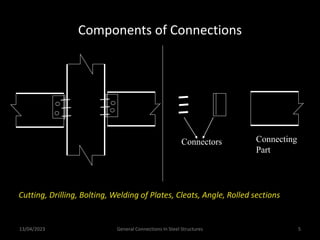
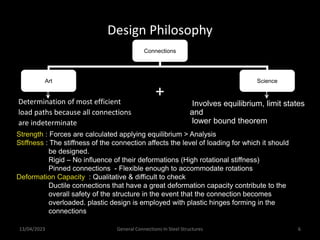
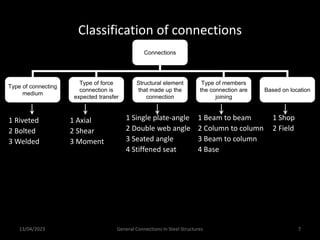
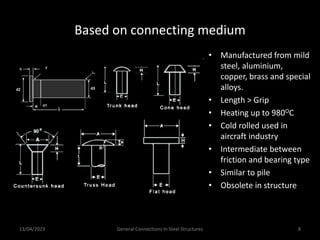
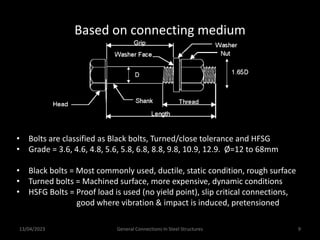
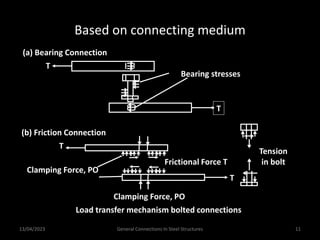
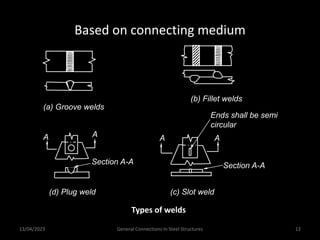
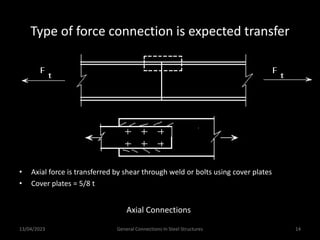
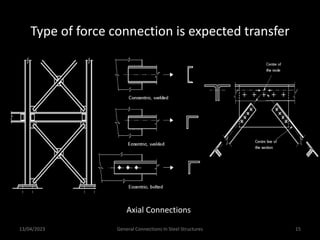
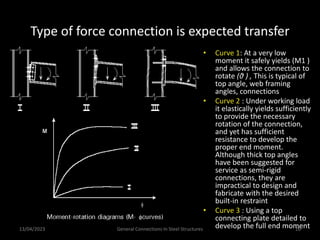
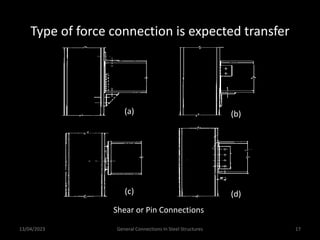
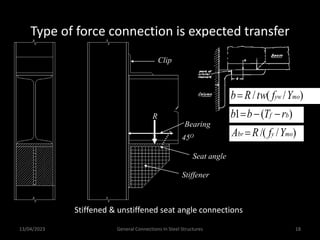
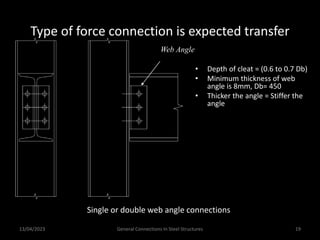
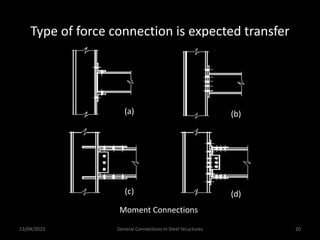
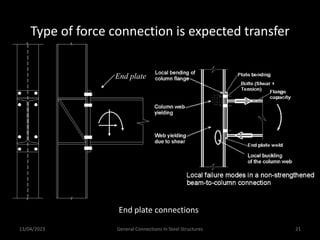
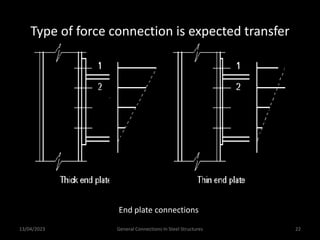
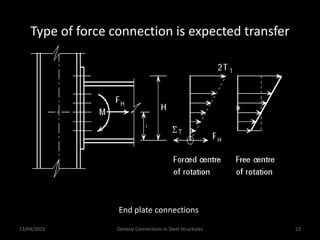
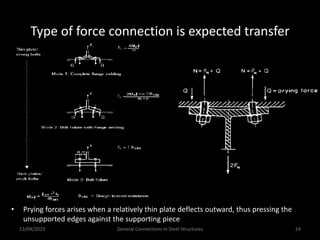
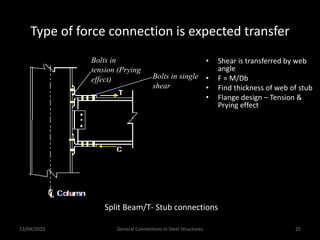
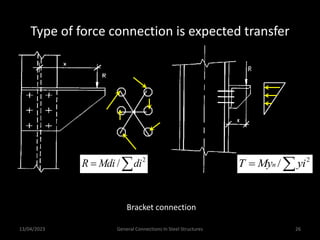
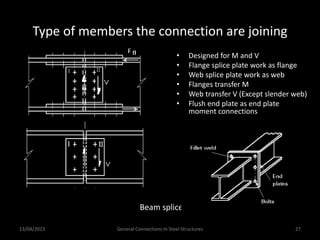
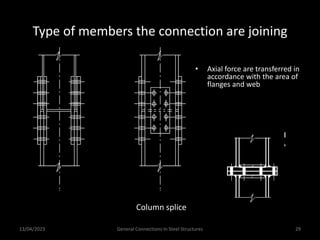
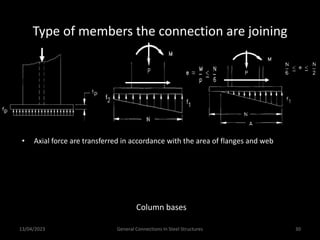
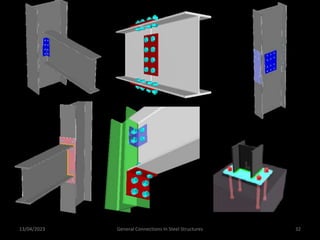
This presentation discusses steel connections, including why steel structures are used, the components and types of connections, and the design philosophy. It covers the classification of connections based on the connecting medium (riveted, bolted, welded), type of force transferred (axial, shear, moment), and members joined (beams, columns, bases). Connection types discussed include axial, shear/pin, moment, end plate, split beam, bracket, beam splice, column splice, and column bases. The objectives are to understand the role of connections in load transfer and structural behavior, as well as the design of different connection configurations.