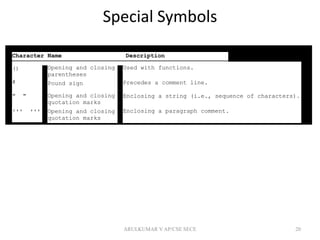
This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is a general purpose, interpreted, object-oriented programming language. The document then covers Python's history, the differences between Python 2 and 3, how to launch Python and run Python scripts, and provides examples of simple Python programs. It also discusses programming style, documentation, and different types of errors. Finally, it introduces GUI programming using the Turtle and Tkinter modules.