1. The displacement method of analysis, also known as moment distribution, is an iterative technique for analyzing indeterminate structures by redistributing internal moments at joints.
2. Key concepts include member stiffness factors (K), which relate the member end moments (M) to angular displacements (θ), joint stiffness factors (KT), which are the sum of the connected member stiffness factors, and distribution factors (DF), which proportion the influence of each member on a joint based on its stiffness factor.
3. The method involves initially assuming end moments, calculating the distribution factors, and using them to calculate new end moments until the values converge within a specified tolerance. This allows determination of the internal forces throughout the structure.

![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
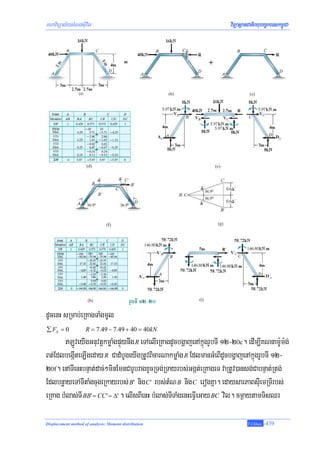
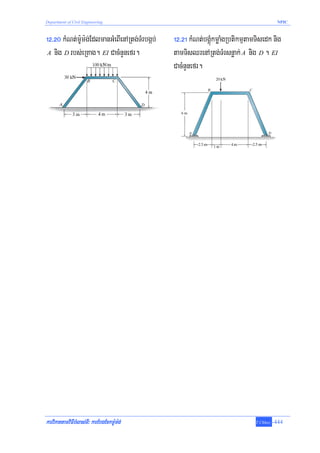
GaRs½yeTAnwgRbePTénkardak;bnÞúk. Ca]TahrN_ FñwmEdlrgbnÞúkdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-2 man
m:Um:g;bgáb;cug FEM = PL / 8 = 800(10) / 8 = 1000 N .m . eKRtUvcMNaMGMBIGMeBIrbs;m:Um:g;TaMgenHmkelI
Fñwm nigkarkMNt;sBaØarbs;eyIg dUcenHeyIgeXIjfa M AB = −1000 N .m ehIy M BA = +1000 N .
emKuNkMrajsMrab;Ggát; (member stiffness factor)³ eKmanFñwmdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-3 Edl
cugmçagRtUv)anRTedayTMrsnøak; nigmçageTotRTedayTMrbgáb;. GMeBIrbs;m:Um:g; M eFVIeGaycug A vil
)anmMurgVil θ A . enAkñúgemeronTI11 eyIg)anP¢ab;TMnak;TMngrvag M nig θ A edayeRbIviFIFñwmnimitþ Edl
M = (4 EI / L )θ A enAkñúgsmIkar 11-1. tYenAkñúgrg;Rkck
4 EI
K= (12-1)
L
cugbgáb;q¶ay
RtUv)aneKeGayeQμaHfaemKuNkMrajenARtg; A . emKuNkMrajCabrimaNénm:Um:g; M EdlcaM)ac;edIm,I
eFVIeGaycug A rbs;Fñwmvil)an θ A = 1rad .
emKuNkMrajsMrab;tMN (joint stiffness factor)³ RbsinebIGgát;CaeRcInRtUv)antP¢ab;edaytMNbgáb;
ehIycugq¶ayrbs;vaCaTMrbgán; enaHedayeKalkarN_tMrYtpl emKuNkMralsrubenARtg;tMNCaplbUkén
emKuNkMrajsMrab;Ggát;enARtg;tMN eBalKW KT = ∑ K . Ca]TahrN_ cUrBicarNatMNrbs;eRKagRtg;
A enAkñúgrUbTI 12-4a. eKkkMNt;témøCaelxrbs;emKuNkMrajsMrab;Ggát;nImYy²BIsmIkar 12-1
ehIybgðajvaenAelIrUb. edayeRbItémøTaMgenH emKuNkMrajsrubéntMN A KW KT = ∑ K = 4000 +
5000 + 1000 = 10000 . TMhMenHCabrimaNénm:Um:g;EdlRtUvkaredIm,IbgViltMNeday)anmMu 1rad .
emKuNEbgEck (Distribution factor DF)³ RbsinebIeKGnuvtþm:Um:g; M eTAelItMNbgáb; enaHGgát;
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -416](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-2-320.jpg)
![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
EdltP¢ab;eTAnwgtMNenaHnwgpþl;nUvcMENkénm:Um:g;Tb;caM)ac;edIm,IbMeBjlMnwgrbs;m:Um:g;enARtg;tMN.
cMENkénm:Um:g;Tb;srubEdlpþl;eGayedayGgát;RtUv)aneKeGayeQμaHfaemKuNEbgEck. edIm,ITTYl
)antémøTaMgenH BinitüemIltMNEdlP¢ab;eday n Ggát;. RbsinebIm:Um:g; M eFVIeGaytMNvil)an θ enaH
Ggát; i nImYy²nwgviledaybrimaNdUcKñaenH. RbsinebIemKuNkMrajrbs;Ggát;TI i Ca K i enaHm:Um:g;Edl
cUlrYmedayGgát;enaHKW M i = K iθ . edaysarsmIkarlMnwgRtUvkar M = M1 + M n = K1θ + K nθ =
θ ∑ K i enaHemKuNEbgEcksRmab;Ggát;TI i KW
Mi K iθ
DFi = =
M θ ∑ Ki
edaysRmYltY θ eyIgeXIjfaemKuNEbgEcksRmab;Ggát;esμInwgplEckénemKuNkRmajrbs;Ggát;elI
emKuNkRmajsrubsMrab;tMN EdlCaTUeTAeKsresr
K
DF = (12-2)
∑K
Ca]TahrN_ emKuNEbgEcksMrab;Ggát; AB / AC nig AD enARtg;tMN A ¬enAkñúgrUbTI 12-4a¦ KW
DFAB = 4000 / 10000 = 0.4
DFAC = 5000 / 10000 = 0.5
DFAD = 1000 / 10000 = 0.1
CalT§pl RbsinebI M = 2000 N .m eFVIGMeBIenARtg;cMNuc A ¬rUbTI 12-4b¦ m:Um:g;lMnwgEdlGnuvtþ
edayGgát;mkelItMN ¬enAkñúgrUbTI 12-4c¦ KW
M AB = 0.4(2000 ) = 800 N .m
M AC = 0.5(2000) = 1000 N .m
M AD = 0.1(2000 ) = 200 N .m
emKuNkRmajeFobrbs;Ggát; (member relative-stiffness factor)³ eBlxøH Fñwm b¤eRKagCab;RtUv
)aneFVIBIsmÖar³EtmYy dUcenHGgát;rbs;vaTaMgGs;RtUvEtmanm:UDuleGLasÞic E dUcKña. kñúgkrNIEbbenH
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -417](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-3-320.jpg)
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
eKGacminKitemKuN 4E EdlmanenAkñúgsmIkar 12-1 BIPaKykénsmIkar 12-2 enAeBlkMNt;emKuN
EbgEcksMrab;tMN. dUcenH eKmanlkçN³gayRsYledayRKan;EtkMNt;emKuNkRmajeFobrbs;Ggát;
I
KR = (12-3)
L
cugbgáb;q¶ay
ehIyeRbIvasRmab;KNnaemKuNEbgEck.
emKuNdMENl (carry-over factor)³ BicarNaFñwmenAkñúgrUbTI 12-3 mþgeTot. enAkñúgemeronTI 11
eyIgeXIjfa M AB = (4EI / L)θ A ¬smIkar 11-1¦ ehIy M BA = (2EI / L)θ A ¬smIkar 11-2¦.
edayedaHRsayrk θ A ehIydak;eGaysmIkarTaMgenHesμIKñaeyIg)an M BA = M AB / 2 . eyIgGac
niyayfa m:Um:g; M enARtg;TMrsnøak;eFVIeGaymanm:Um:g; M ' = M / 2 enARtg;CBa¢aMg. emKuNdMENlCa
cMENkén M EdlRtUv)anepÞrBIsnøak;eTACBa¢aMg. dUcenH enAkñúgkrNIrbs;FñwmEdlmancugq¶ayCaTMrbgáb;
emKuNdMENlKW + 1 / 2 . sBaØabUkmann½yfam:Um:g;TaMgBIreFVIkarkñúgTisedAdUcKña.
!@>@> karEbgEckm:Um:g;sRmab;Fñwm (Moment distribution for beams)
karEbkEckm:Um:g;KWQrelIeKalkarN_Rsay nigTb;tMNrbs;rcnasm<½n§bnþbnÞab;KñaedIm,IGnuBaØat
eGaymankarEbgEckm:Um:g; nigeFVIeGaym:Um:g;mantulüPaBenARtg;tMN. meFüa)ayd¾l¥kñúgkarBnül;viFI
KWkarBnül;edayeRbI]TahrN_.
eKmanFñwmmYyEdlmanm:UDuleGLasÞic E efr nigmanTMhM nigbnÞúkdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-6a.
munnwgeyIgcab;epþIm dMbUgeyIgRtUvKNnaemKuNEbgEckenARtg;cugTaMgBIrrbs;ElVgnImYy².
edayeRbIsmIkar 12-1 ¬ K = 4EI / L ¦ emKuNkRmajenAEpñksgxagrbs; B KW
4 E (120)( 6 )
= 4 E (40)( 6 )mm 4 / m
10
K BA = 10
3
4 E (240 )(10 6 )
K BC = = 4 E (60)(106 )mm 4 / m
4
dUcenH edayeRbIsmIkar 12-2 DF = K / ∑ K sRmab;cugEdltP¢ab;eTAniwgtMN B eyIg)an
4 E (40)
DFBA = = 0.4
4 E (40) + 4 E (60 )
4 E (60)
DFBC = = 0.6
4 E (40 ) + 4 E (60)
enARtg;CBa¢aMg ¬tMN A nigtMN C ¦ emKuNEbgEckGaRs½ynwgemKuNkRmajrbs;Ggát; nigemKuN
kRmajrbs;CBa¢aMg. edaysarenAkñúgRTwsþI eKRtUvkarm:Um:g;EdlmanTMhMGnnþedIm,IbgVilCBa¢aMgeGay)an
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -418](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-4-320.jpg)
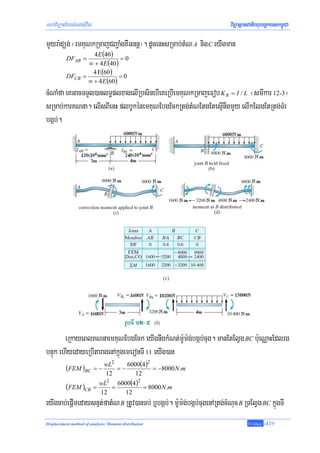
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
taMgbgáb; b¤TItaMgTb;dUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-5b. CakarBit enHvaminEmnCasßanPaBlMnwgCak;EsþgenA
Rtg;tMN B edaysarm:Um:g;enAelIEpñknImYy²rbs;tMNenHRtUvEtesμIKña nigmanTisedApÞúyKña. edIm,IEk
sMrYlva eyIgRtUvGnuvtþm:Um:g; 8000 N.m EdlmanTisedApÞúyKñaeTAelItMN nigGnuBaØateGaytMNvileday
esrI ¬rUbTI 12-5c¦. CalT§pl Epñkénm:Um:g;enHRtUv)anEbgEckeTAElVg BC nig BA edayeKarBtam
emKuNEbgEck ¬b¤emKuNkRmaj¦ rbs;ElVgenARtg;tMN. m:Um:g;enAkñúg BA KW 0.4(8000) = 3200 N.m
ehIym:Um:g;enAkñúg BC KW 0.6(8000) = 4800 N.m . cugeRkay edaysarkarvilEdlekItmanenARtg; B
m:Um:g;enHRtUv)anepÞr edaysarm:Um:g;EdlekItmanenARtg;cugq¶ayrbs;ElVg. edayeRbIemKuNdMENl
+ 1 / 2 enaHlT§plRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-5d.
]TahrN_enHbgðajfaCMhandMbUgEdlcaM)ac;enAeBlEbgEckm:Um:g;enARtg;tMNKW³ kMNt;m:Um:g;
GtulüPaBEdlmanGMeBIenARtg;tMNEdlbgáb;dMbUg/ RsayPaBbgáb;rbs;tMNenaH/ rYcGnuvtþm:Um:g;
GtulüPaBEdlmanTMhMesμIKña EtTisedApÞúyKñaedIm,IEktRmUvlMnwg/ EbgEckm:Um:g;kñúgcMeNamElVgEdlt
P¢ab;/ ehIyepÞrm:Um:g;kñúgElVgrbs;vaeTAcugmçageTot. CaTUeTA CMhanTaMgenHRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgtarag
¬rUbTI 12-5e¦. enATIenH Dist, CO bgðajfam:Um:g;RtUv)anEbgEck nigepÞr. enAkñúgkrNIBiessenH eK
RtUvkareFVIkarEbgEckm:Um:g;EtmYyCMub:ueNÑaH edaysarCBa¢aMgenARtg; A nig C RsUbykm:Um:g; ehIymin
mantMNq¶ayÉNaeTotEdleKRtUveFVIeGaymantulüPaB b¤RsaykarTb;edIm,IbMeBjlkçxNÐlMnwgrbs;
tMNeT. eRkayeBlEbgEcktamrebobenH eKeFVIplbUkm:Um:g;Rtg;tMNnImYy²EdleFVIeGayeKTTYl)an
lT§plcugeRkayEdlbgðajenAkñúgbnÞat;xageRkamrbs;taragénrUbTI 12-5e. cMNaMfa LÚvtMN B
sßitkñúgsßanPaBlMnwg. edaysar M BC GviC¢man enaHm:Um:g;enHmanGMeBIelIElVg BC RcasRTnicnaLika
dUcbgðajenAelIdüaRkamGgÁesrIrbs;ElVgFñwmenAkñúgrUbTI 12-5f. edaysareyIgsÁal;m:Um:g;cug eyIg
GacKNnakmøaMgkat;enAxagcugrbs;Ggát;BIsmIkarlMnwgedayGnuvtþeTAelIElVgnImYy².
LÚvBicarNaFñwmdUcKña EtTMr C CaTMrkl; ¬rUbTI 12-6a¦. enAkñúgkrNIenHmanEtGgát;mYyenA
Rtg;tMN C dUcenHemKuNEbgEcksRmab;Ggát; CB enARtg;tMN C KW
4 E (60)
DFCB = =1
4 E (60)
emKuNEbgEckepSgeTot nigm:Um:g;bgáb;cugdUcKñanwgkarKNnaelIkmun. BYkvaRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgCYr
edkTI1 nigTI2éntaragenAkñúgrUbTI 12-6b. CadMbUg eyIgnwg]bmafatMN B nigtMN C RtUv)anTb;.
eyIgcab;epþImedayRsaytMN C nigedaydak;m:Um:g; − 8000 N.m enARtg;tMNenaH. m:Um:g;TaMgmUlRtUv)an
EbgEckeTAkñúgGgát; CB edaysar (1)(− 8000)N .m = −8000 N .m . sBaØaRBYjenARtg;CYredkTI3bgðaj
fa (− 8000)N .m / 2 = −4000 N .m RtUv)anepÞreTAtMN B edaysareKGnuBaØateGaytMN C vileday
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -420](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-6-320.jpg)

![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
edayRsaytMN B nigtMN C kñúgeBldMNalKña ¬tMN A RtUv)anbgáb;rhUt¦ bnÞab;mkm:Um:g;RtUv)anepÞr
eTAcugénElVgnImYy² ¬CYredkTI4¦. tMNRtUv)anTb;mþgeTot ehIym:Um:g;RtUv)anEbgEck nigeFVIeGay
manlMnwg ¬CYredkTI 5¦. karRsaytMNenHmþgeTotGnuBaØateGaymankarepÞrm:Um:g; dUcbgðajenAkñúgCYr
edkTI 6. edaykarKNnaCabnþbnÞab; eyIgTTYl)anlT§plcugeRkay ¬dUckarKNnaelIkmun¦ Edl
bgðajenAkñúgCYredkTI 24. edayeFVIkareRbobeFob viFIenHpþl;nUvcemøIyrYmtUcyWtCagviFIelIkmun b:uEnþ
enAkñúgkrNICaeRcInviFIenHmanRbsiT§PaBkñúgkarGnuvtþCag ehIysMrab;ehtuplEbbenHeyIgnwgeRbIvaenA
kñúg]TahrN_bnþbnÞab;. cugeRkayedayeRbIlT§plenAkñúgrUbTI 12-6b b¤ 12-6c, düaRkamGgÁesrI
rbs;ElVgFñwmnImYy²RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-6d.
eTaHbICa viFIenHBak;B½n§nwgCMhanCaeRcInedIm,ITTYl)anlT§plcugeRkay. viFIenHk¾TamTarnUvviFI
saRsþEdr edaysarvaRtUvkarkarGnuvtþnUves‘rIénCMhanEdlmanlkçN³nBVnþCaCagkaredaHRsaysMnMuén
smIkardUcenAkñúgviFI slope-deflection. b:uEnþ eKRtUvcMNaMfa dMeNIrkarCamUldæanénkarEbgEckm:Um:g;
GnuvtþdUcnwgdMeNIrkarénviFIbMlas;TIdéTeTotEdr. dMeNIrkarKwkarbegáItTMnak;TMngrvagbnÞúk nigbMlas;TI
edaykMNt;nUvbMlas;TImMud¾RtwmRtUvsMrab;tMN ¬lkçxNÐRtUvKña¦. b:uEnþ enATIenH lkçxNÐlMnwg niglkç-
xNÐRtUvKñarbs;mMurgVilenARtg;tMNRtUv)anbMeBjedaypÞal;edayeRbIdMeNIrkarEdleFVIeGaym:Um:g;man
tulüPaBEdlcUlrYmCamYynwgTMnak;TMngrvagbnÞúk nigPaBdab ¬emKuNkRmaj¦. eKmanlT§PaBkñúgkar
sRmYlbnþeTotkñúgkareRbIR)as;karEbgEckm:Um:g;EdleyIgnwgelIkylmkerobrab;enAkñúgkfaxNÐxag
mux.
dMeNIrkarkñúgkarviPaK (Procedure for analysis)
xageRkamCaCMhanEdlpþl;nUvviFITUeTAsRmab;kMNt;m:Um:g;cugenAelIElVgFñwmEdleRbIkarEbgEck
m:Um:g;.
emKuNEbgEck nigm:Um:g;bgáb;cug³ eKRtUvkMNt;emKuNkRmajsRmab;ElVgnImYy²enARtg;tMN.
edayeRbItémøTaMgenH eyIgGacKNnaemKuNEbgEckBI DF = K / ∑ K . cMNaMfa DF = 0 sRmab;cug
bgáb; ehIy DF = 1 sMrab;TMrsnøak; b¤TMrkl;.
eyIgkMNt;mU:m:g;bgáb;cugsMrab;ElVgEdlrgbnÞúknImYy²edayeRbItaragEdleGayenAkñúgemeron
TI11. m:Um:g;bgáb;cugviC¢maneFVIGMeBIRsbTisRTnicnaLikavil ehIy FEM GviC¢maneFVIGMeBIRcasRTnic
naLika. edIm,IPaBgayRsYl eKGacerobcMtémøTaMgenHenAkñúgtaragEdlmanlkçN³dUctaragEdl
bgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-6c.
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -422](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-8-320.jpg)
![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
dMeNIrkarEbgEckm:Um:g;³ snμt;fatMNTaMgGs;EdleyIgRtUvkarkMNt;m:Um:g;enAkñúgElVgEdltP¢ab;RtUv
)anTb;. bnÞab;mk
!> kMNt;m:Um:g;EdleFVIeGaytMNnImYy²manlMnwg.
@> RsaytMN ehIyEbgEckm:Um:g;GtulüPaBeTAeGayElVgEdltP¢ab;nwgtMNnImYy².
#> epÞrm:Um:g;enAkñúgElVgnImYy²eTAkan;cugnImYy²rbs;vaedayKuNm:Um:g;TaMgenaHedayemKuN
dMENl (carry-over moment) + 1/ 2 .
edaykarTb; nigkarRsaytMNsarcuHsareLIg eyIgeXIjfakarEktMrUvm:Um:g;RtUv)ankat;bnßy
edaysarFñwmGacQaneTArkrUbragdabcugeRkay. enAeBlEdleyIgTTYl)antémøsMrab;karEktRmUvtUc
lμm eKRtUvbBaÄb;dMeNIrkarsarcuHsareLIgRtg;karepÞrm:Um:g;cugeRkayeK. eKRtUvbUkbBa©ÚlKñanUvtémø
FEM / m:Um:g;Edl)anBIkarEbgEck nigm:Um:g;Edl)anBIkarepÞrtamCYrQrnImYy². RbsinebIeyIgeFVIEbb
enH)anRtwmRtUv eyIgnwgTTYl)ansßanPaBlMnwgénm:Um:g;Rtg;tMNnImYy².
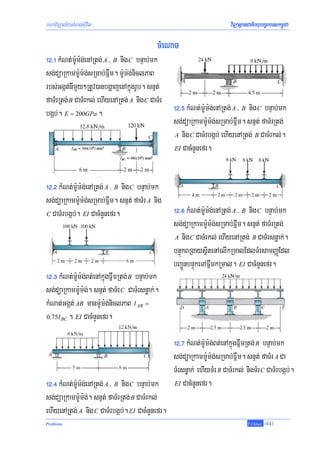
]TahrN_ 12-1³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;tMNnImYy²rbs;FñwmEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-7a. EI Ca
cMnYnefr.
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -423](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-9-320.jpg)
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
dMeNaHRsay³ dMbUg eKRtUvkMNt;emKuNEbgEckenARtg;tMNnImYy². emKuNkRmajsMrab;Ggát;KW *
4EI 4EI 4EI
K AB = K BC = K CD =
12 12 8
dUcenH DFAB = DFDC = 0 DFBA = DFBC =
4 EI / 12
4 EI / 12 + 4 EI / 8
= 0.5
4 EI / 12 4 EI / 8
DFCB = = 0.4 DFCD = = 0.6
4 EI / 12 + 4 EI / 8 4 EI / 12 + 4 EI / 8
m:Um:g;bgáb;cugKW
wL2 20(12 )2
(FEM )BC =− =− = −240kN .m
12 12
2
20(12 )2
(FEM )CB = wL = = 240kN .m
12 12
− PL 250(8)
(FEM )CD = =− = −250kN .m
8 8
PL 250(8)
(FEM )DC = = = 250kN .m
8 8
edaycab;epþImCamYynwg FEM CYredkTI4 ¬rUbTI 12-7b¦ m:Um:g;enARtg;tMN B nig C RtUv)anEbgEck
kñúgeBlEtmYy ¬CYredkTI5¦. bnÞab;mk m:Um:g;TaMgenHRtUv)anepÞreTAcugénElVgerog²xøÜn ¬CYredkTI6¦.
m:Um:g;EdlTTYl)anRtUv)anEbgEck nigepÞrkñúgeBlEtmYymþgeTot ¬CYredkTI 7 nigTI8¦. dMeNIrkarRtUv
)anbnþrhUtdl;m:Um:g;RtUv)ankat;bnßyrhUtdl;TMhMmYysmrmü ¬CYredkTI 13¦. m:Um:g;EdlCalT§pl
RtUv)ankMNt;edayeFVIplbUk ¬CYredkTI14¦.
edaydak;m:Um:g;enAelIFñwmnImYy² nigedayGnuvtþsmIkarlMnwgeyIgTTYl)ankmøaMgkat;enAxagcug
ElVgdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-7c ehIydüaRkamm:Um:g;sMrab;FñwmTaMgmUlRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-
7d.
]TahrN_ 12-2³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;TMrnImYy²rbs;FñwmEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-8a. m:Um:g;
niclPaBénElVgnImYy²RtUv)an.
dMeNaHRsay³ enAkñúgcMeNaTenH m:Um:g;mnRtUv)anEbgEckenAkñúgElVgly AB eT dUcenHemKuNEbg
i
Eck (DF )BA = 0 . kRmajrbs;ElVg BC KWEp¥kelI 4EI / L edaysarTMrsnøak;minEmnsßitenAcugq¶ay
rbs;Fñwm. emKuNkRmaj emKuNEbgEck nigm:Um:g;bgáb;cugRtUv)anKNnadUcxageRkam³
4 E (300)(106 ) 4 E (240)( 6 )
= 300(106 )E = 320( 6 )E
10
K BC = K CD = 10
4 3
*
enATIenH eyIgeRbIemKuNkRmah 4EI / L b:uEnþeyIgk¾GaceRbIemKuNkRmajeFob I / L pgEdr.
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -424](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-10-320.jpg)
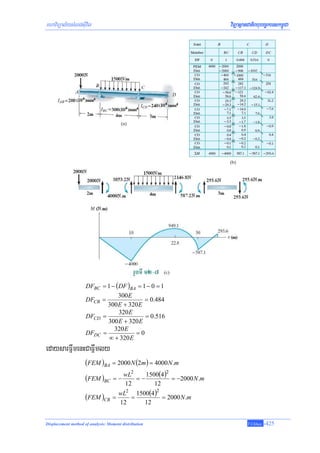
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
témøTaMgenHRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgCYredkTI4rbs;taragkñúgrUbTI 12-8b. ElVgEdllyeFVIeGayekItman
m:Um:g;Bt; − 4000 N.m enAxageqVg B . edIm,IeFVIeGaytMN B mantulüPaB eKRtUvmanm:Um:g;Bt; − 4000 N.m
manGMeBIenAxagsþaM B . dUcbgðajenAkñúgCYredkTI 5 eKRtUvbEnßm − 2000 N.m eTAelI BC edIm,IbMeBj
lkçxNÐ. dMeNIrkarénkarEbgEck nigkarepÞrm:Um:g;RtUv)anbnþtamrebobFmμtadUcbgðaj.
edaysareKsÁal;m:Um:g;Bt; eKGacsg;düaRkamm:Um:g;sRmab;FñwmdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-8c.
!@>#> karEktRmUvemKuNkRmaj (Stiffness-factor modification)
enAkñúg]TarhrN_énkarEbgEckm:Um:g;elIkmun eyIg)anBicarNaElVgénFñwmnImYy²manTMrbgáb;
¬tMNRtUv)anTb;¦ enAxagcugq¶ayrbs;vaenAeBl
EbgEck nigepÞrm:Um:g;. sRmab;ehtuplenH eyIg
)anKNnaemKuNkRmaj emKuNEbgEck nigem
KuNdMENledayQrenAelIkrNIdUcbgðajenAkñúg
rUbTI 12-9. Cak;Esþg enATIenHemKuNkRmajKW
K = 4 EI / L ¬smIkar 12-1¦ ehIyemKuNdMENlKW + 1 / 2 .
enAkñúgkrNIxøH eKmanlT§PaBEkERbemKuNkRmajrbs;ElVgFñwmBiess ehtudUcenHeKGacsMrYl
dl;dMeNIrkarEbgEckm:Um:g;. eyIgnwgBicarNakrNIbIEdlekIteLIgjwkjab;enAkñúgkarGnuvtþ.
Ggát;EdlmanTMrsnøak;enAcugq¶ay³ FñwmminkMNt;xøHmanElVgxageRkAeKbMputRTedayTMrsnøak;dUcenA
kñúgkrNIéntMN B enAkñúgrUbTI 12-10a. enATIenH m:Um:g; M bgVilcug A )an θ . edIm,IkMNt; θ eKRtUv
kMNt;kmøaMgkat;enARtg;cMNuc A' énFñwmnimitþ ¬rUbTI 12-10b¦. eyIgman
1⎛ M ⎞ ⎛2 ⎞
+ ∑ M B' = 0 V A ' ( L ) − ⎜ ⎟ L⎜ L ⎟ = 0
2 ⎝ EI ⎠ ⎝ 3 ⎠
ML
V A' = θ =
3EI
b¤ M =
3EI
L
θ
dUcenH emKuNkRmajsRmab;FñwmenHKW
3EI
K= (12-4)
L
cugq¶ayCaTMrsnøak; b¤TMrkl;
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -426](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-12-320.jpg)
![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
ehIy eKRtUvcgcaMfaemKuNdMENlKWsUnü edaysarsnøak;enARtg; A' minTb;Tl;m:Um:g;eT. tamkar
eRbobeFob RbsinebIcugq¶ayCaTMrbgáb;eKRtUvEktRmUvemKuNkRmaj K = 4EI / L eday 3 / 4 edIm,I
eGayeTACakrNIEdlmancugq¶ayRTedayTMrsnøak;. RbsinebIeKKitkarEktRmUvenH dMeNIrkarénkar
EbgEckm:Um:g;RtUv)ansRmYledaysareKminRtUvkarTb; nigRsayvaCabnþbnÞab;enAeBlEbgEckm:Um:g;eT.
ehIyedaysarEtcugElVgRtUv)anRTedayTMrsnøak; eKkMNt;m:Um:g;bgáb;cugsMrab;ElVgedayeRbItémøenA
kñúgCYrQrxagsþaMéntaragenAkñúgemeronTI11. ]TahrN_ 12-4 bgðajBIrebobGnuvtþkarsRmYlenH.
FñwmsIuemRTIrgbnÞúksIuemRTI³ RbsinebIFñwmmanragsIuemRTI ehIyrgbnÞúksIuemRTI düaRkamm:Um:g;Bt;
sRmab;Fñwmk¾nwgmanlkçN³sIuemRTIEdr. CalT§pl eKGaceFVIkarEktRmUvemKuNkRmajsRmab;ElVg
kNþal dUcenHeKRtUvkarEbgEckm:Um:g;enAkñúgFñwmtamry³tMNEdlsßitenAelIFñwmEtBak;kNþal. edIm,I
EktRmUvemKuNkRmajeGay)anRtwmRtUv eyIgnwgBicarNaFñwmEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-11a. eday
sarPaBsIuemRTI m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg; B nig C RtUvEtesμIKña. edaysnμt;témøenHesμInwg M FñwmnimitþsMrab;
ElVg BC RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-11b. dUcenH mMurgVil θ enARtg;cugnImYy²KW
⎛ M ⎞ ⎛L⎞
+ ∑ M C' = 0 − V B ' ( L ) + ⎜ ⎟ L⎜ ⎟ = 0
⎝ EI ⎠ ⎝ 2 ⎠
ML
VB ' = θ =
2 EI
b¤ M =
2 EI
L
θ
dUcenH emKuNkRmajsRmab;ElVgkNþalKW
2 EI
K= (12-5)
L
FñwmsIuemRTI nigrgbnÞúksIuemRTI
dUcenH eKGacEbgEckm:Um:g;sRmab;EtBak;kNþalFñwmRbsinebIeKKNnaemKuNkRmajsMrab;ElVgkNþal
edayeRbIsmIkar 12-5. tamkareRbobeFob emKuNkRmajkNþalElVgesμInwgBak;kNþalénemKuN
kRmajEdleRbI K = 4EI / L .
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -427](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-13-320.jpg)

![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
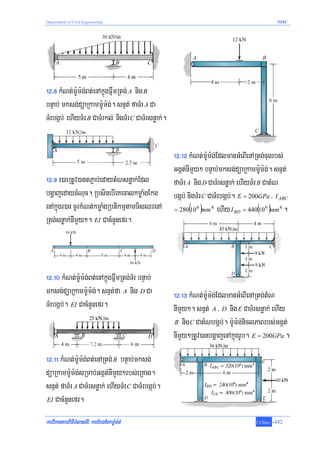
]TahrN_ 12-3³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;TMrsRmab;FñwmEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-13a. EI CacMnYn
efr.
dMeNaHRsay³ tamkarGegát Fñwm nigbnÞúkmanlkçN³sIuemRTI. dUcenH eyIgnwgGnuvtþ K = 2EI / L
edIm,IKNnaemKuNkRmajrbs;ElVgkNþal BC ehIyeyIgnwgviPaKEtkMNat;Bak;kNþalxageqVgrbs;
FñwmEtb:ueNÑaH. eKGackat;bnßykarviPaKeGaykat;EtxøIEfmeTotedayeRbI K = 3EI / L sRmab;kar
KNnaemKuNkRmajsMrab;kMNat;Ggát; AB edaysarcugq¶ay A CaTMrsnøak;. elIsBIenH eKGacrMlg
karEbgEckm:Um:g;enARtg;cMNuc A edayeRbIm:Um:g;bgáb;cugsRmab;bnÞúkragRtIekaNmanGMeBIelIElVgEdl
manTMrmçagCaTMrsnøak; nigTMrmçageTotCaTMgbgáb;. dUcenH
K AB =
3EI
3
¬edayeRbIsmIkar 12-4¦
K BC =
2EI
4
¬edayeRbIsmIkar 12-5¦
3EI / 3
DFAB = =1
3EI / 3
3EI / 3
DFBA = = 0.667
3EI / 3 + 2 EI / 4
2 EI / 4
DFBC = = 0.333
3EI / 3 + 2 EI / 4
2
100(3)2
(FEM )BA = wL = = 60kN .m
15 15
2
100(4 )2
(FEM )BC = − wL =− = −133.3kN .m
12 12
TIinñn½yTaMgenHRtUv)anerobcMenAkñúgtarageénrUbTI 12-13b. karKNnaemKuNkRmajdUcbgðajxagelI
BitCakat;bnßykarviPaKy:ageRcIn edaysarmanEttMN B EtmYybueNÑaHEdleKRtUvkareFVIeGayman
lMnwg ehIyeKminRtUvkarepÞrm:Um:g;eTAtMN A nigtMN C eT. eyIgeXIjfatMN C rgm:Um:g; 108.9kN.m
dUctMN B Edr.
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -429](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-15-320.jpg)
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
]TahrN_ 12-4³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;TMrsRmab;FñwmEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-14a. m:Um:g;nicl
PaBrbs;ElVgTaMgBIrRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUb.
dMeNaHRsay³ edaysarFñwmRtUv)anRTedayTMrkl;enAcugq¶ay C kRmajrbs;ElVg BC RtUv)anKNna
edayQrelI K = 3EI / L . eyIg)an
K AB = =
( )
4 EI 4 E (120) 10 6
( )
= 160 10 6 E
L 3
K BC =
3EI 3E (240) 106
=
( ) ( )
= 180 106 E
L 4
dUcenH DFAB =
160 E
∞ + 160 E
=0
160 E
DFBA = = 0.4706
160 E + 180 E
180 E
DFBC = = 0.5294
160 E + 180 E
180 E
DFCB = =1
180 E
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -430](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-16-320.jpg)
![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
eKGacsRmYlviFIEbgEckm:Um:g;sRmab;cMeNaTenHedayRtUvdwgfaeKGaceRbIm:Um:g;bgáb;cugeTalsRmab;
ElVg BC . edayeRbICYrxagsþaMéntaragénemeronTI11 sMrab;ElVgEdlrgbnÞúkrayesμImanTMrmçagCaTMr
bgáb; nigmçageTotCaTMrsnøak; enaHeyIg)an
wL2 6000(4 )2
(FEM )BC =− =− = −12000 N .m
8 8
Tinñn½yTaMgGs;RtUv)anbBa©ÚleTAkñúgtaragenAkñúgrUbTI 12-14b ehIykarEbgEckm:Um:g;RtUv)an
Gnuvtþ. edayeRbobeFobCamYynwgrUbTI 12-6b viFIenHBitCasRmYldl;karEbgEcky:agxøaMg.
edayeRbIlT§plEdlTTYl)an kmøaMgkat;xagcugrbs;Fñwm nigdüaRkamm:Um:g;RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúg
rUbTI 12-14c.
!@>$> karEbgEckm:Um:g;sMrab;eRKagmineyal
(Moment distribution for frames: No sidesway)
karGnuvtþénviFIEbgEckm:Um:g;sRmab;eRKagEdlmineyalmanlkçN³dUcnwgdMeNIrkarsRmab;
viPaKFñwm. edIm,Ikat;bnßy»kasénkMhusqÁg eKENnaMeGayeFVIkarviPaKedayeRbItaragdUcenAkñúg
]TahrN_elIkmun. ehIyeKGackat;bnßykarEbgEckm:Um:g; RbsinebIeKEktRmUvemKuNkRmajdUc
bgðajenAkñúgkfaxNÐmun.
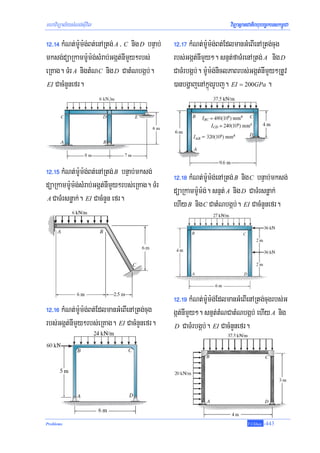
]TahrN_ 12-5³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;tMNéneRKagEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-15a. eKmanTMr
snøak;enARtg; E nig D nigmanTMrbgáb;enARtg; A . EI CacMnYnefr.
dMeNaHRsay³ tamkarGegát snøak;enARtg; E nigkarBareRKagkMueGayeyal. eKGacKNnaemKuN
kRmajrbs; CD nig CE edayeRbI K = 3EI / L edaysarcugq¶ayCaTMrsnøak;. ehIy bnÞúk 60kN min
)abbegáItm:Um:g;bgáb;cugeT edaysarvaGnuvtþenARtg;cMN B . dUcenH
4EI 4EI 3EI 3EI
K AB = K BC = K CD = K CE =
5 6 5 4
DFAB = 0
4 EI / 5
DFBA = = 0.545
4 EI / 5 + 4 EI / 6
DFBC = 1 − 0.545 = 0.455
4 EI / L
DFCB = = 0.330
4 EI / 6 + 3EI / 5 + 3EI / 4
3EI / 5
DFCD = = 0.298
4 EI / 6 + 3EI / 5 + 3EI / 4
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -431](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-17-320.jpg)
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
DFCE = 1 − 0.33 − 0.298 = 0.372
DFDC = 1 DFEC = 1
wL2 − 45(6 )2
(FEM )BC =− = = −135kN .m
12 12
2
45(6 )2
(FEM )CB = wL = = 135kN .m
12 12
Tinñn½yRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgtaragénrUbTI 12-15b. enATIenH karEbgEckm:Um:g;RtUv)aneFVIbnþbnÞab;Et
eTAelItMN B nig C . m:Um:g;cugeRkayRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgCYredkcugeRkayeK.
edayeRbITinñn½yTaMgenH eyIgGacsg;düaRkamm:Um:g;sRmab;eRKagEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-
15c.
!@>%> karEbgEckm:Um:g;sMrab;eRKagEdleyal
(Moment distribution for frames: Sidesway)
BIkaxNÐ 11-5 eyIgeXIjehIyfaeRKagEdlmanlkçN³minsIuemRTI b¤eRKagEdlrgbnÞúkminsIu-
emRTInwgeyal. ]TahrN_énkrNIEbbenHRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-16a. enATIenH bnÞúkGnuvtþn_
P nwgbegáItm:Um:g;enARtg; B nig C minesμIKña dUcenHeRKagnwgmankMhUcRTg;RTay Δ eTAsþaM. edIm,IkMNt;
kMhUcRTg;RTayenH nigm:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;tMNedayeRbIkarEbgEckm:Um:g; eyIgnwgeRbIeKalkarN_tRmYt
pl. enAkñúgrUbTI 12-16b dMbUgeKKitfaeRKagRtUv)anTb;mineGayeyaledayGnuvtþtMNTMrnimitþenA
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -432](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-18-320.jpg)
![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
Rtg; C . eKGnuvtþkarEbgEckm:Um:g; ehIybnÞab;mkeKKNnakmøaMgTb; R edaysmIkarsþaTic. kmøaMg
Tb;EdlmanTMhMesμIKña EtTisedApÞúyKñaRtUv)anGnuvtþeTAelIeRKag ¬rUbTI 12-16c¦ ehIym:Um:g;enAkñúg
eRKagRtUv)anKNna. viFImYysRmab;edaHRsayCMhancugeRkayenHTamTarnUvkarsnμt;CadMbUgnUvtémøCa
elxsRmab;m:Um:g;Bt;mYy ¬ M 'BA ¦. edayeRbIkarEbgEckm:Um:g; nigsmIkarsþaTic eyIgGackMNt;kMhUc
RTg;RTay Δ' nigkmøaMgxageRkA R EdlRtUvnwgtémøsnμt; M 'BA . edaysarvaCakMhUcRTg;RTayeGLa-
sÞiclIenEG‘r enaHkmøaMg R' begáItm:Um:g;enAkñúgeRKagEdlsmamaRteTAnwgm:Um:g;EdlbegáIteGayman R .
Ca]TahrN_ RbsinebIeKsÁal; M 'BA nig R' enaHm:Um:g;enARtg; B EdlbegáIteday R Ca M BA = M 'BA
(R / R') . karbEnßmm:Um:g;Rtg;tMNsMrab;krNITaMgBIr ¬rUbTI12-16b nig c¦ nwgeFVIeGayeKTTYl)an
m:Um:g;Cak;EsþgenAkñúgeRKag ¬rUbTI 12-16a¦. karGnuvtþénbec©keTsenHRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúg]Ta-
hrN_ 12-6 dl; 12-8.
eRKageRcInCan;³ CaerOy² rcnasm<½n§EdlmaneRcInCan;nwgmanbMlas;TIÉkraCüeRcIn Cavi)akkarEbg
Eckm:Um:g;edayeRbIbec©keTsxagelInwgTamTarnUvkarKNnaeRcIn. ]TahrN_ BicarNaeRKagBIrCan;Edl
bgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-17a. rcnasm<½n§enHGacmanbMlas;TIÉkraCüBIr edaysarcm¶ayeyal Δ1
rbs;Can;TImYyÉkraCüBIbMlas;TI Δ 2 rbs;Can;TIBIr.
CaGkusl bMlas;TITaMgenHminRtUv)andwgenAdMNak;kaldMbUg dUcenHkarviPaKRtUveFVIeLIgeday
QrelIeKalkarN_tRmYtplEdlmanlkçN³dUcKñanwgkarENnaMxagelI. enAkñúgkrNIenH eKRtUvGnuvtþ
kmøaMgTb;BIrKW R1 nig R2 ¬rUbTI 12-17b¦ ehIym:Um:g;bgáb;cugRtUv)anKNna nigEbgEck. edayeRbI
smIkarlMnwg eKGackMNt;témøCaelxrbs; R1 nig R2 . bnÞab;mk eKRtUvRsaykarTb;enARtg;kRmal
énCan;TImYy ehIykRmalenaHRtUv)andak;eGaymanbMlas;TI Δ' . bMlas;TIenHeFVIeGaymanm:Um:g;bgáb;
cugenAkñμúgeRKagEdleKGackMNt;Catémøelx. edayEbgEckm:Um:g;enH nigedayeRbIsmIkarlMnwg eKGac
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -433](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-19-320.jpg)
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
kMNt;témøCaelxén R'1 nig R'2 . tamrebobdUcKña kRmalénCan;TIBIrRtUv)aneGaymanbMlas;TI Δ' '
¬rUbTI 12-17d¦. edaysnμt;témøCaelxsRmab;m:Um:g;bgáb;cug karEbgEckm:Um:g; nigsmIkarlMnwgnwg
pþl;nUvtémø R"1 nig R"2 . edaysarCMhancugeRkayTaMgBIr ¬rUbTI 12-17c nig d¦ GaRs½ynwgtémø
snμt;énm:Um:g;bgáb;cug eKRtUvGnuvtþemKuNEktMrUv (correction factor) C ' nig C" eTAelIm:Um:g;EdlEbg
Eck. eyagtamkmøaMgTb;enAkñúgrUbTI 12-17c nig 12-17d eyIgRtUvkarGnuvtþkmøaMg R1 nig R2 Edl
manTMhMesμIKñaEtTisedApÞúyKñaeTAelIeRKag Edl
R2 = −C ' R ' 2 +C" R"2
R1 = +C ' R '1 −C" R"1
dMeNaHRsayénRbB½n§smIkarenHeGaynUvtémøén C ' nig C" . bnÞab;mkeKRtUvKuNemKuNTaMgenHCamYy
nwgm:Um:g;Bt;Rtg;tMNEdlkMNt;BIkarEbgEckm:Um:g;enAkñúgrUbTI 12-17c nig 12-17d. bnÞab;mkeK
kMNt;m:Um:g;ersIusþg;edayeFVIplbUkm:Um:g;EktRmUvCamYynwgm:Um:g;EdlTTYl)anenAkñúgrUbTI 12-17b.
eKGacviPaKeRKagRbePTepSgeTotEdlmanbMlas;TIÉkraCüedayeRbIdMeNIkardUcKña b:uEnþeKRtUv
dwgfaviFIxagelIEdlmanerobrab;RtUvkarkarKNnay:ageRcIn. EteTaHCay:agNak¾eday eK)anbegáIt
bec©keTsxøHedIm,Ikat;bnßykarKNna ¬CakarRbesIreKKYredaHRsaycMeNaTRbePTenHedayeRbIkMuBüÚ-
T½r¦ CaTUeTAedayeRbIkarviPaKedaym:aRTIs. bec©keTssRmab;karviPaKEbbenHRtUv)anbgðajenAkñúg
emeronTI 16.
]TahrN_ 12-6³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;tMNéneRKagEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-18a. EI CacMnYn
efr.
dMeNaHRsay³ dMbUgeyIgKitfaeRKagRtUv)anTb;mineGayeyaldUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-18b.
eyIgman
16(4)2 (1)
(FEM )BC =− = −10.24kN .m
(5)2
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -434](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-20-320.jpg)

![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
M BA = 5.78 +
0.92
(− 60) = 4.79kN .m
56.0
M BC = −5.78 +
0.92
(60) = −4.79kN .m
56.0
M CB = 2.72 +
0.92
(60) = 3.71kN .m
56.0
M CD = −2.72 +
0.92
(− 60) = −3.71kN .m
56.0
M DC = −1.32 +
0.92
(− 80) = −2.63kN .m
56.0
]TahrN_ 12-7³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;tMNnImYy²rbs;eRKagEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19a.
m:Um:g;niclPaBénGgát;nImYy²RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUb.
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -436](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-22-320.jpg)
![mhaviTüal½ysMNg;sIuvil viTüasßanCatiBhubec©keTskm<úCa
dMeNaHRsay³ dMbUgeRKagRtUv)anTb;mineGayeyaldUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19b. m:Um:g;niclPaB
RtUv)anKNnaenARtg;tMNdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19d. enATIenH eKKNnaemKuNkRmajrbs; CD
edayeRbI 3EI / L edaysarvamanTMrsnøak;enARtg; D . karKNnakmøaMgRbtikmμtamTisedkenARtg; A
nig D RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19e. dUcenH sMrab;eRKagTaMgmUl
∑ Fx = 0 R = 5.784 − 2 = 3.78kN
eKGnuvtþkmøaMgEdlmanTispÞúyKñaeTAelIeRKagdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19c. dUcenAkñúg]TahrN_
elIkmun eyIgnwgBicarNakmøaMg R' EdlmanGMeBIdUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19f. CalT§pl tMN B nig
C pøas;TI)an Δ ' dUcKña. eyIgKNnam:Um:g;bgáb;cugsRmab; BA BI
(FEM ) = (FEM ) = − 6 EIΔ = − 6 E (1000)(10 )Δ'
6
AB BA
L2 (5)2
b:uEnþ BItaragenAkñúgemeronTI10 sRmab; CD eyIgman
(FEM ) = − 3EIΔ = − 3E (1250)(10 )Δ'
6
CD
L2 (5)2
Displacement method of analysis: Moment distribution T.Chhay -437](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-23-320.jpg)
![Department of Civil Engineering NPIC
edaysnμt;fam:Um:g;bgáb;cugsRmab; AB KW − 100kN.m dUcbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19f enaHeKkMNt;m:Um:g;
bgáb;cugenARtg; C EdleFVIeGaymanbMlas;TI Δ' dUcKña edaykareRbobeFob eBalKW
Δ' = −
(− 100)(5)2 = − (FEM )CD (7.5)2
6 E (1000)( 6 )
10 3E (1250)( 6 )
10
(FEM )CD = −27.78kN .m
karEbgEckm:Um:g;sRmab;m:Um:g;bgáb;cugTaMgenHRtUv)anbgðajkñúgtaragénrUbTI 12-19g. karKNna
kmøaMgRbtikmμenARtg; A nig D RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-19h. dUcenH sRmab;eRKagTaMgmUl
∑ Fx = 0 R ' = 21.98 + 3.11 = 25.1kN
dUcenH m:Um:g;ers‘ultg;enAkñúgeRKagKW
⎛ 3.78 ⎞
M AB = 9.58 + ⎜ ⎟(− 69.91) = −0.948kN .m
⎝ 25.1 ⎠
⎛ 3.78 ⎞
M BA = 19.34 + ⎜ ⎟(− 40.01) = −13.3kN .m
⎝ 25.1 ⎠
⎛ 3.78 ⎞
M BC = −19.34 + ⎜ ⎟(40.01) = 13.3kN .m
⎝ 25.1 ⎠
⎛ 3.78 ⎞
M CB = 15.00 + ⎜ ⎟(23.31) = 18.5kN .m
⎝ 25.1 ⎠
⎛ 3.78 ⎞
M CD = −15.00 + ⎜ ⎟(− 23.31) = −18.5kN .m
⎝ 25.1 ⎠
]TahrN_ 12-8³ kMNt;m:Um:g;Bt;enARtg;tMNnImYy²rbs;eRKagEdlbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-20a.
EI CacMnYnefr.
dMeNaHRsay³ dMbUg kareyalRtUv)ankarBaredaykmøaMgTb; R ¬rUbTI 12-20b¦. m:Um:g;bgáb;cug
sRmab;Ggát; BC KW
(FEM )BC = − 16(5) = −10kN .m (FEM )CB = 16(5) = 10kN .m
8 8
edaysarGgát; AB nig DC manTMrsnøak; emKuNkRmajRtUv)anKNnaedayeRbI 3EI / L . karEbgEck
m:Um:g;RtUv)anbgðajenAkñúgrUbTI 12-20d.
edaylT§plTaMgenH eKkMNt;kmøaMgRbtikmμtamTisedkenARtg; A nig D edayeRbIsmIkar
lMnwgénGgát;nImYy² ¬rUbTI 12-20e¦. edayeFVIplbUkm:Um:g;Rtg;cMNuc B nig C enAelIeCIgnImYy²
eyIg)an³
+ ∑MB = 0 − 5.97 + Ax (4) − 8(3) = 0 Ax = 7.49kN
+ ∑ MC = 0 5.97 − D x (4) + 8(3) = 0 D x = 7.49kN
karviPaKtamviFIbMlas;TI³ karEbgEckm:Um:g; T.Chhay -438](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-displacementmethodofanalysismomentdistribution-100718054817-phpapp01/85/12-displacement-method-of-analysis-moment-distribution-24-320.jpg)