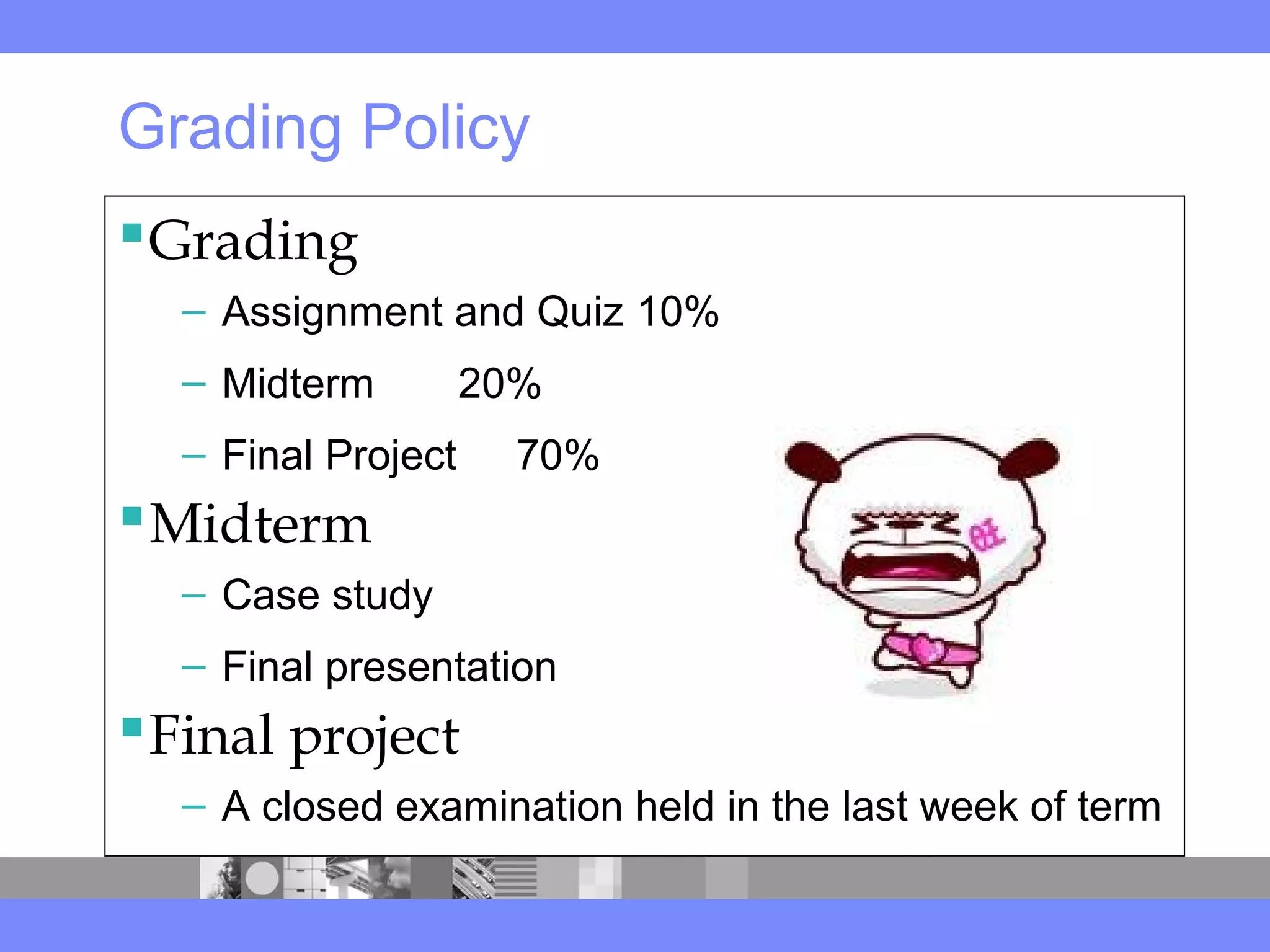
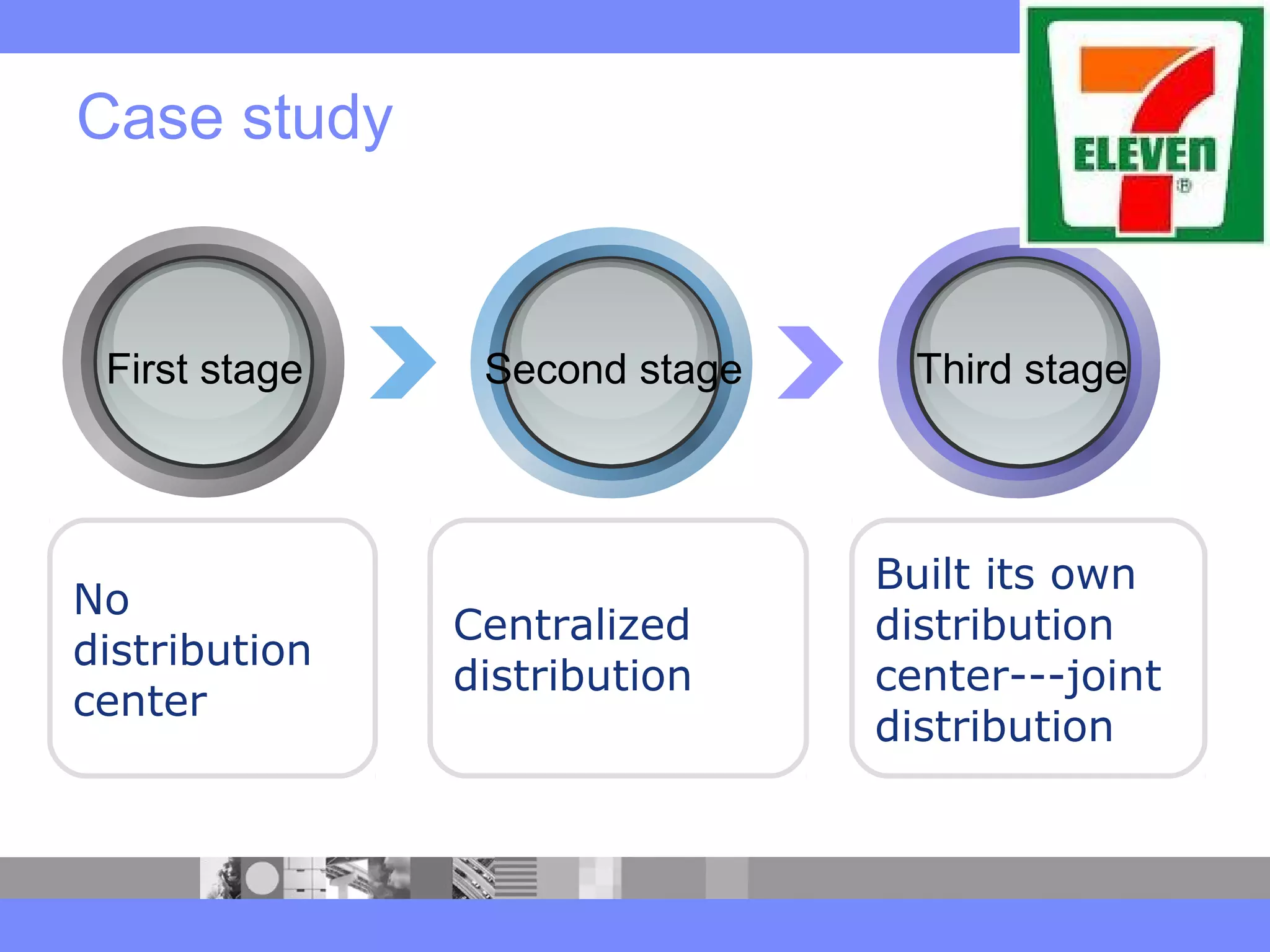
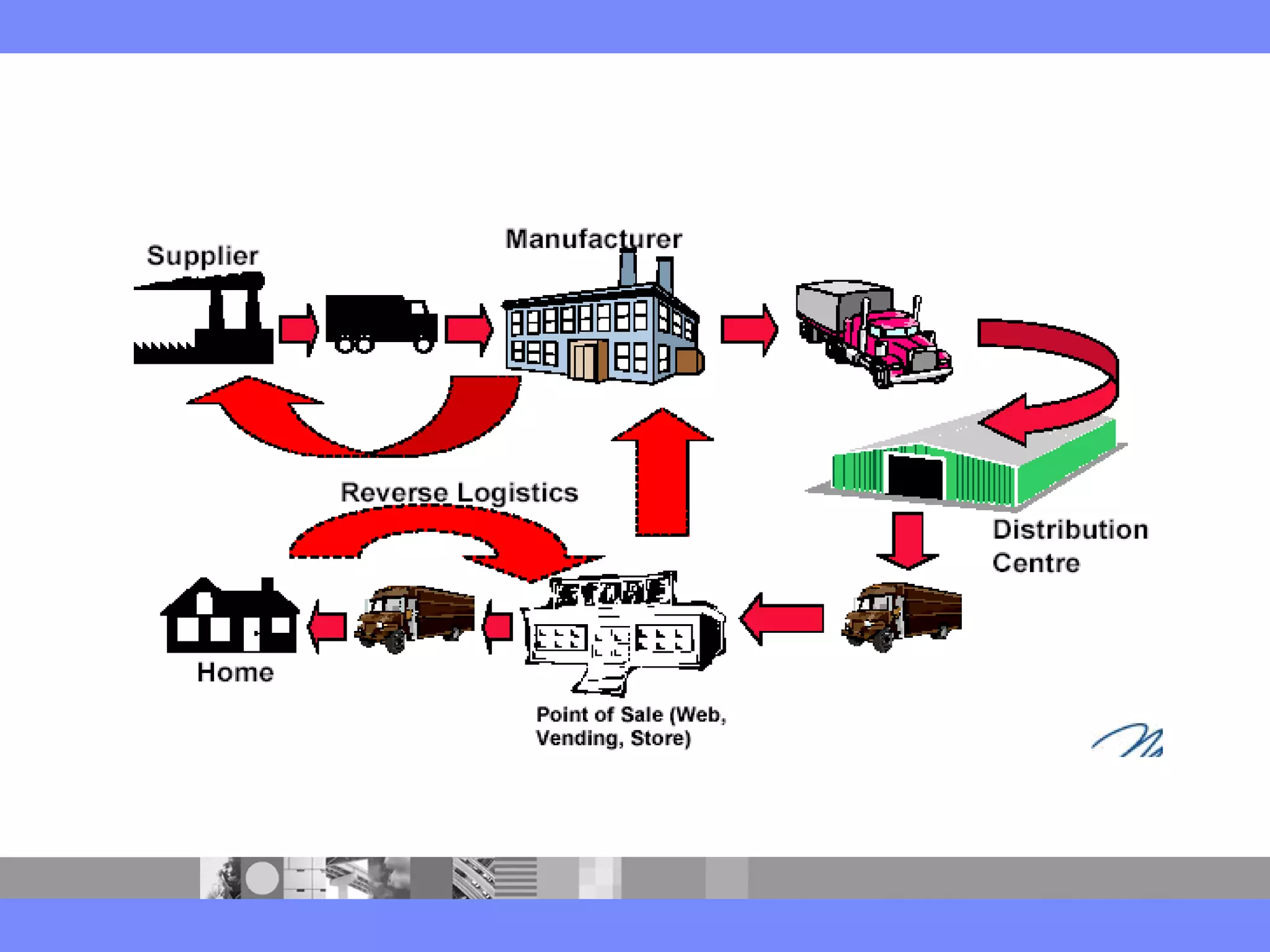
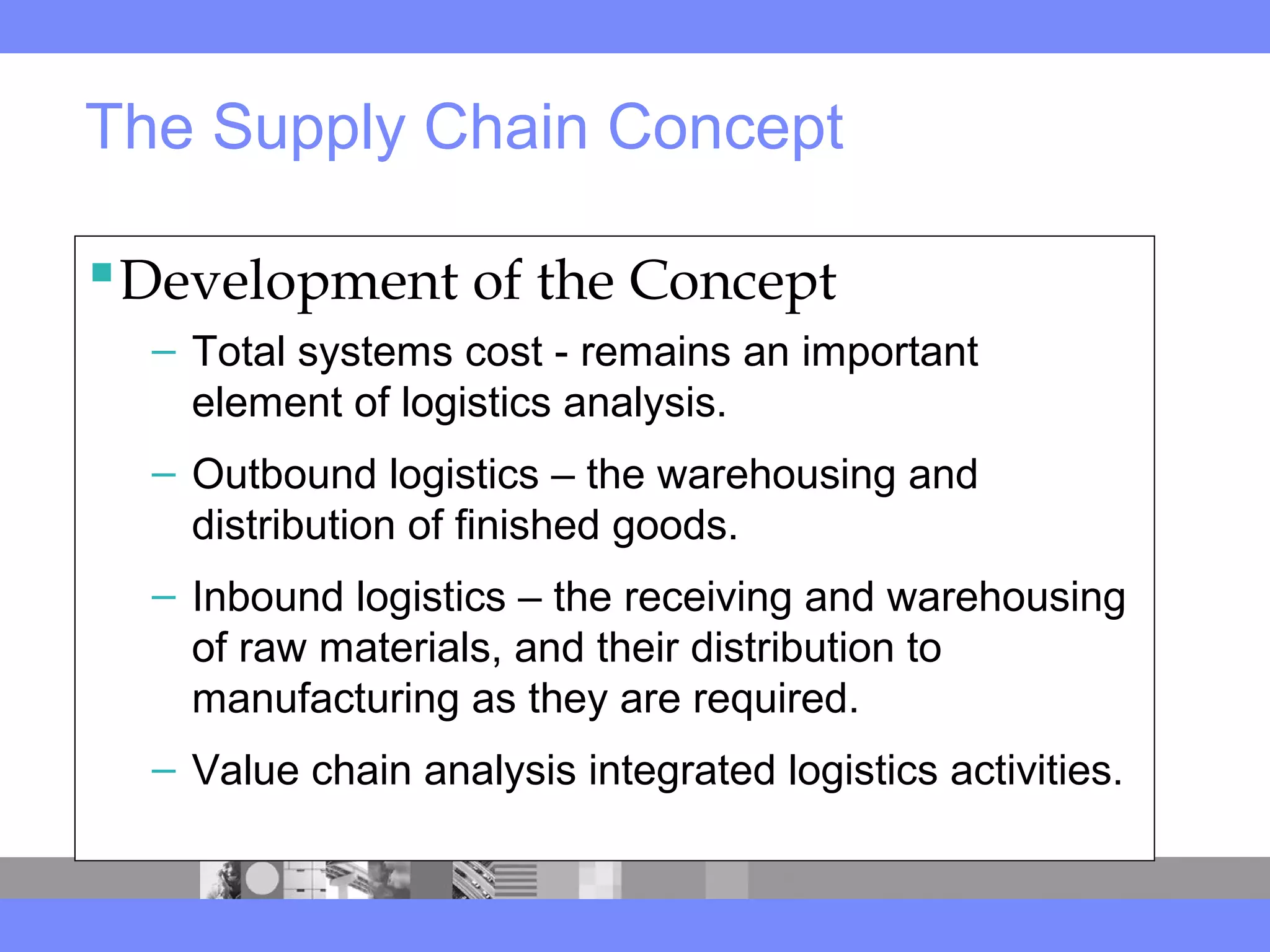
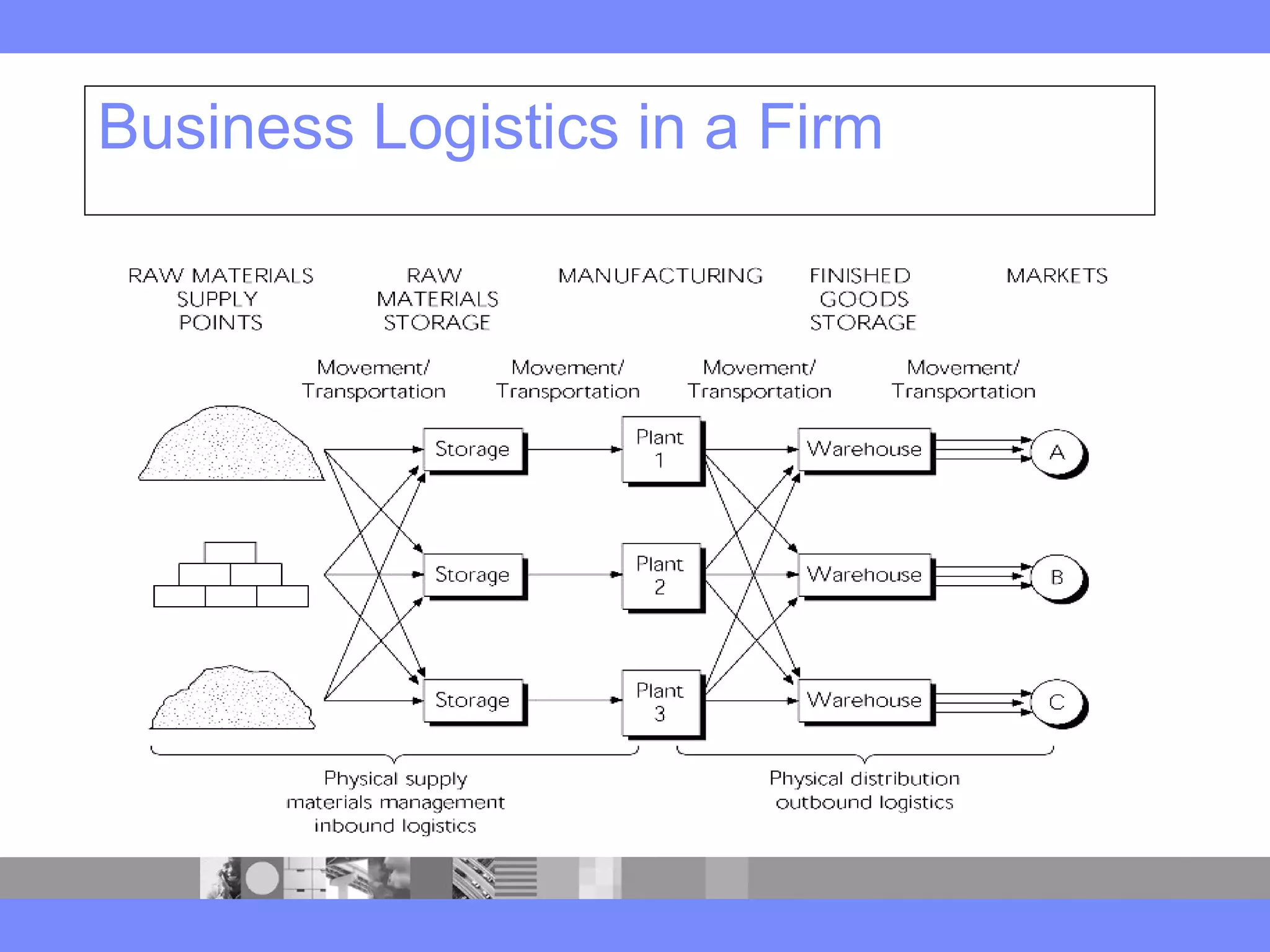
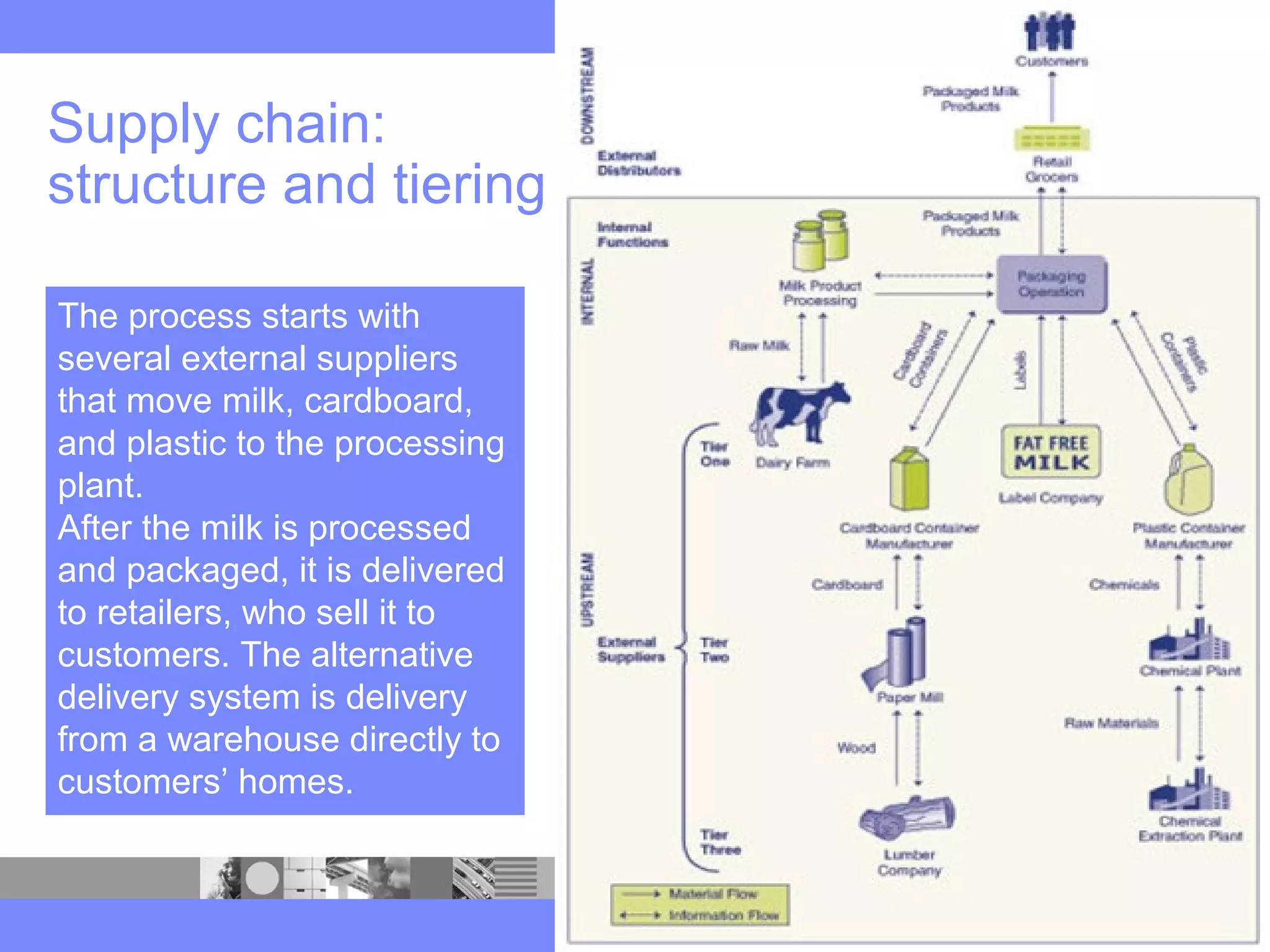
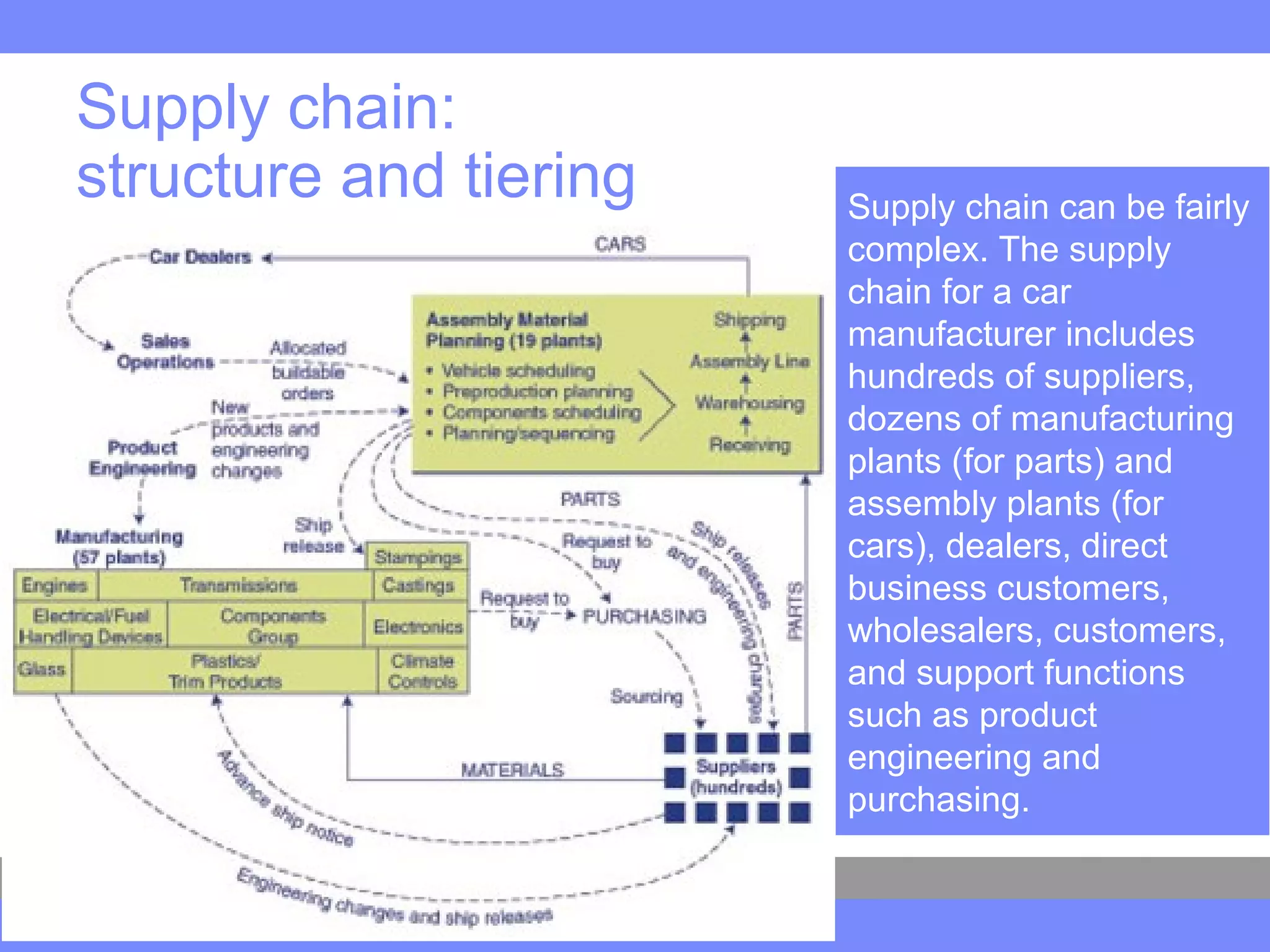
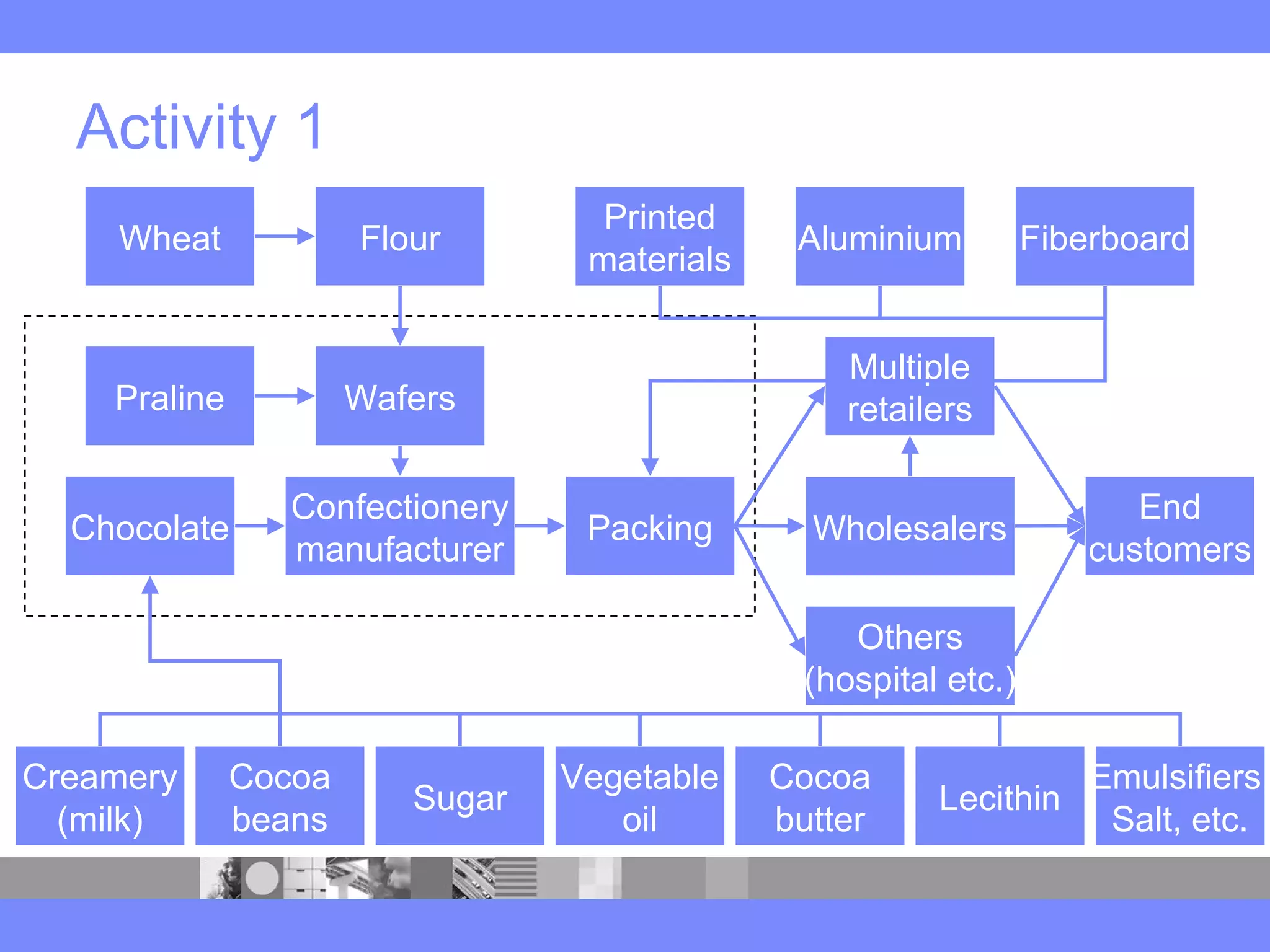
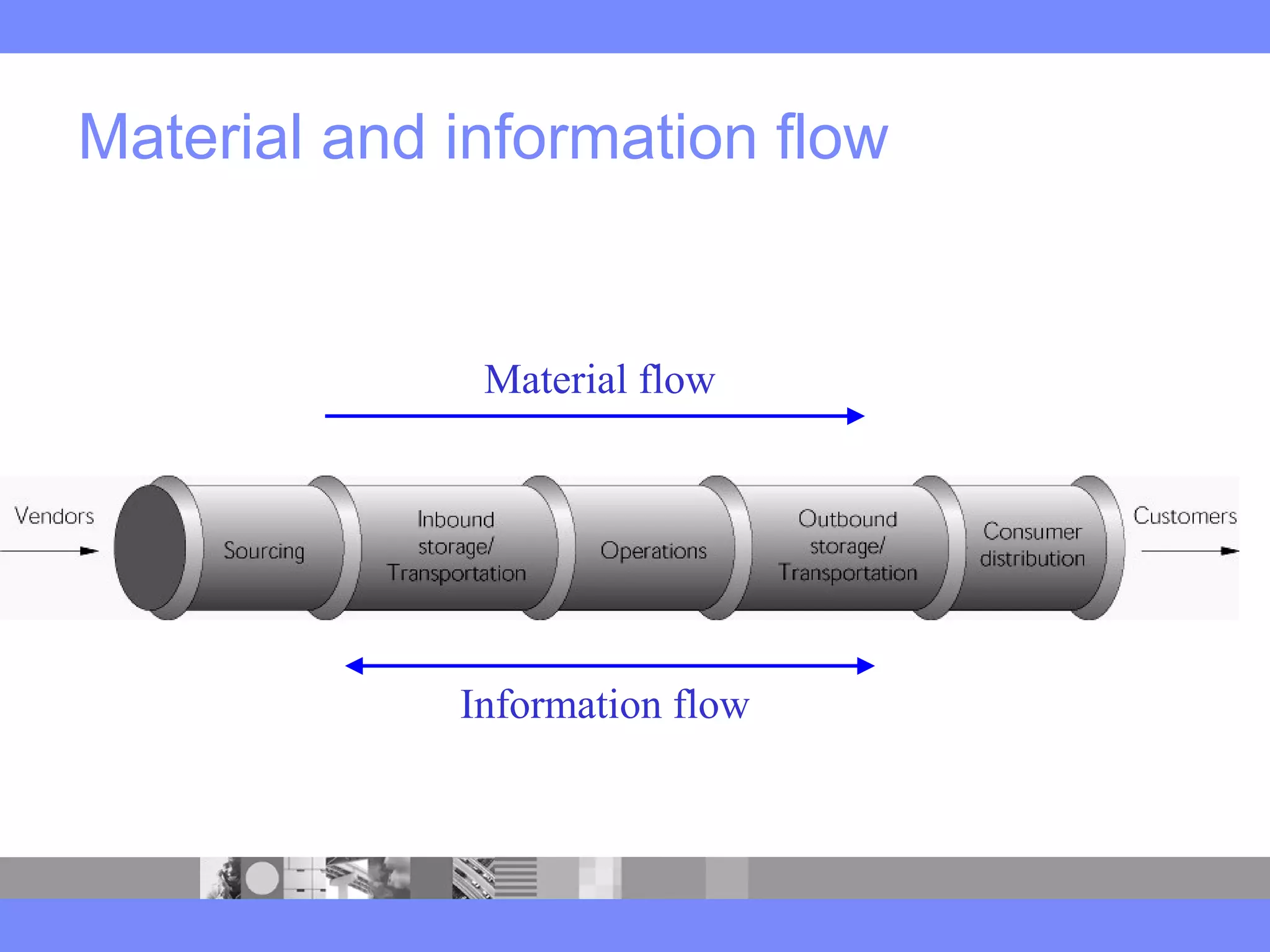
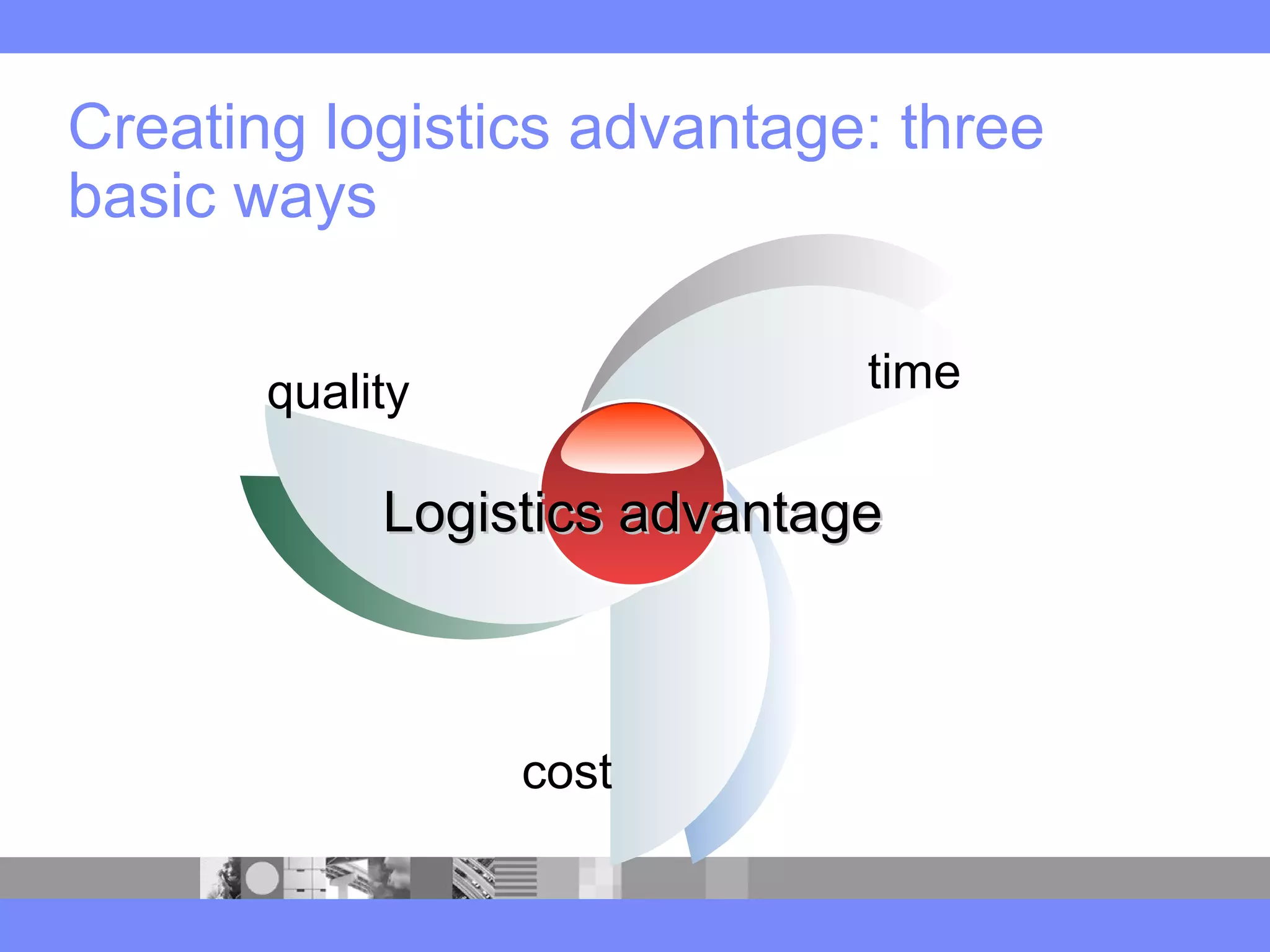
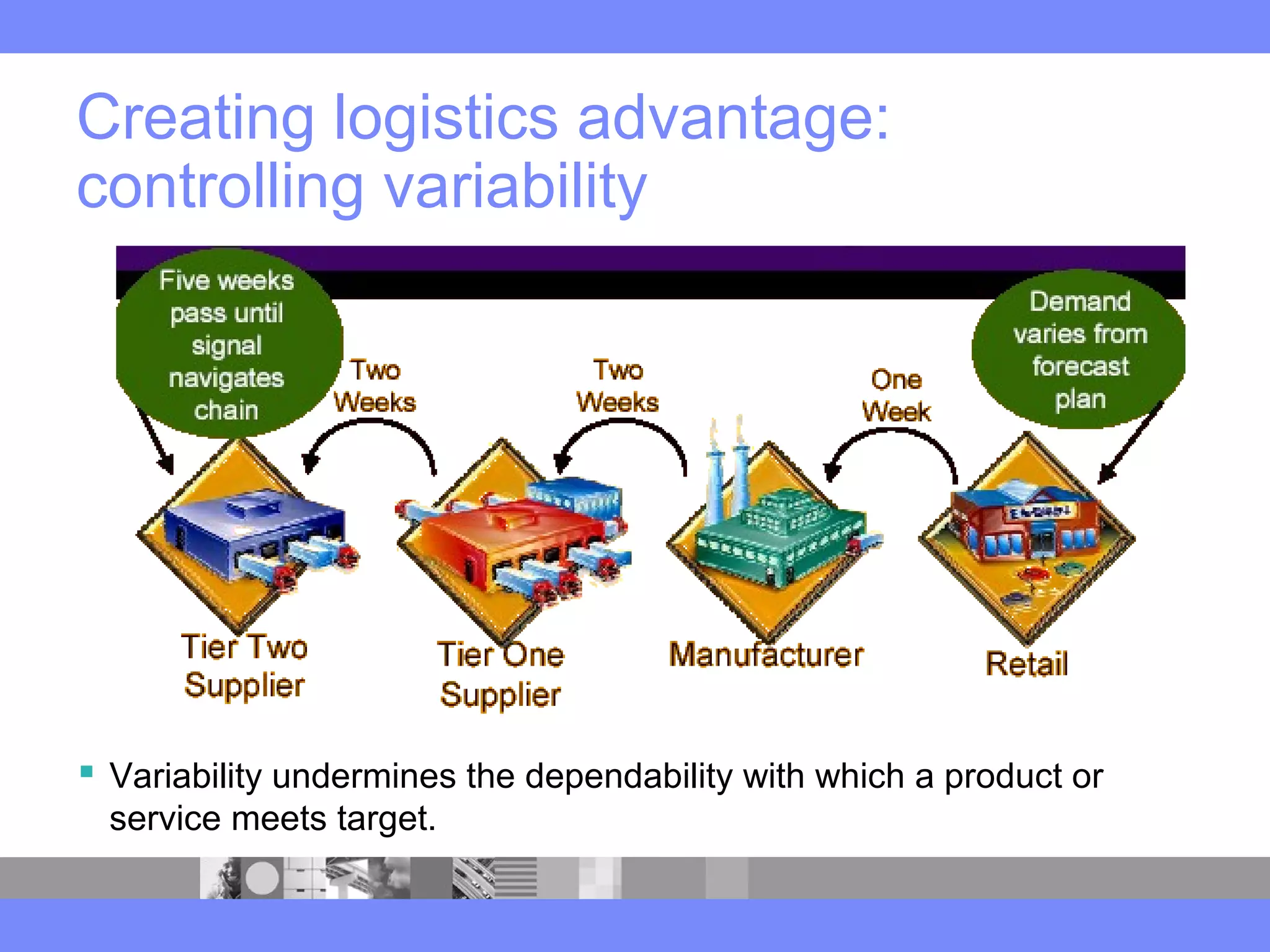
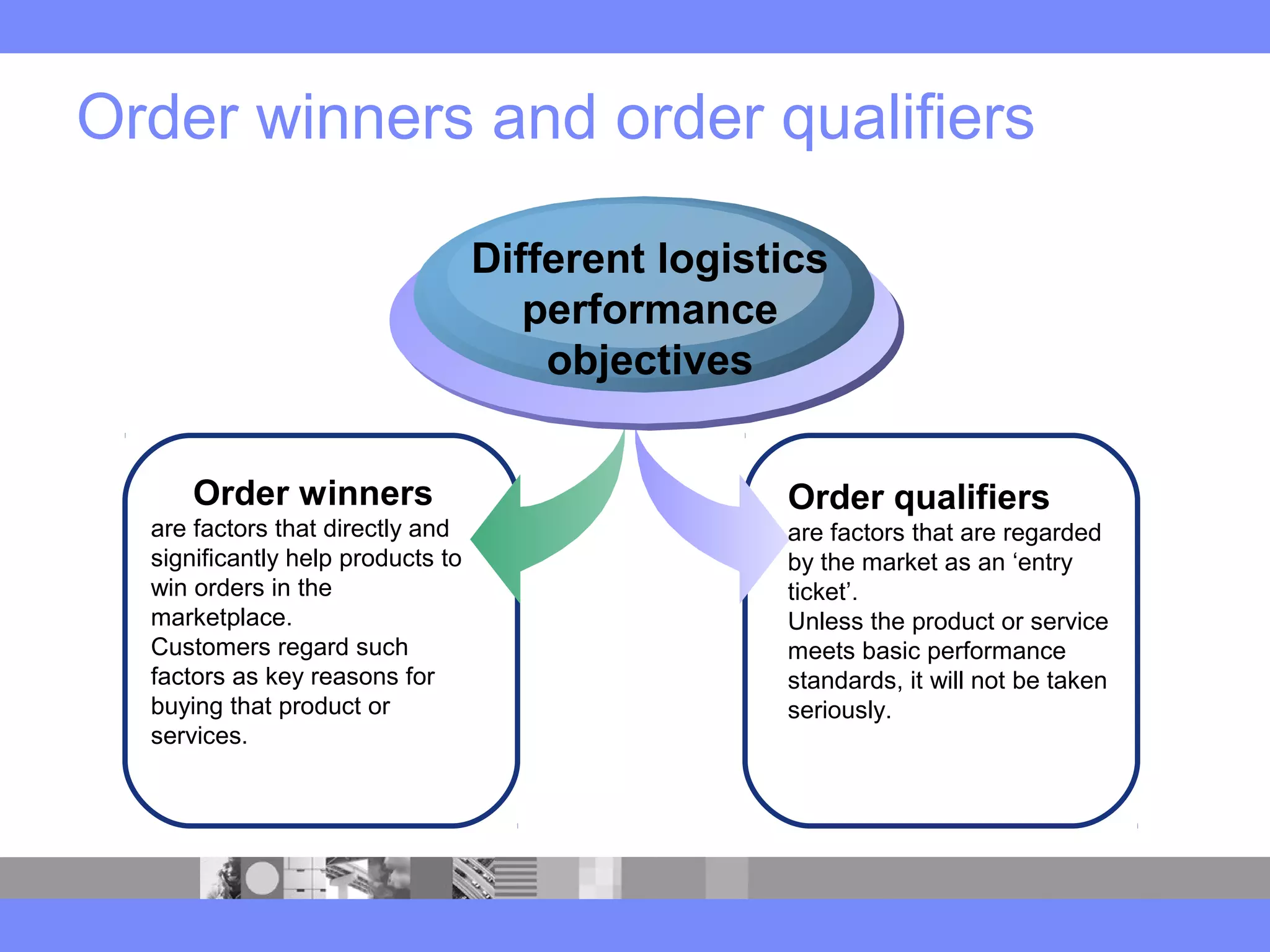
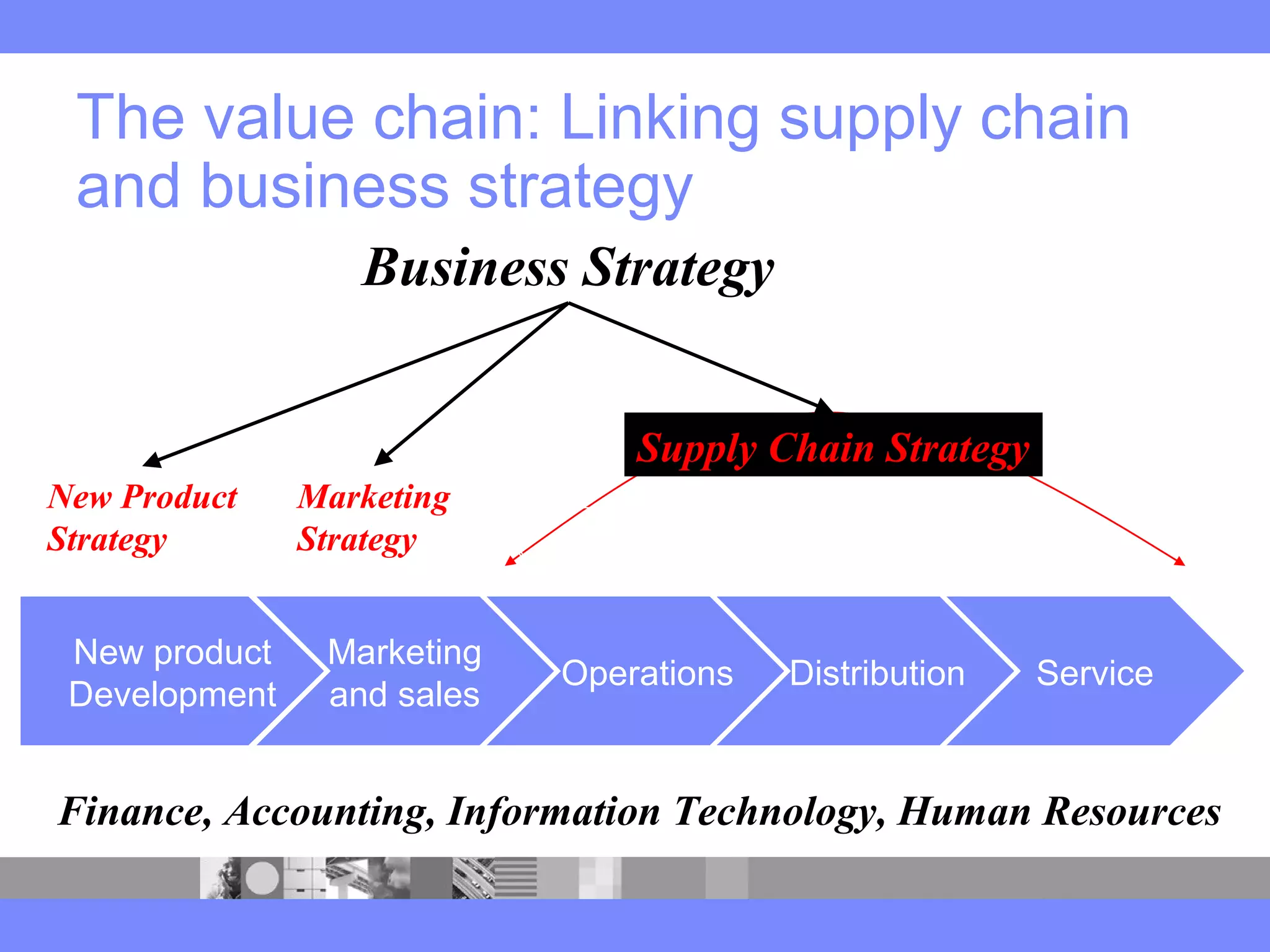
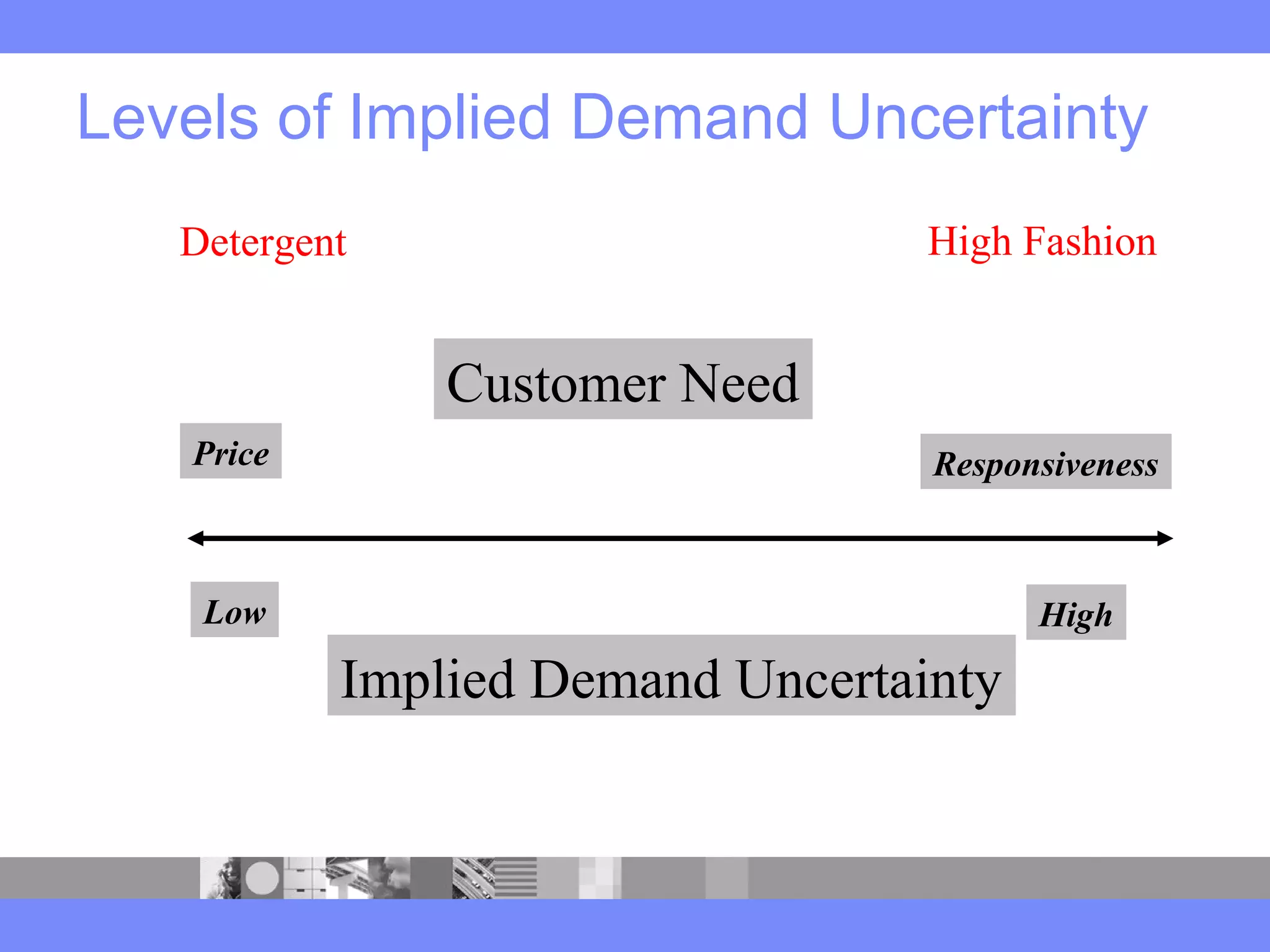
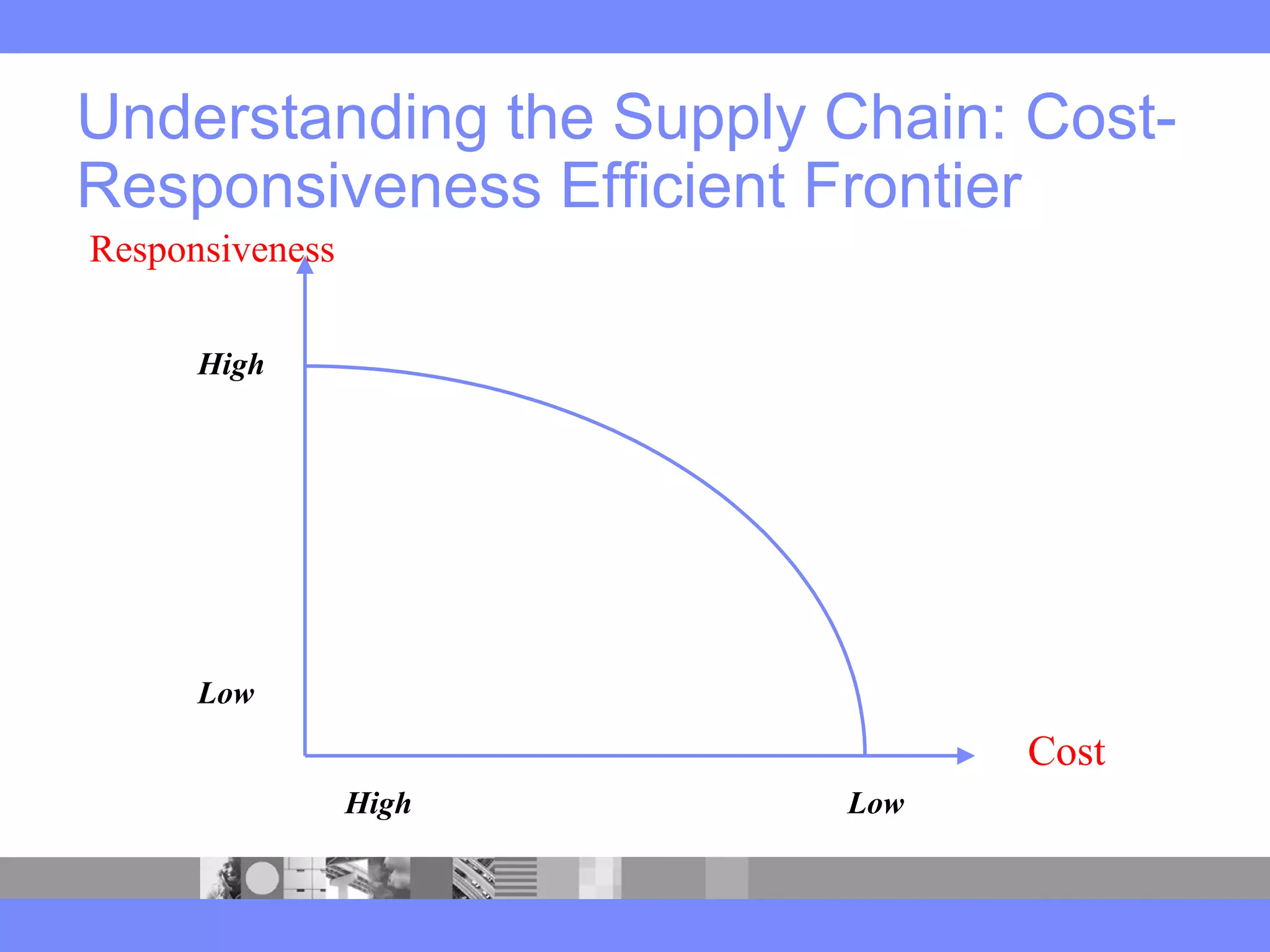
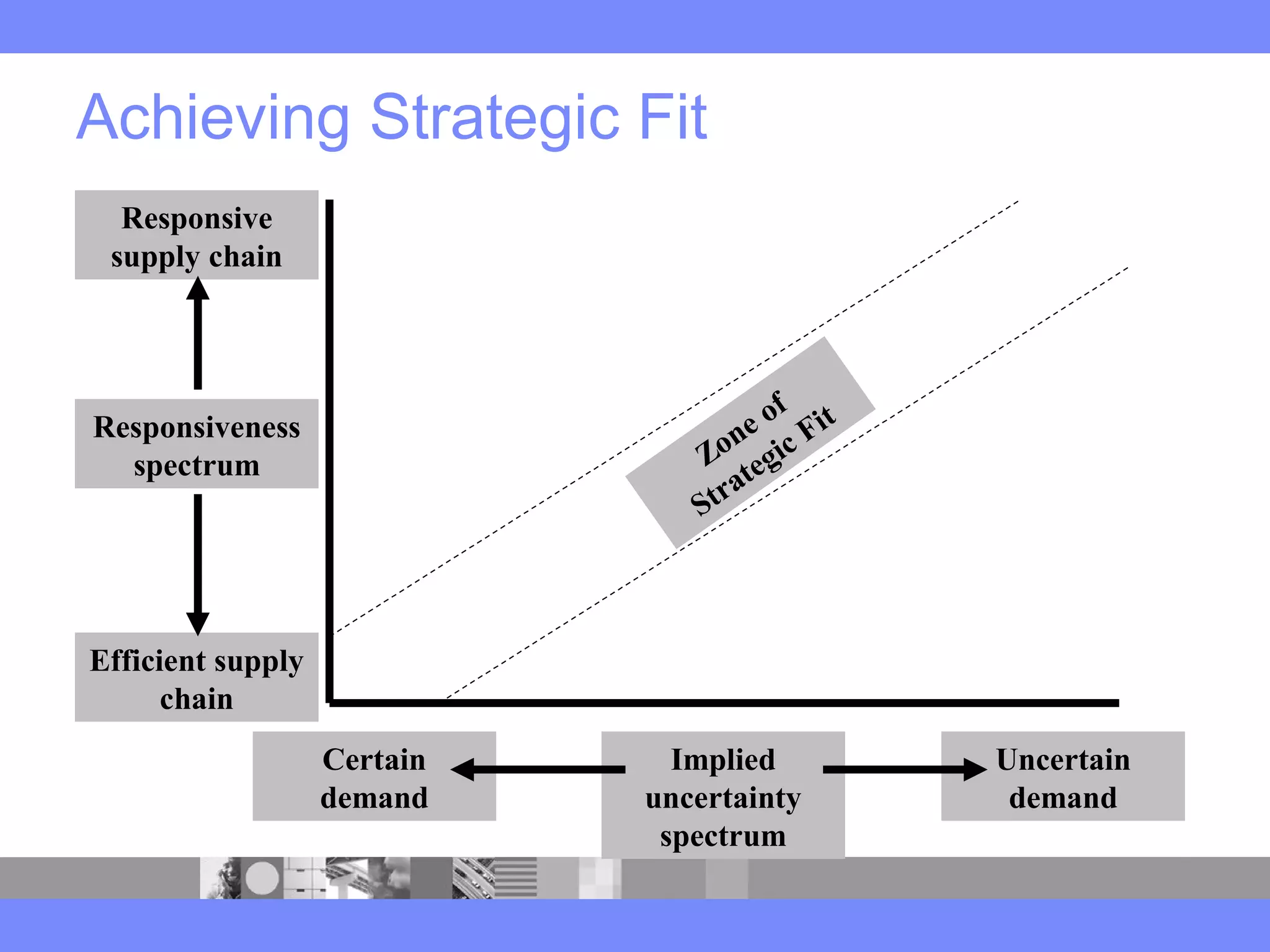
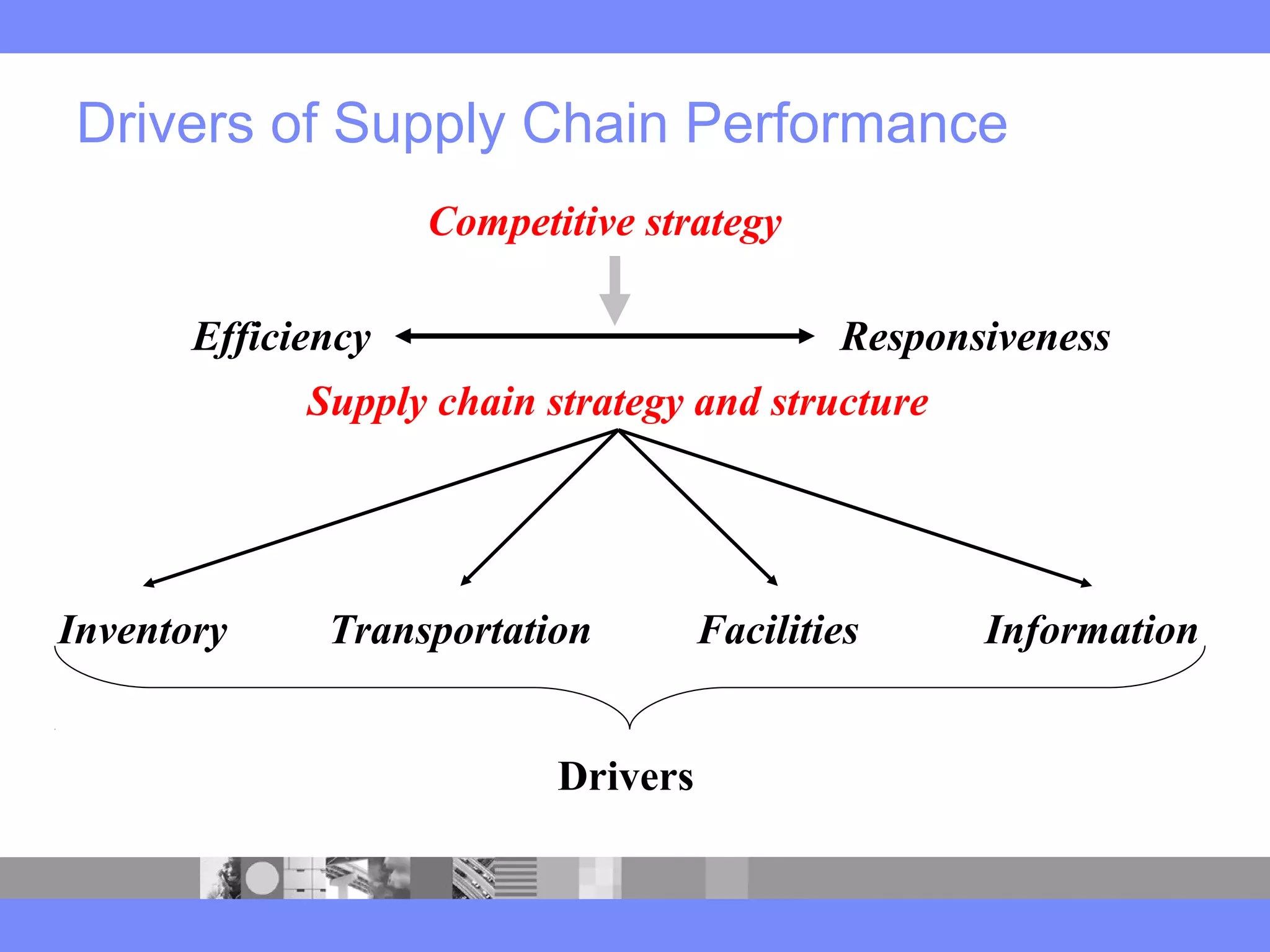
This document provides an introduction to a logistics management course. It outlines the course description, learning objectives, textbooks, grading policy and schedule. The course will cover topics such as logistics systems and supply chain management. It will include lectures, videos, group exercises and case study discussions. Students will be graded based on assignments, midterm exam, case study presentation and a final project. The goal is for students to understand the strategic role of supply chains and how to solve business problems through logistics.