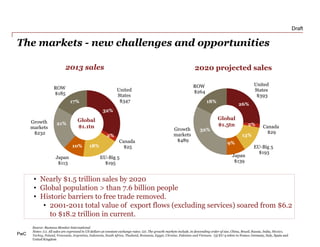
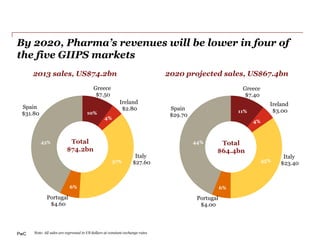
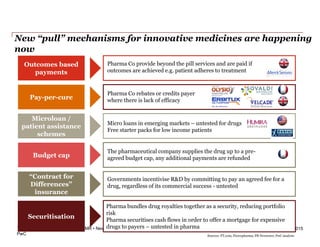
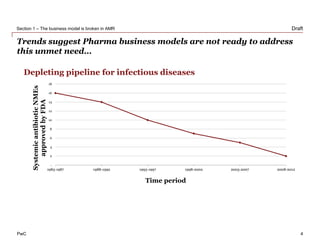
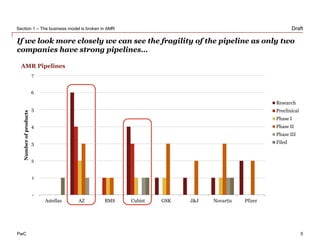
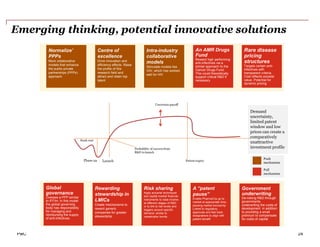
The document discusses how the current business model for developing antibiotics is broken, as evidenced by the declining antibiotic pipeline. New approaches are needed to incentivize research and development of new antibiotics given the challenges of demand uncertainty, limited patent windows, and low prices which make antibiotics an unattractive investment. Potential solutions proposed include establishing a global governance body to oversee public-private partnerships for anti-infective development and reimbursement. Other ideas involve rewarding generic companies for stewardship and applying risk sharing models and financial instruments to raise funds for antibiotic research and development.