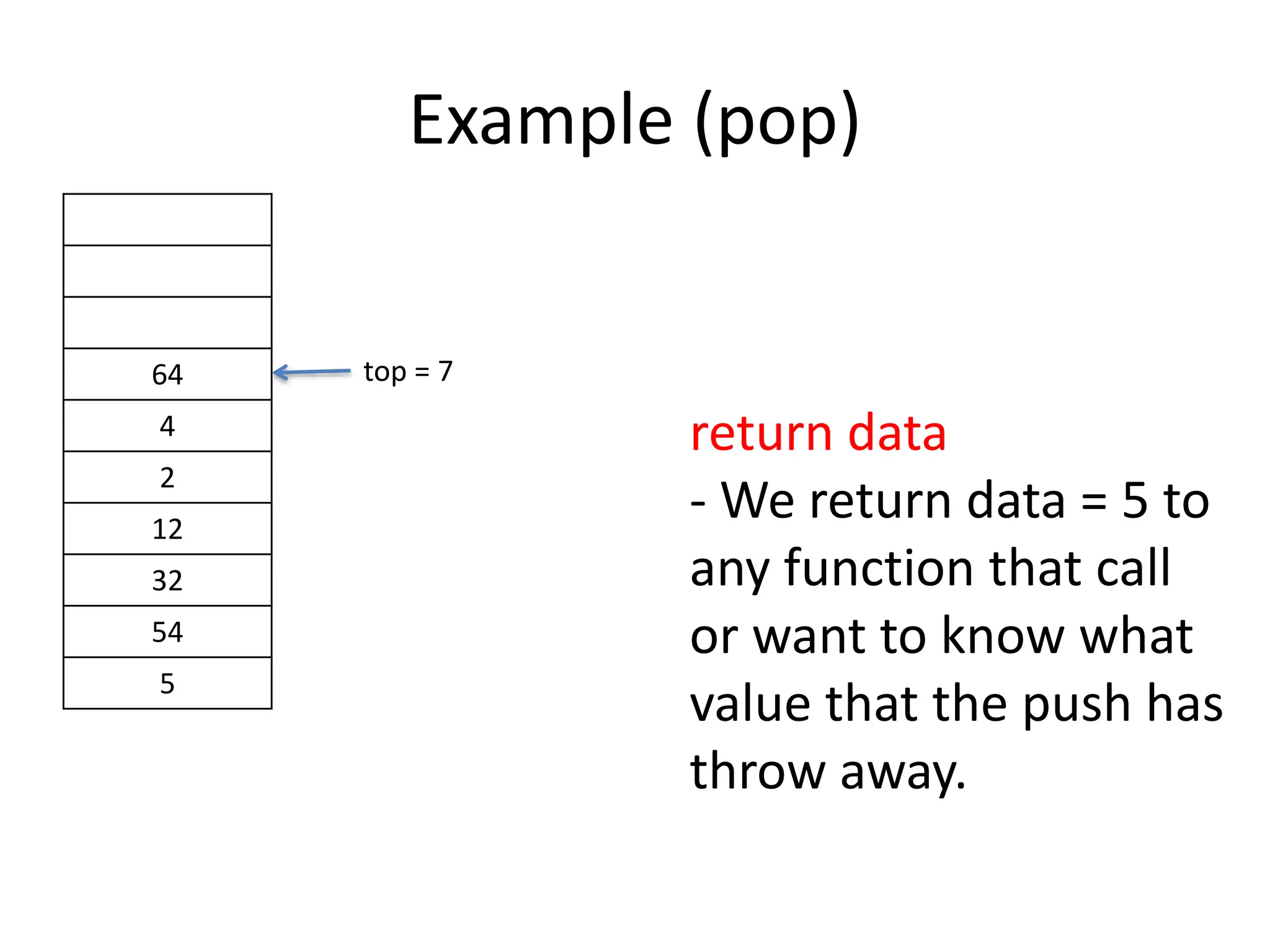
![Example (pop)
64
4
2
12
32
54
5
top = 7
arr[top]= NULL
- arr[7] = NOTHING
INSIDE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-28-2048.jpg)

![#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10 // MAXIMUM STACK CONTENT
class stack
{
private:
int arr[MAX]; // Contains all the Data
int top; //Contains location of Topmost Data pushed onto Stack
public:
stack() //Constructor
{
top=-1; //Sets the Top Location to -1 indicating an empty
stack
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-32-2048.jpg)
![void push(int a) // Push ie. Add Value Function
{
top++; // increment to by 1
if(top<MAX)
{
arr[top]=a; //If Stack is Vacant store Value in Array
}
else
{
cout<<"STACK FULL!!"<<endl;
top--;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-33-2048.jpg)
![int pop() // Delete Item. Returns the deleted
item
{
if(top==-1)
{
cout<<"STACK IS EMPTY!!!"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
else
{
int data=arr[top]; //Set Topmost Value in data
arr[top]=NULL; //Set Original Location to NULL
top--; // Decrement top by 1
return data; // Return deleted item
}
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/126508911-240704082254-c78bec01/75/12650891-1-ppthhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh-34-2048.jpg)