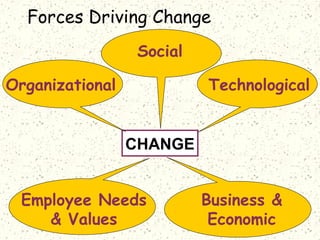
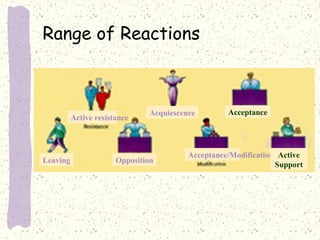
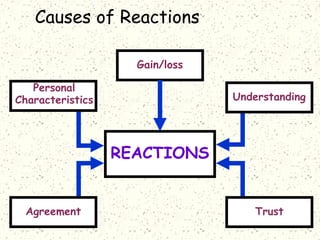
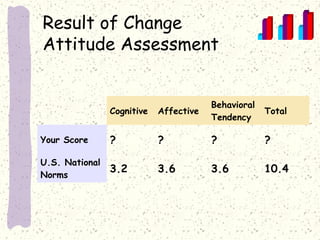
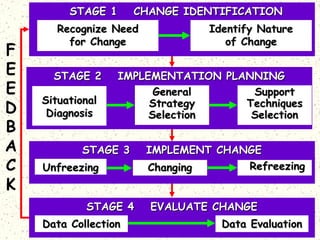
This document discusses organizational change and managing change efforts. It covers the forces driving change, potential reactions to change and the causes of reactions. It also examines personality traits and attitudes toward change. The document then outlines techniques that can be used to develop support for change, including communication, participation, support programs and incentives. Finally, it presents a systematic four-stage model for identifying the need for change, planning an implementation strategy, implementing the change, and evaluating the results.