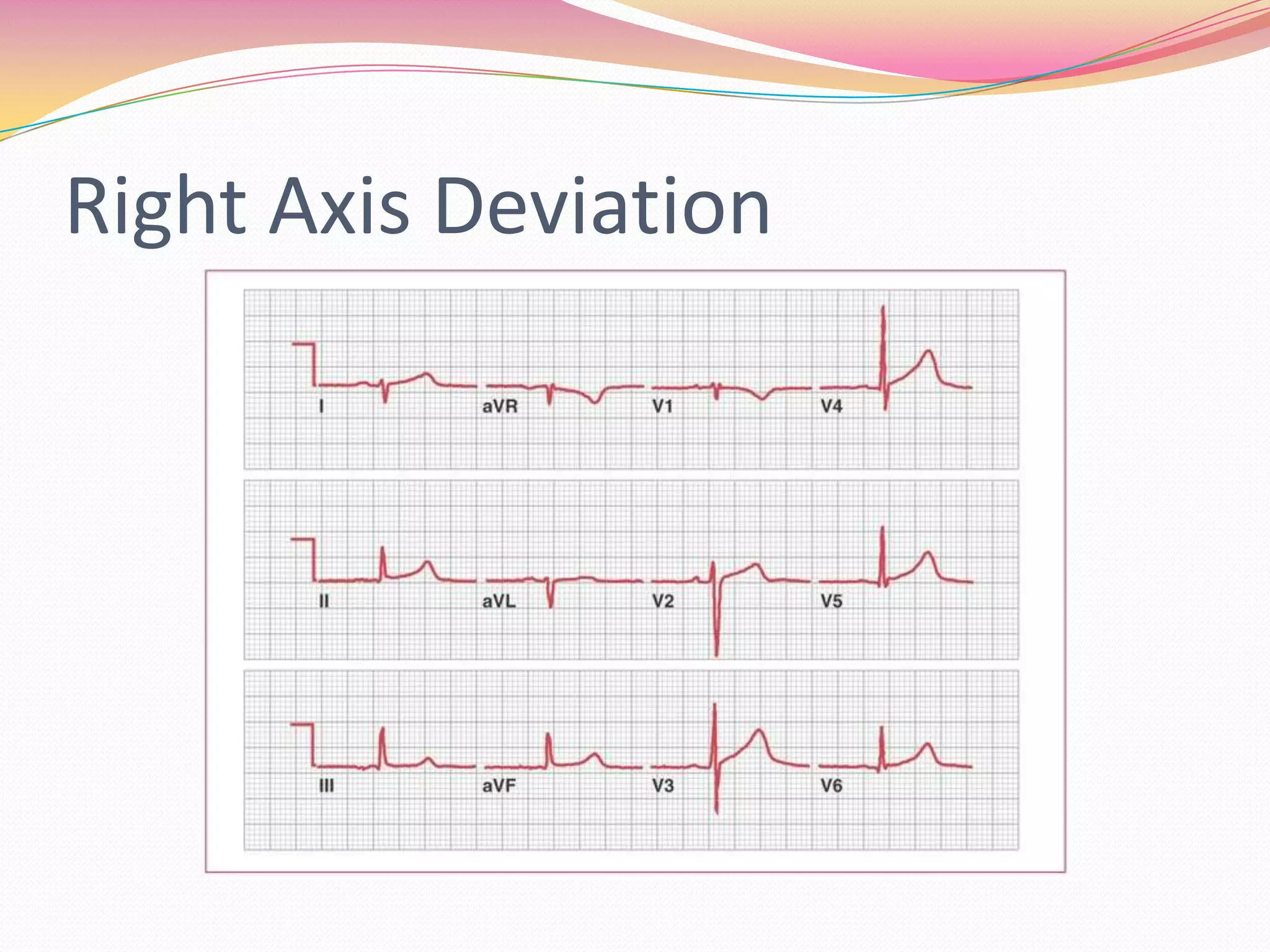
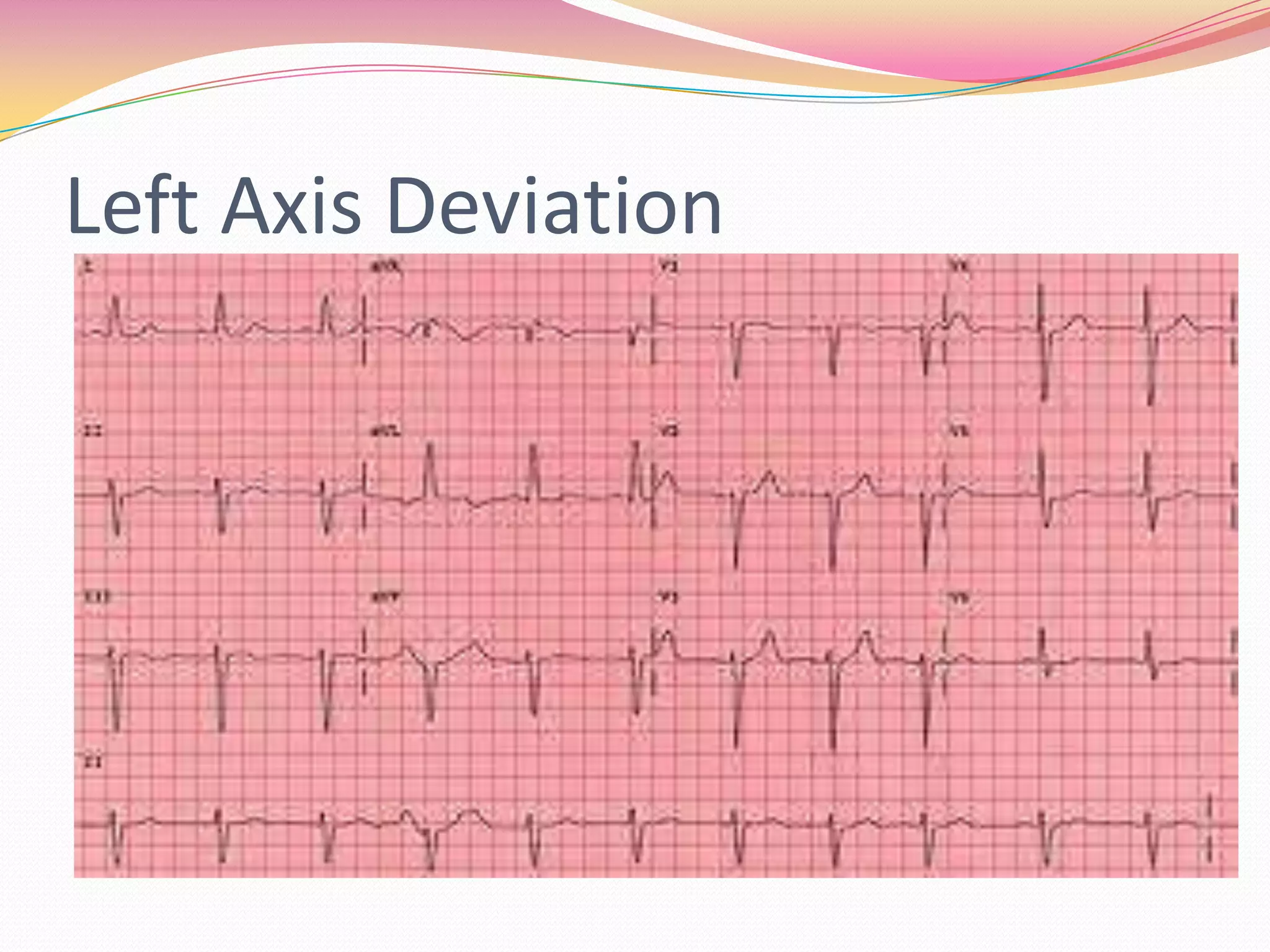
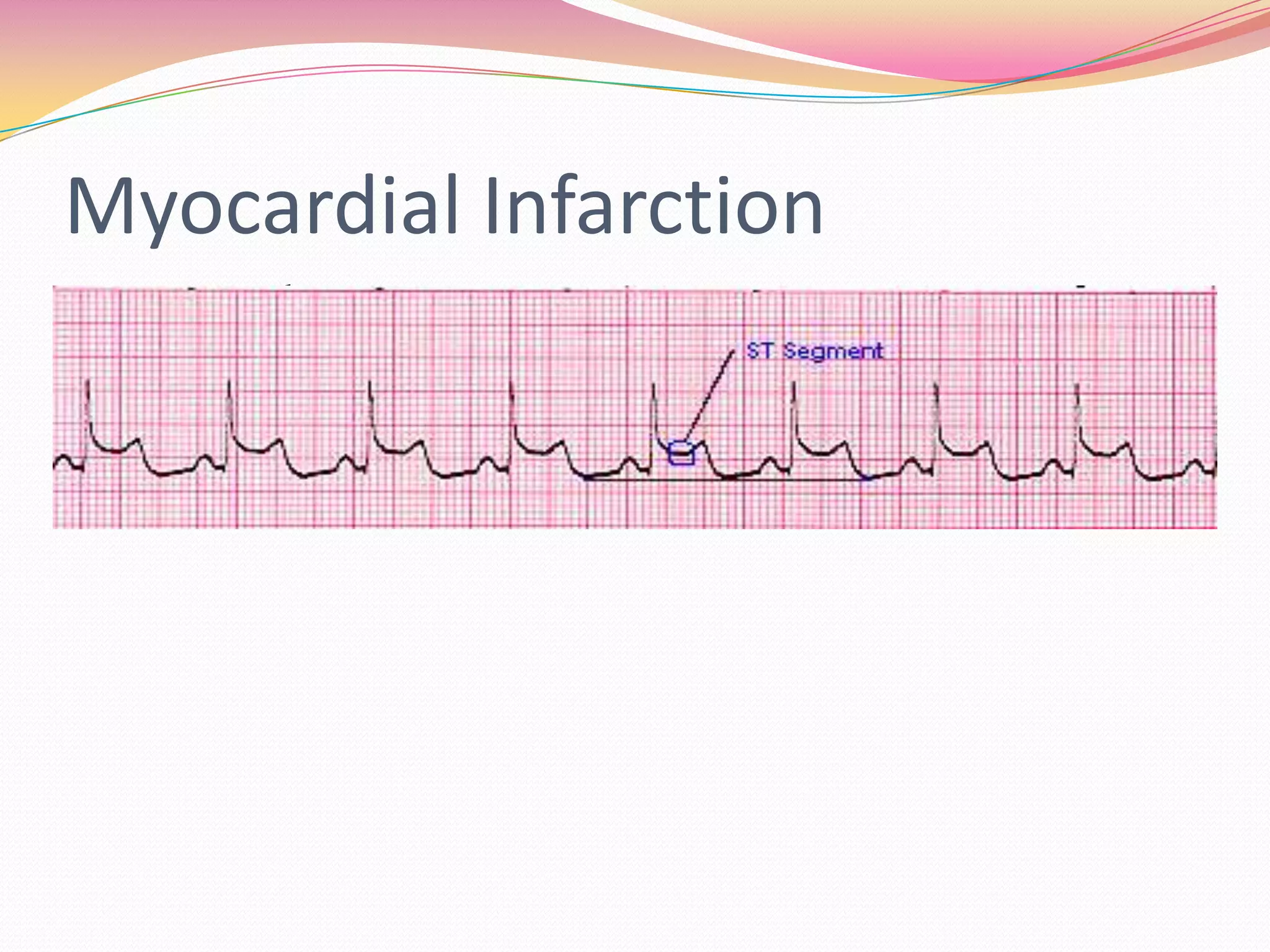
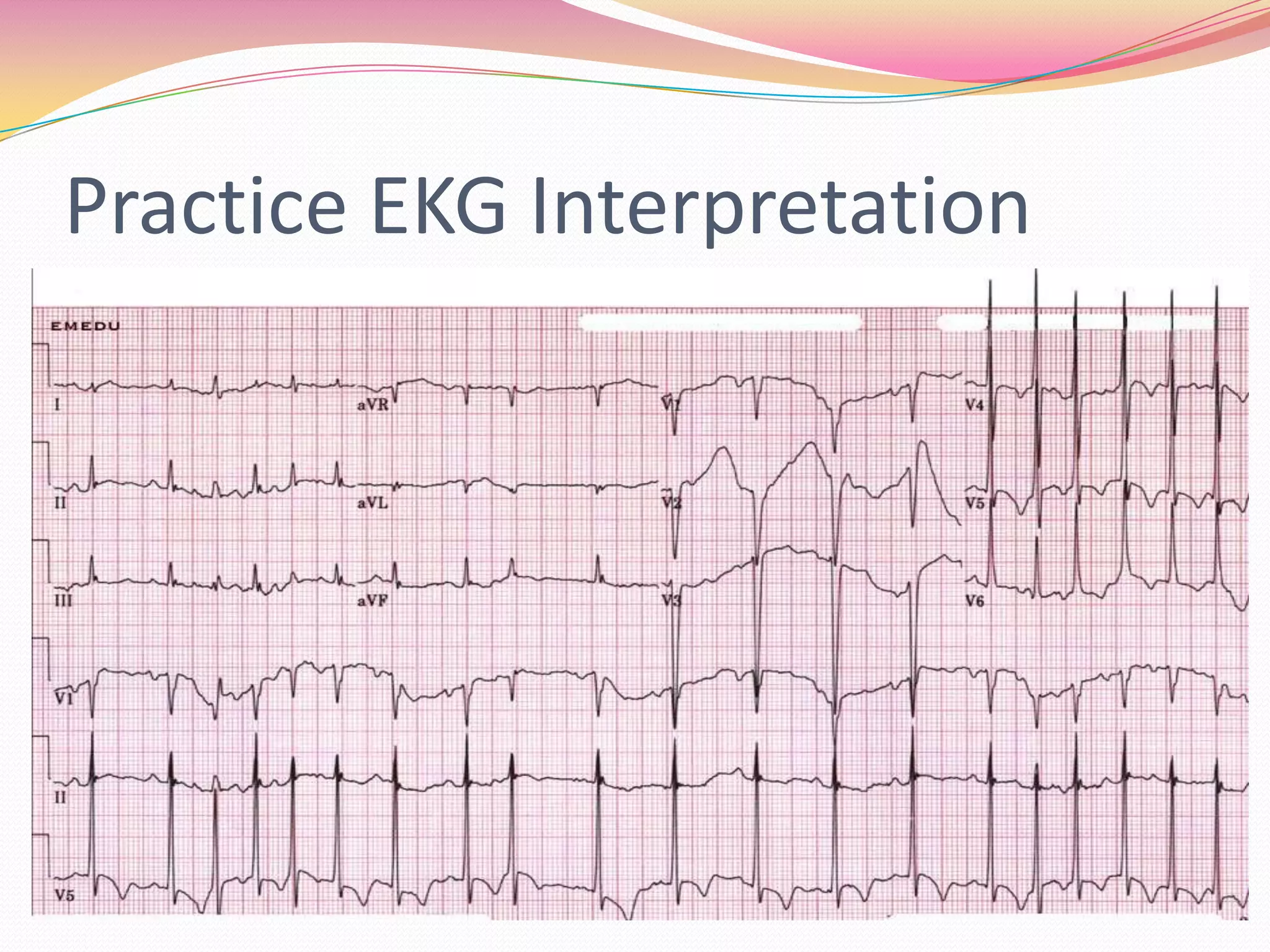
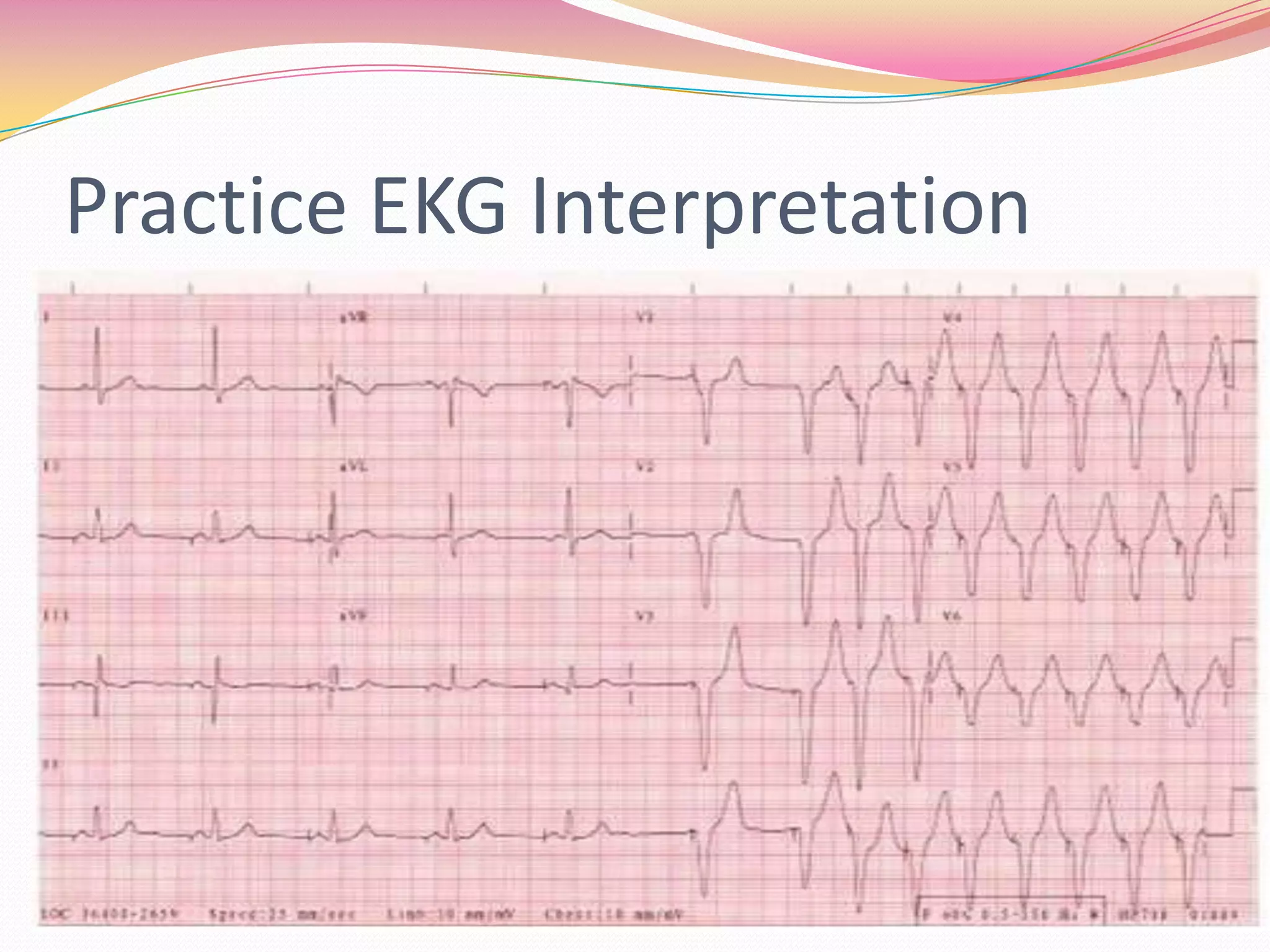
The document provides an overview of 12 lead EKG interpretation in 17 steps. It discusses evaluating the rate, rhythm, axis deviation, and signs of hypertrophy or infarction. Common rhythms reviewed include normal sinus rhythm, various arrhythmias, conduction blocks, and tachycardias. The document emphasizes interpreting location of infarction and enlargement based on EKG findings and provides examples of practice EKG interpretations.